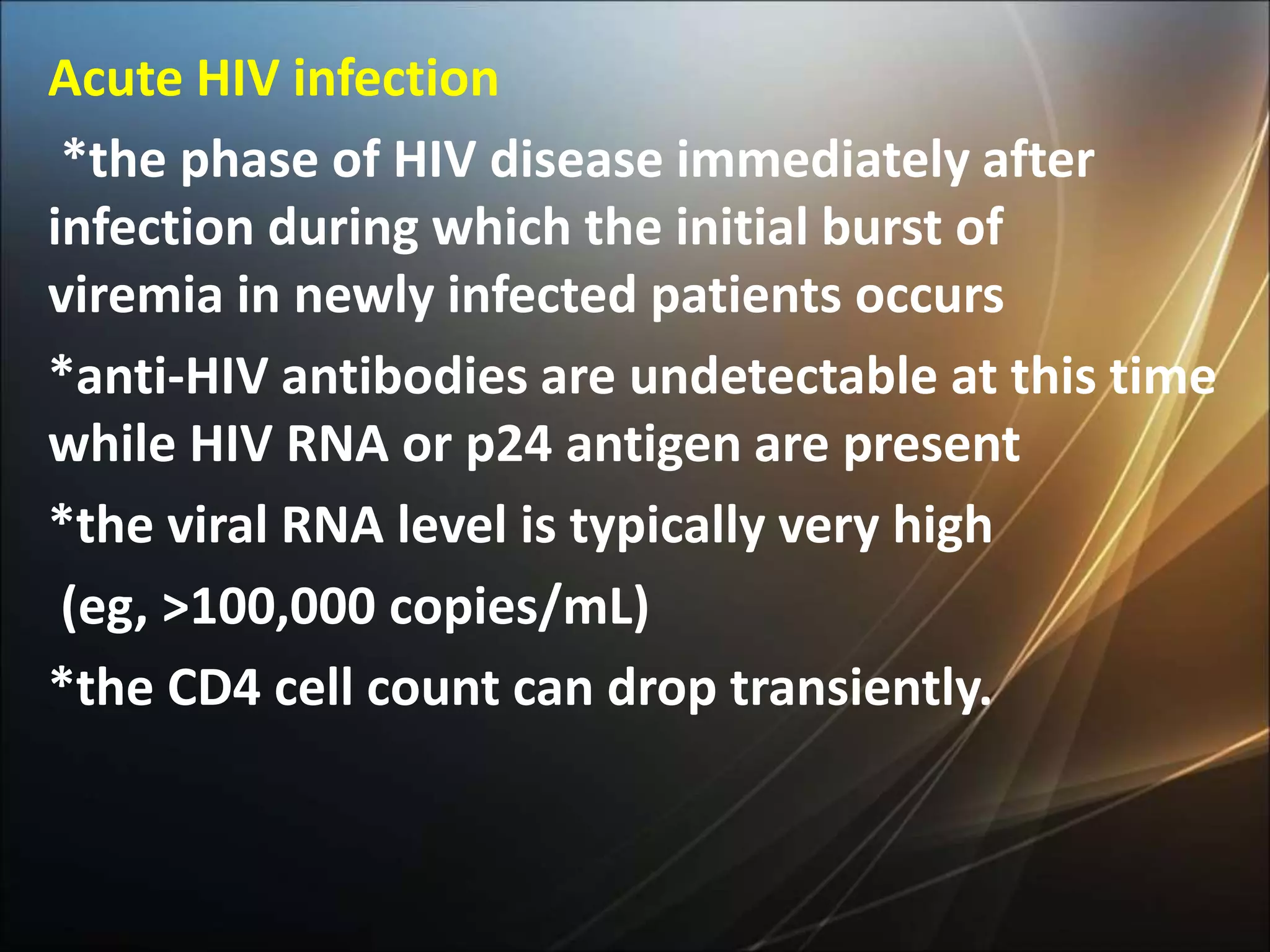
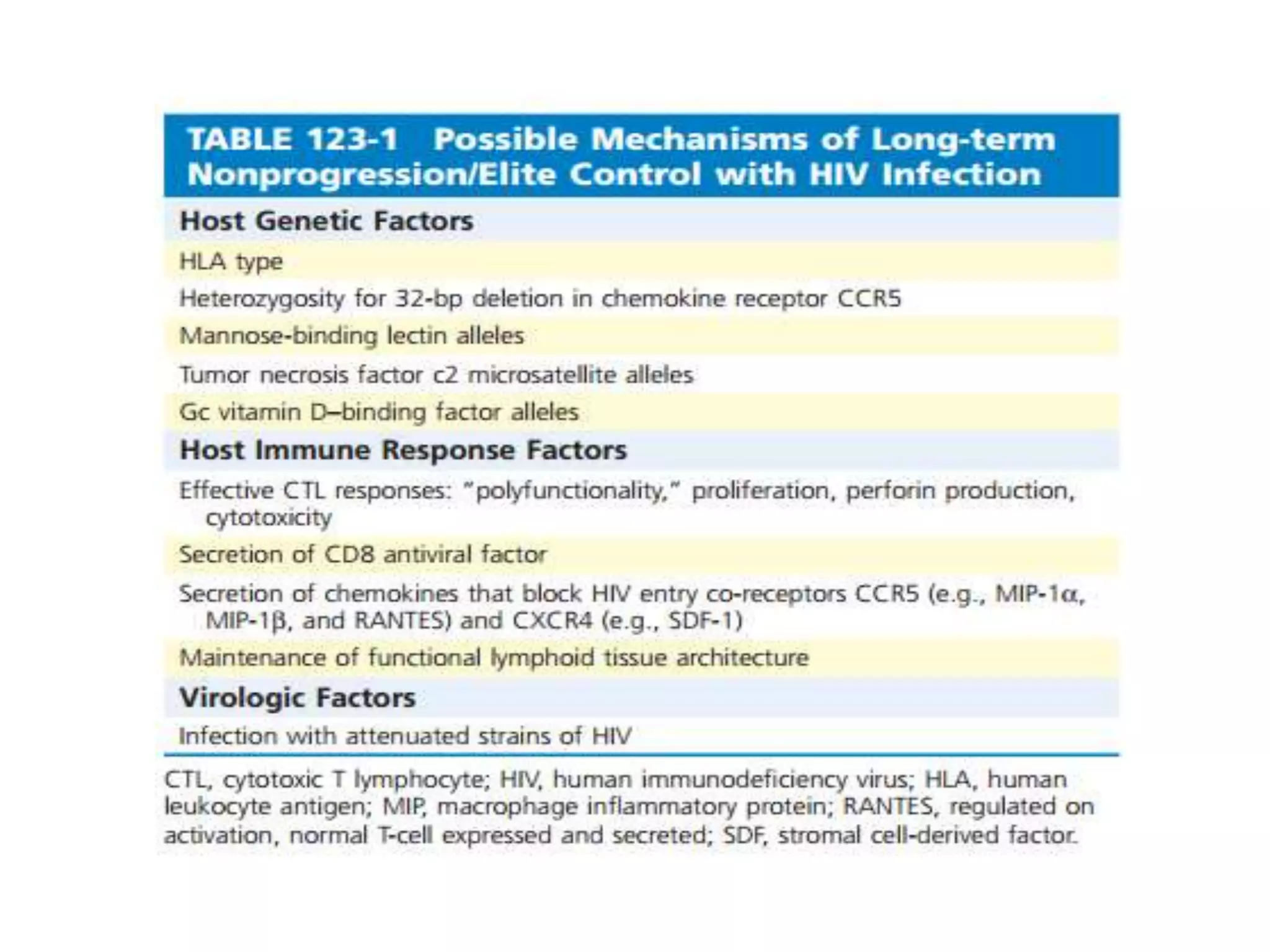
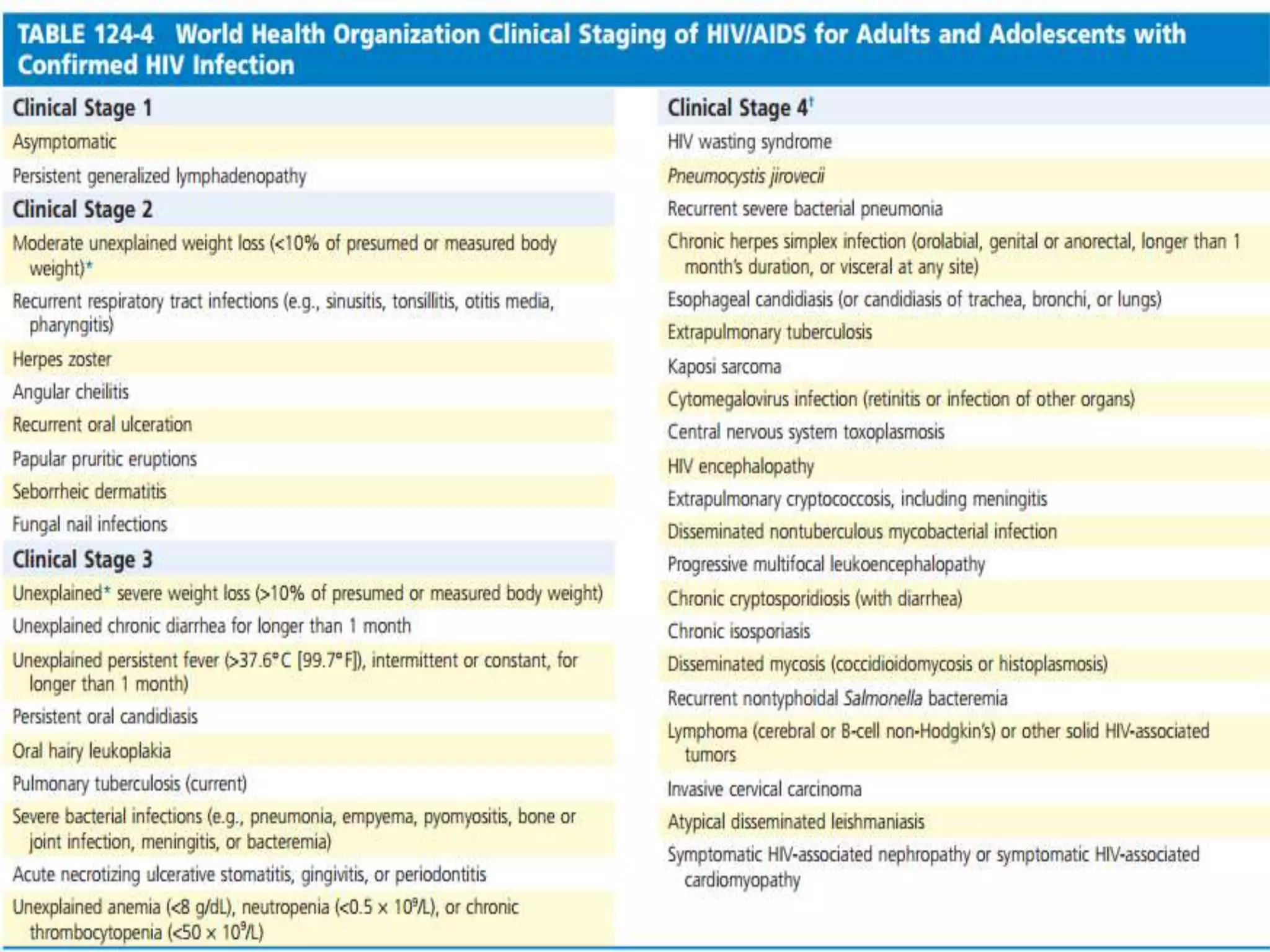
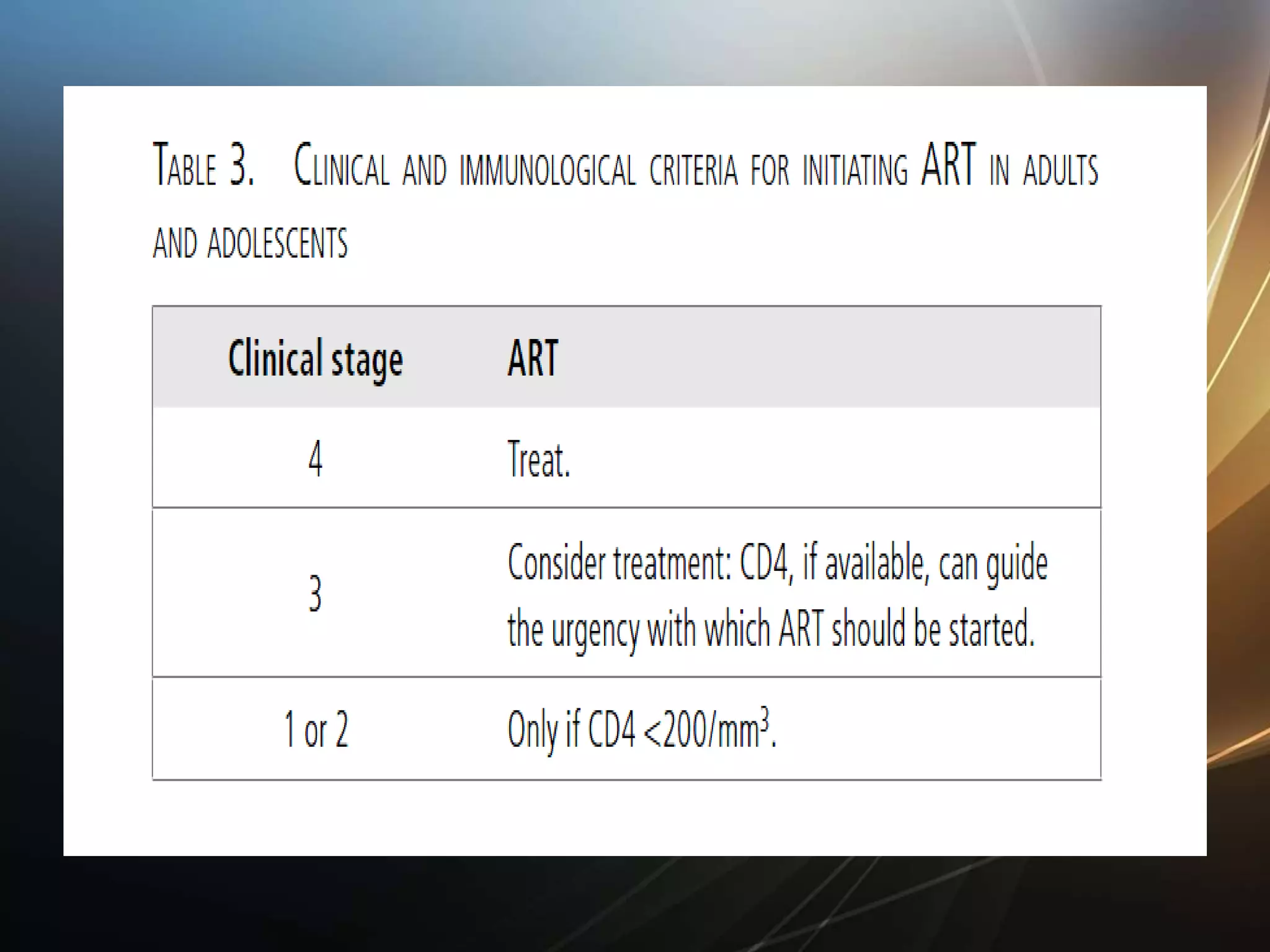
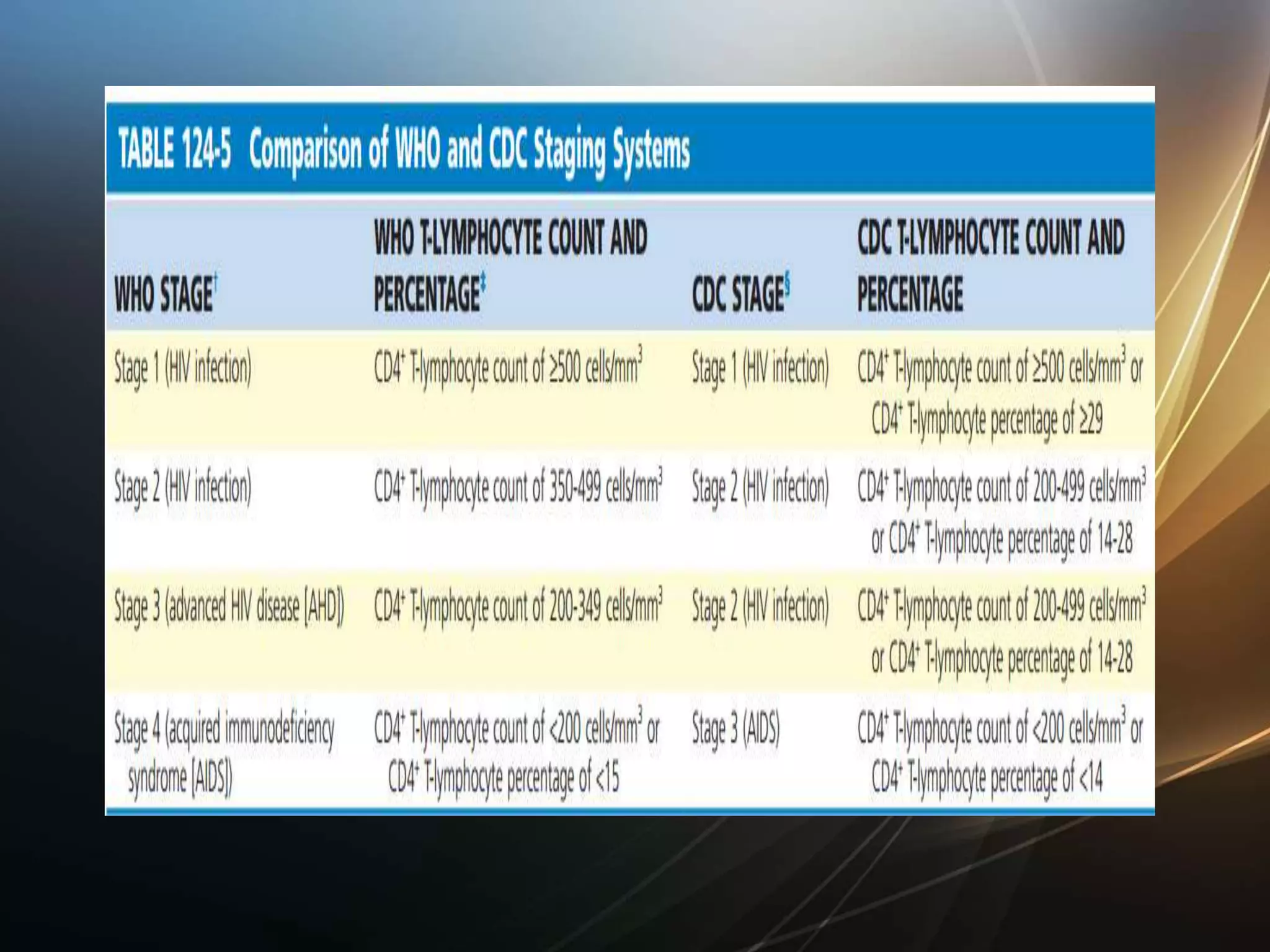
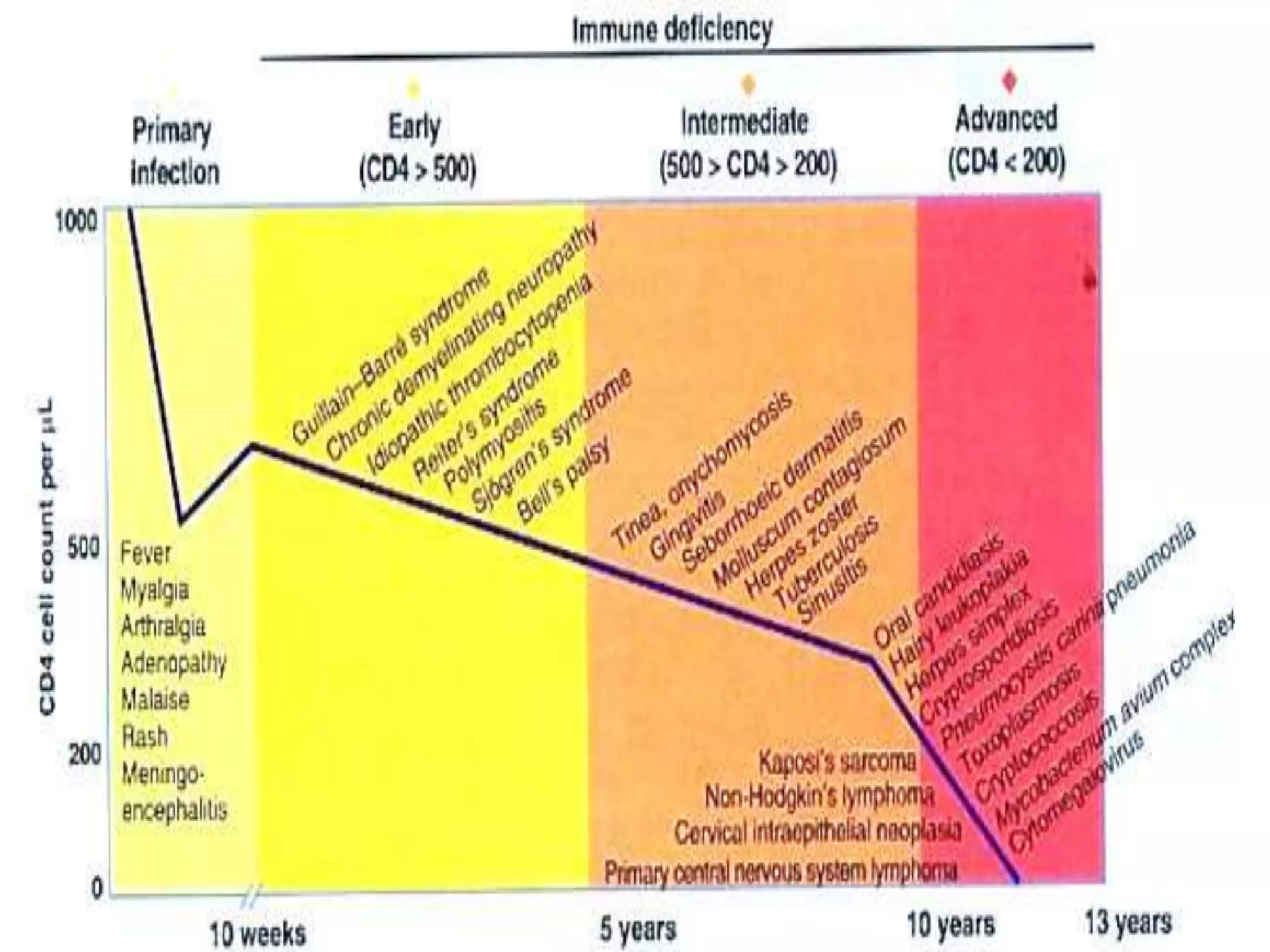
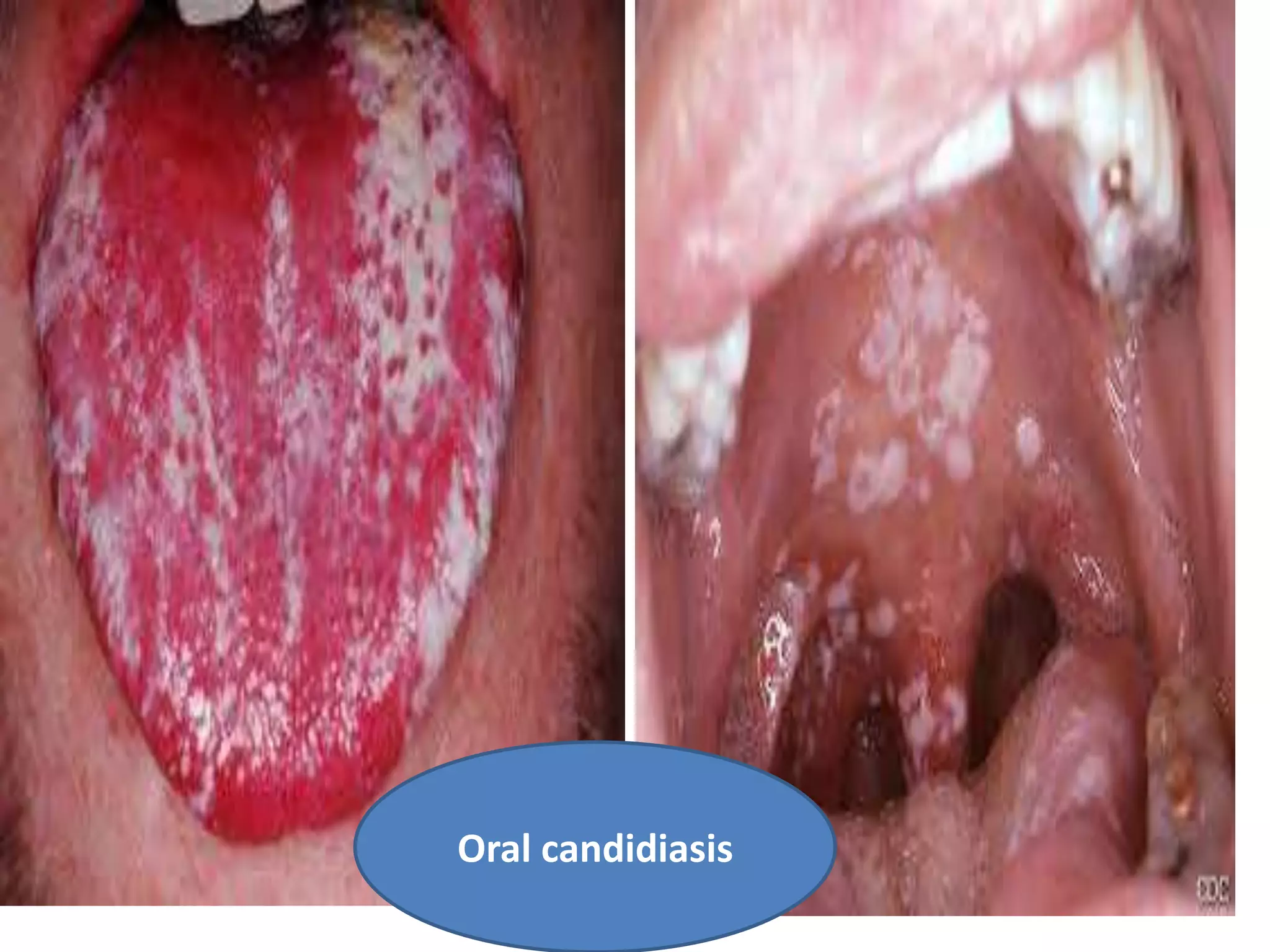
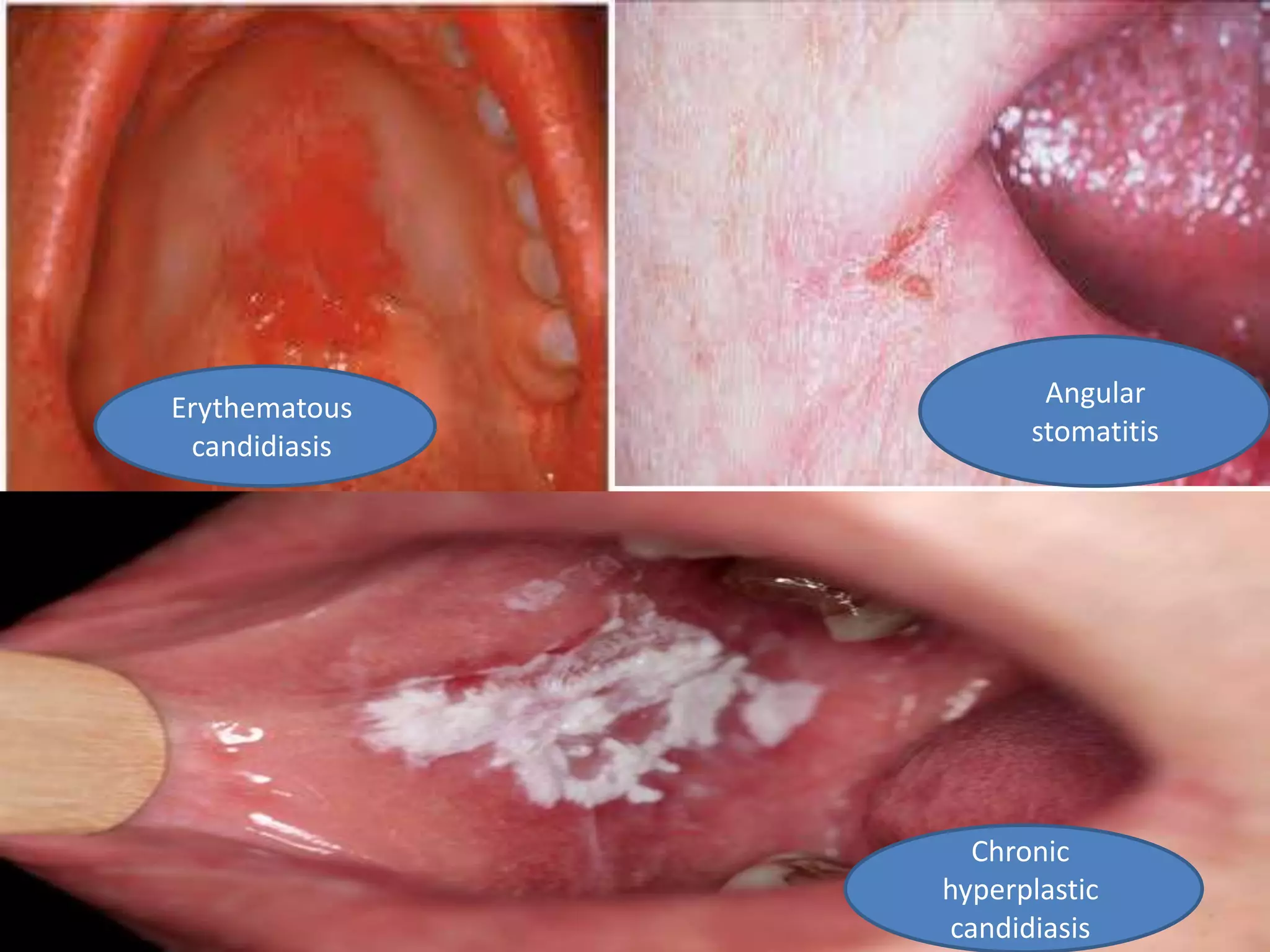
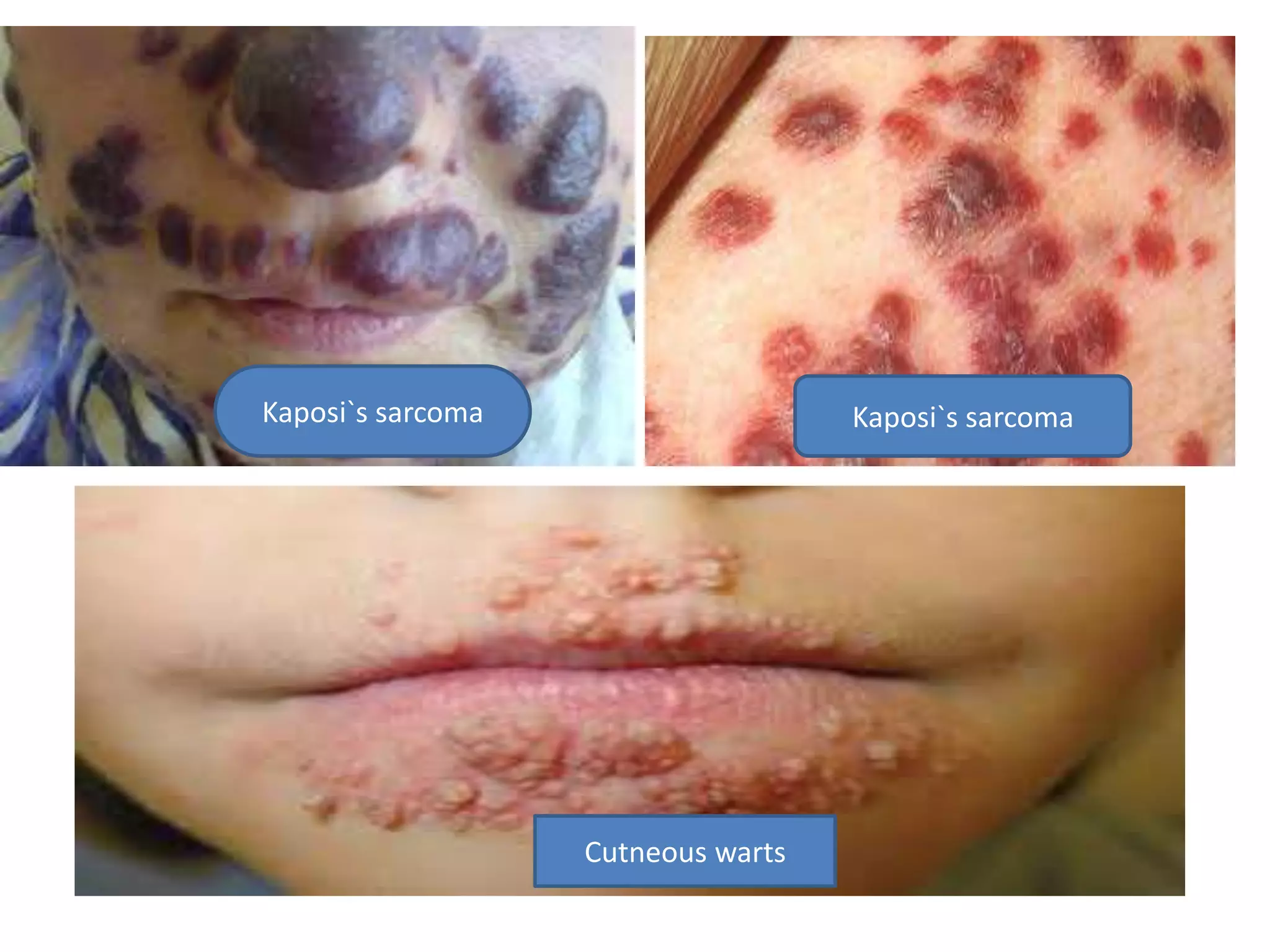
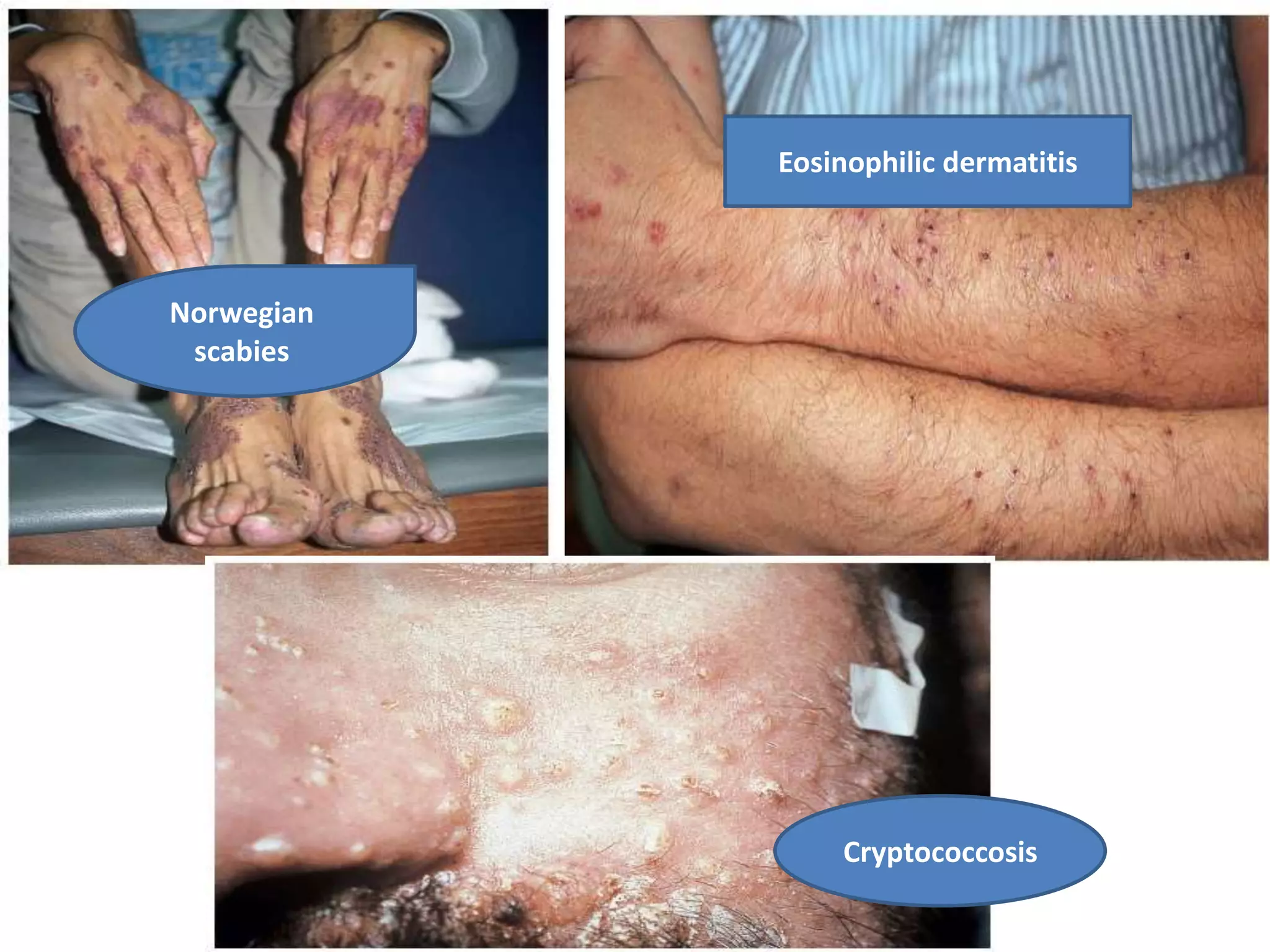
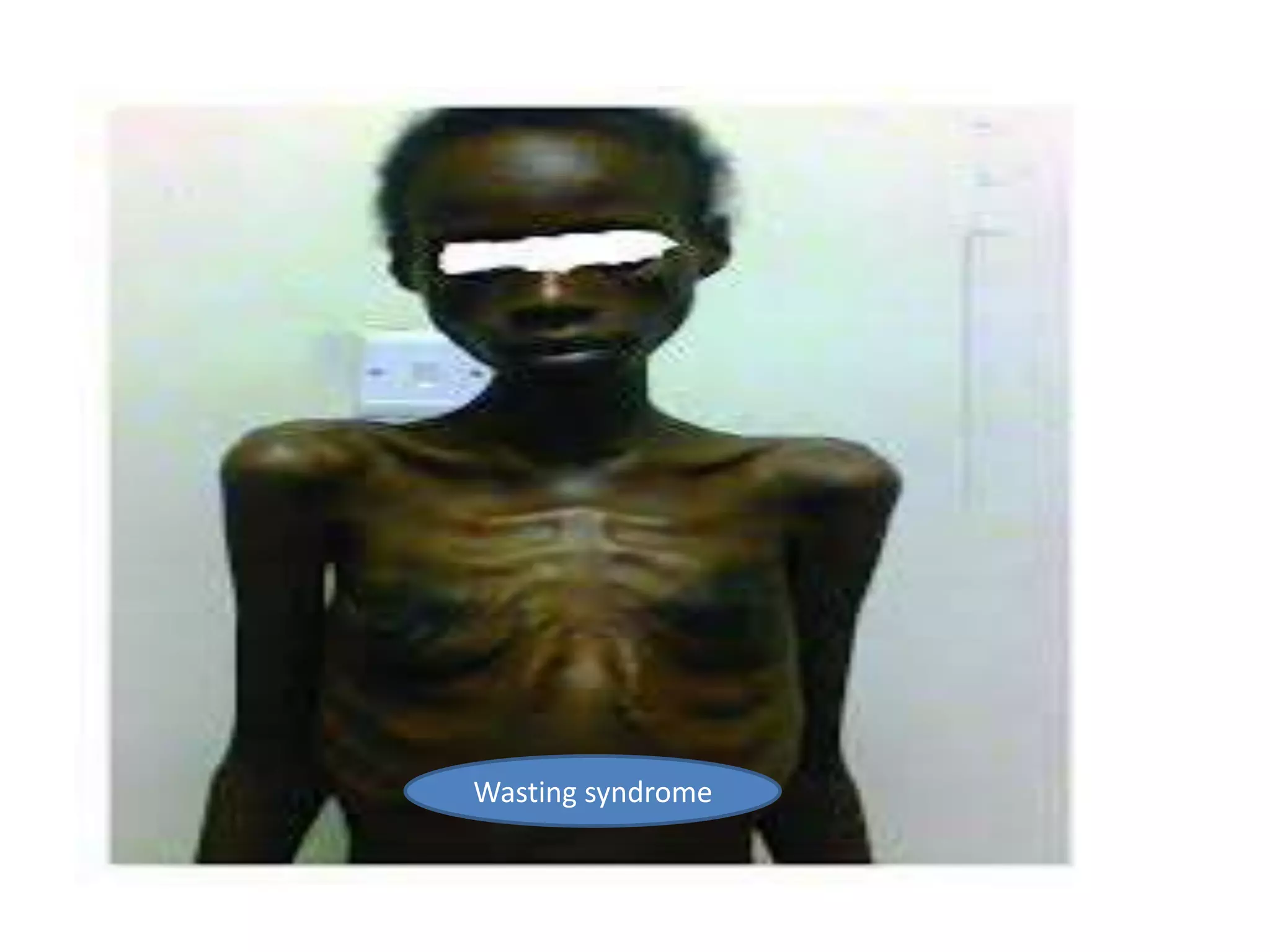
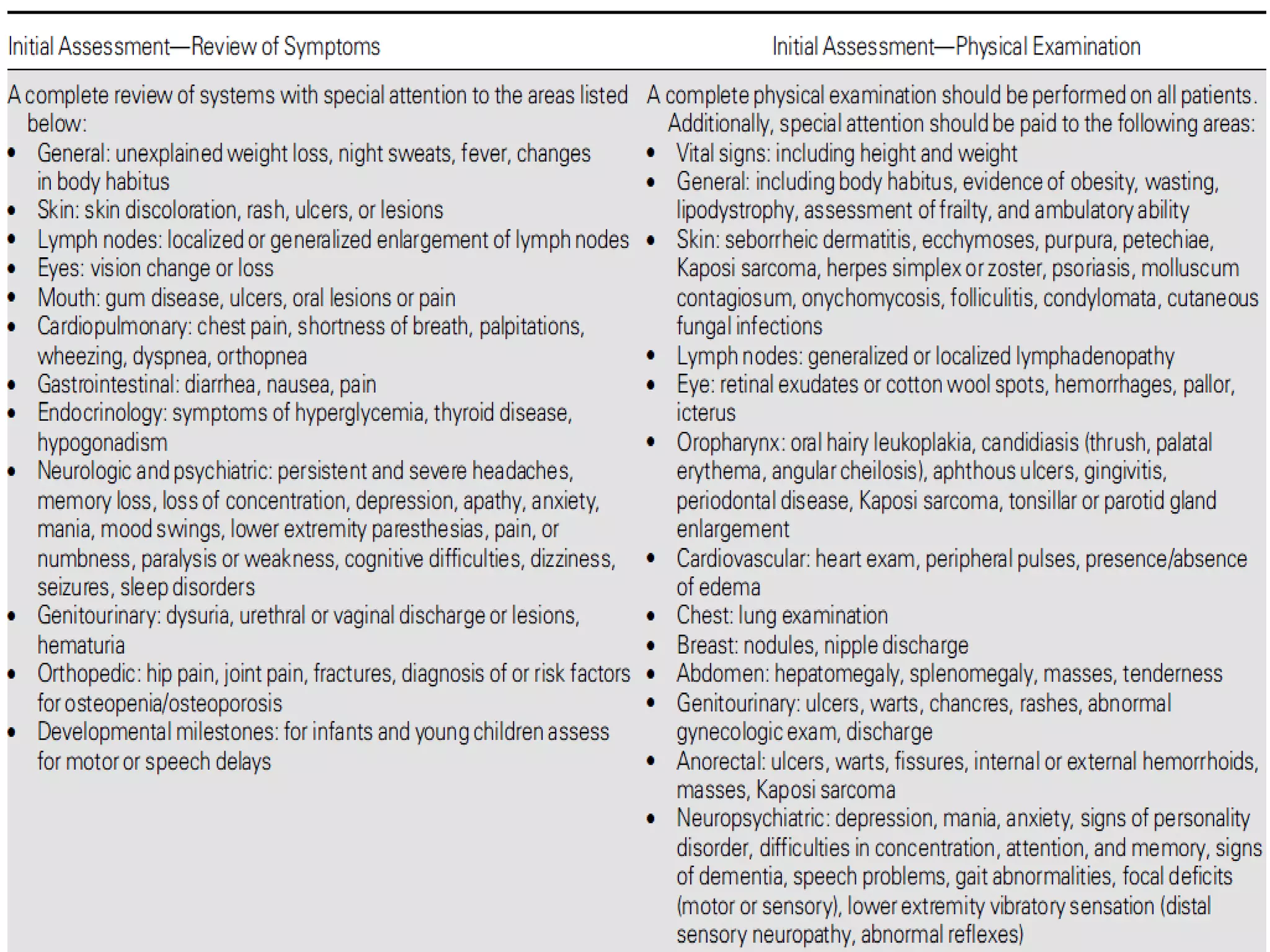
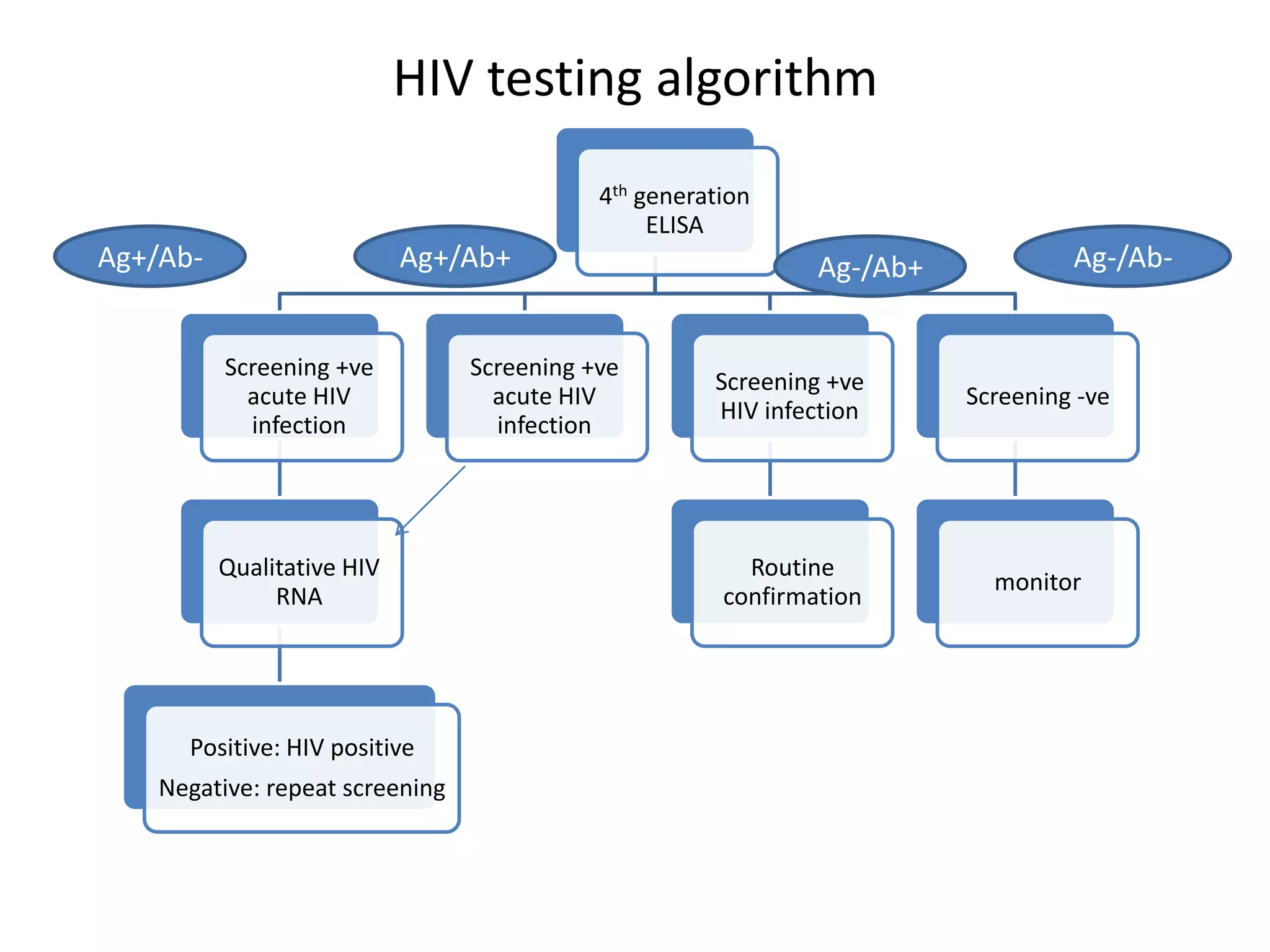
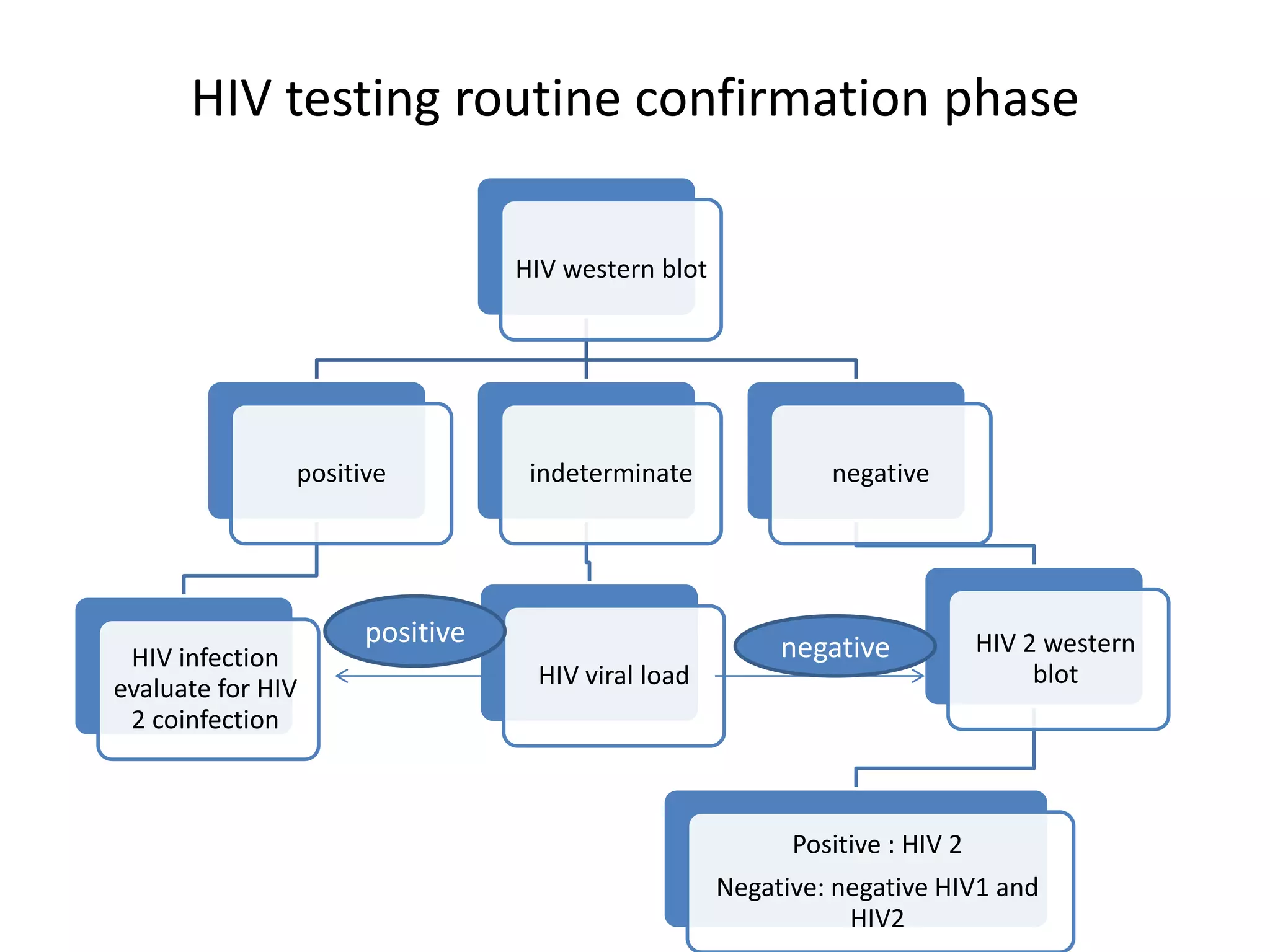
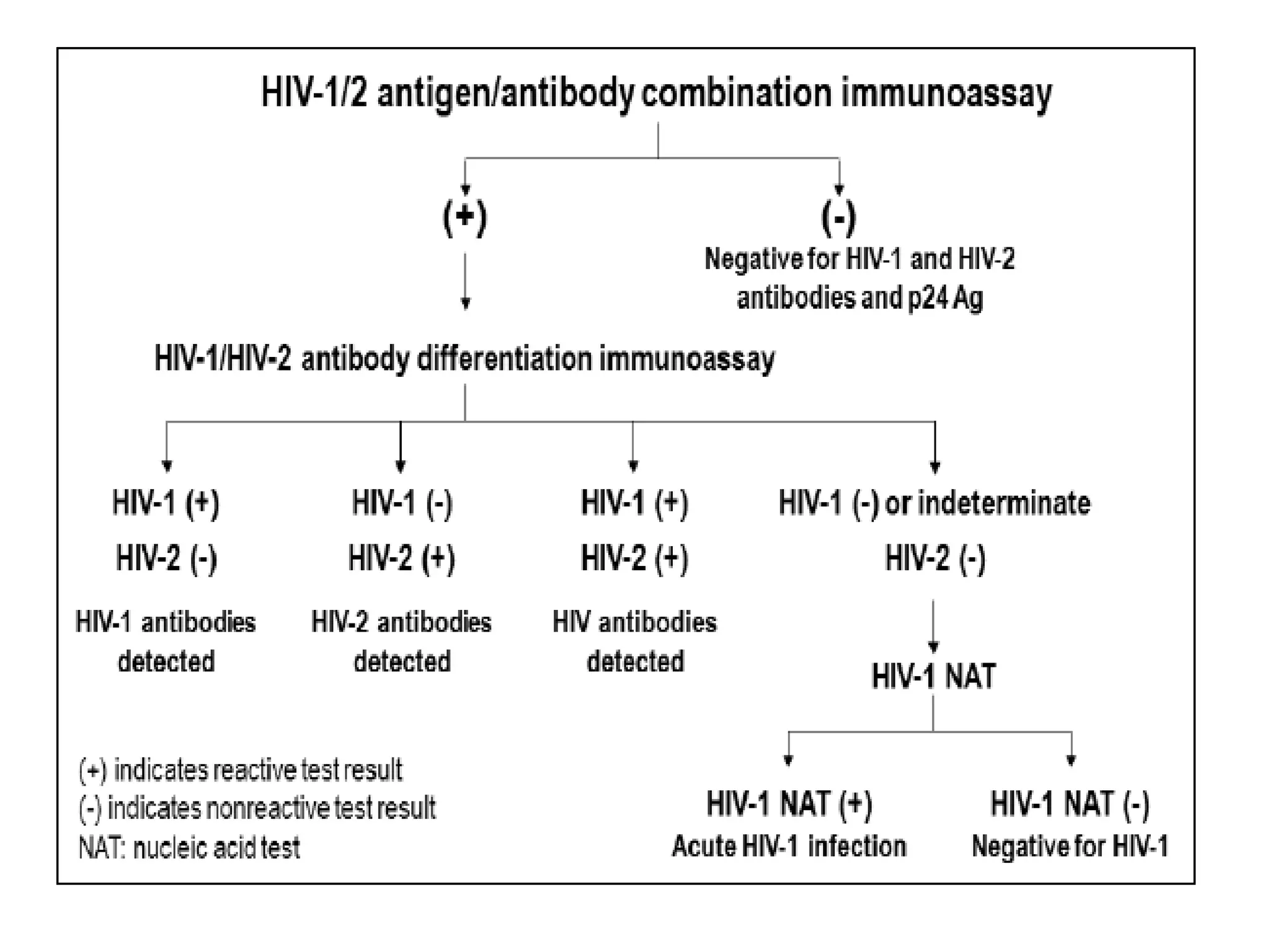
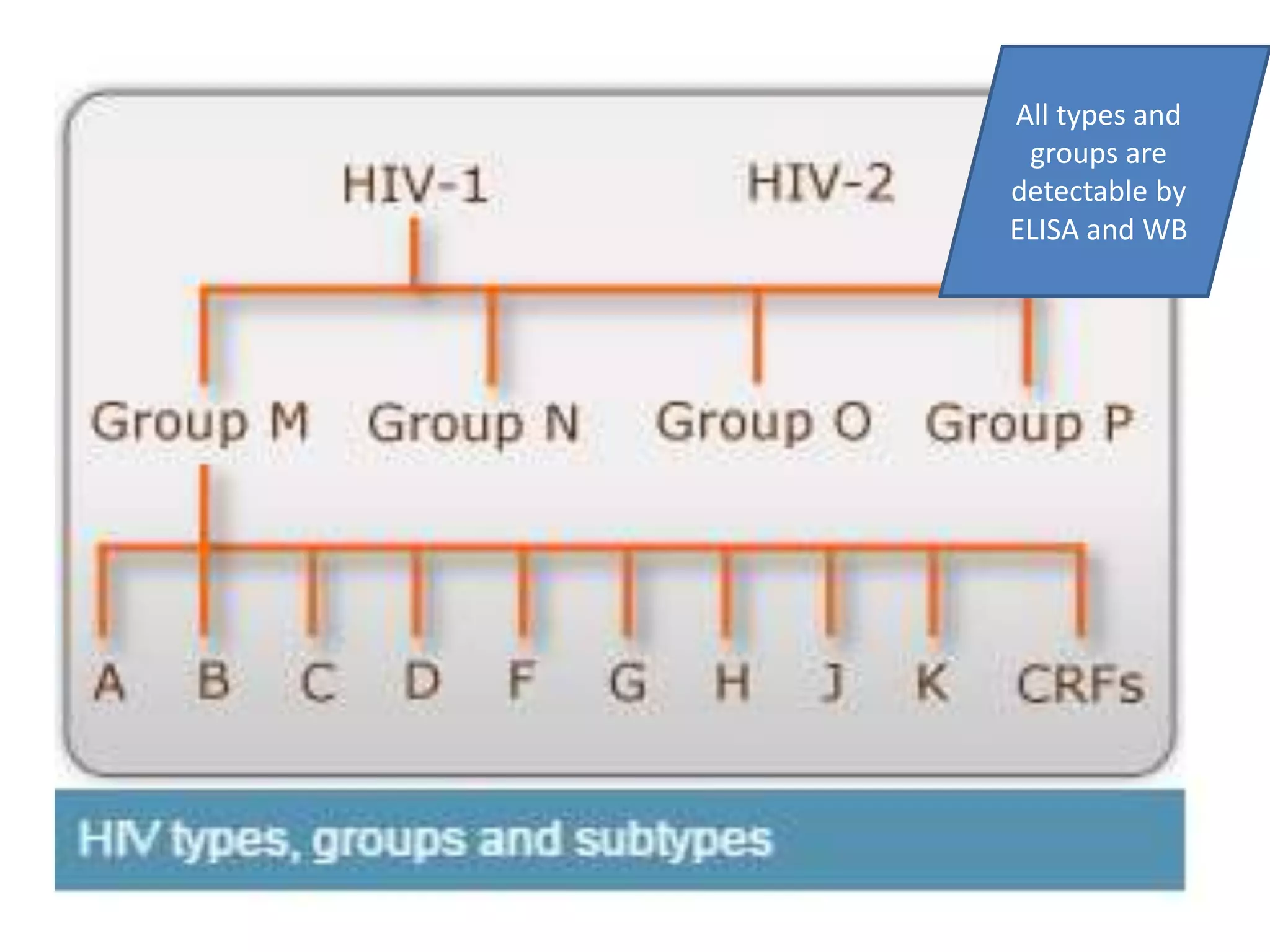
HIV infection is caused by a retrovirus that can lead to AIDS if not treated. It is transmitted through bodily fluids and can be diagnosed through viral load tests, p24 antigen tests, HIV antibody tests, and Western blot. If left untreated, it progresses from acute infection to asymptomatic infection and eventually symptomatic infection and AIDS. Antiretroviral therapy is recommended for all infected individuals to suppress the virus and preserve immune function. The goals of treatment are to durably suppress the virus, restore immune function, and prevent transmission. Response is monitored through clinical, virologic, and immunologic measures.


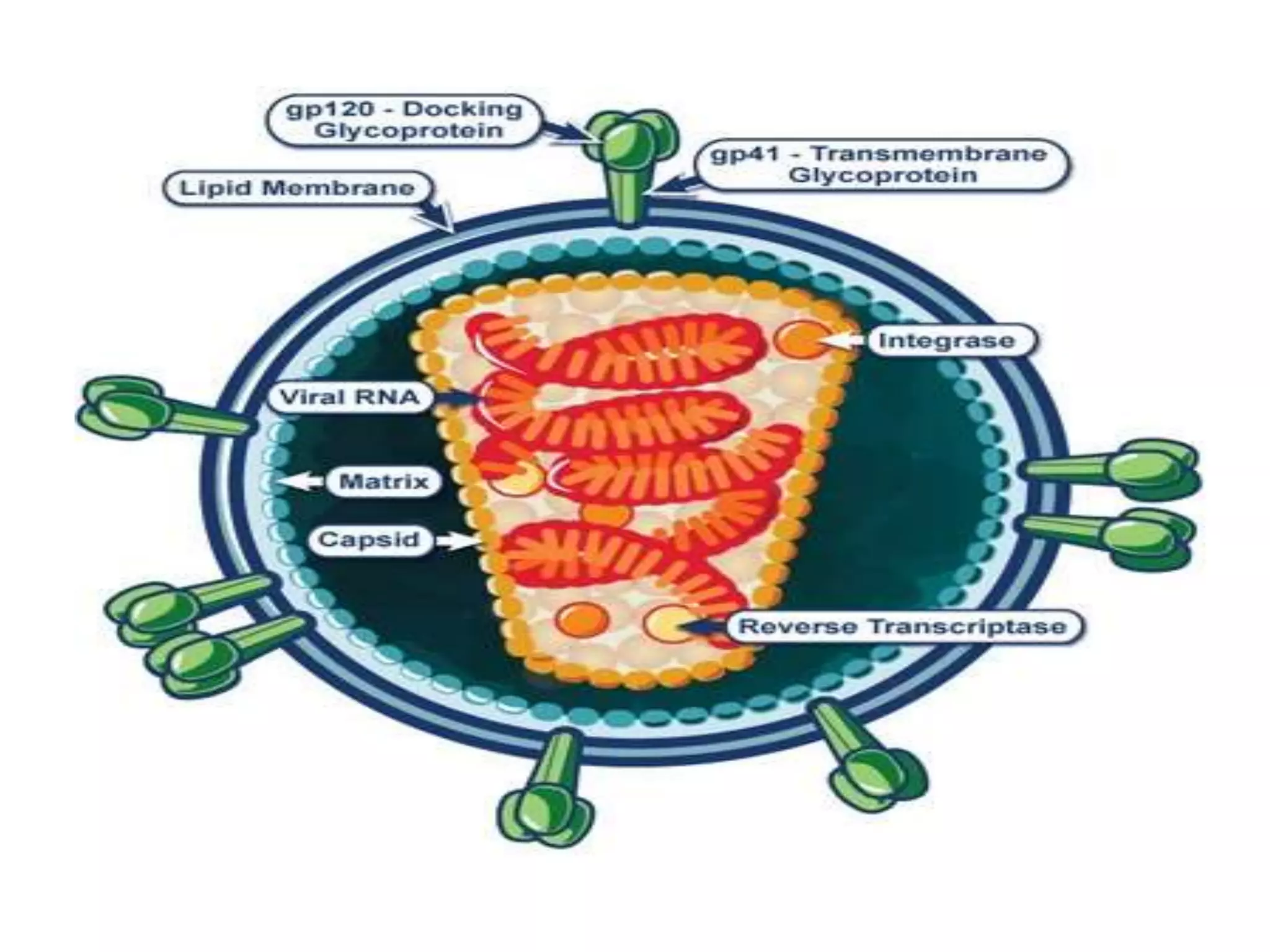
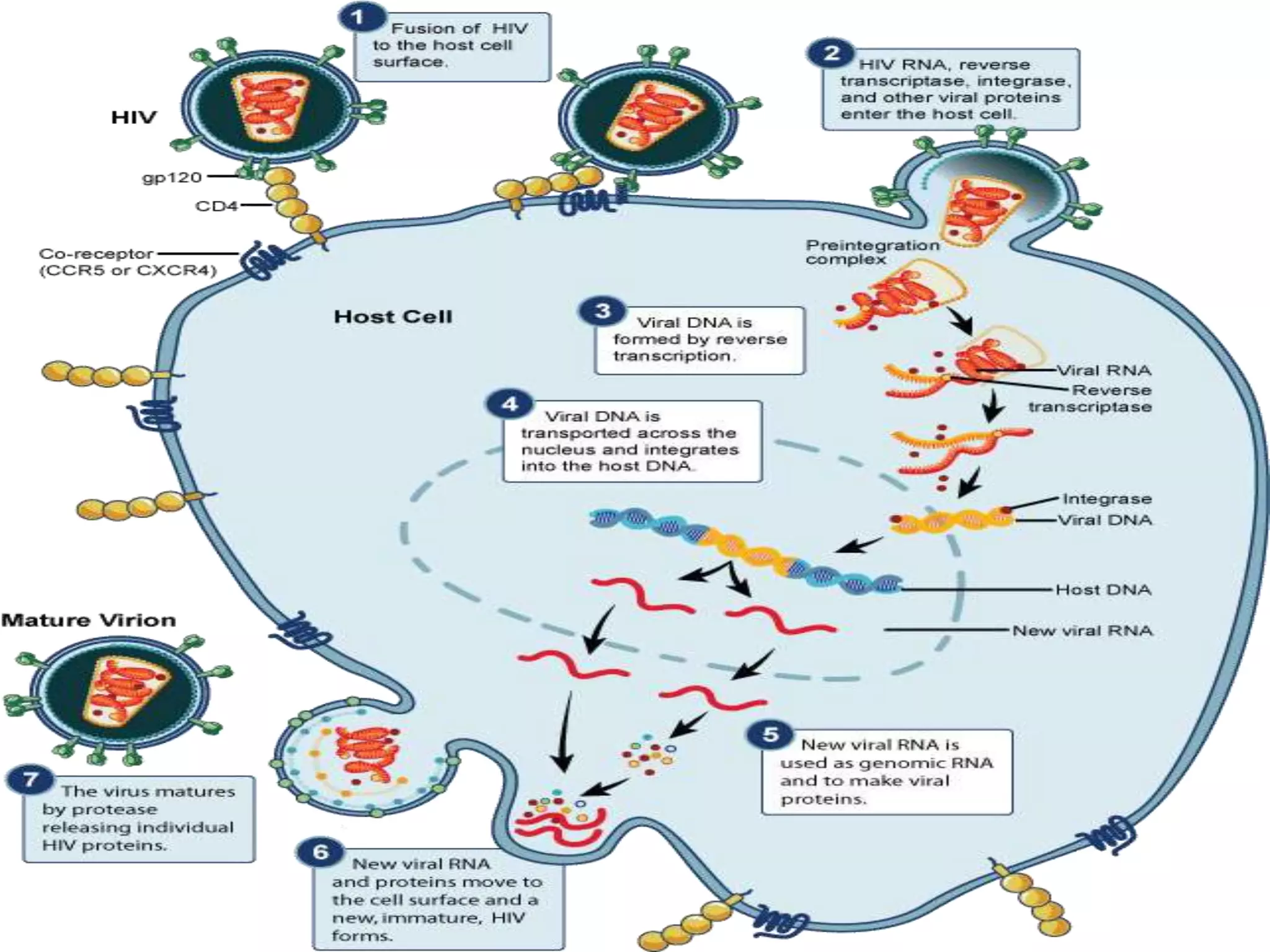
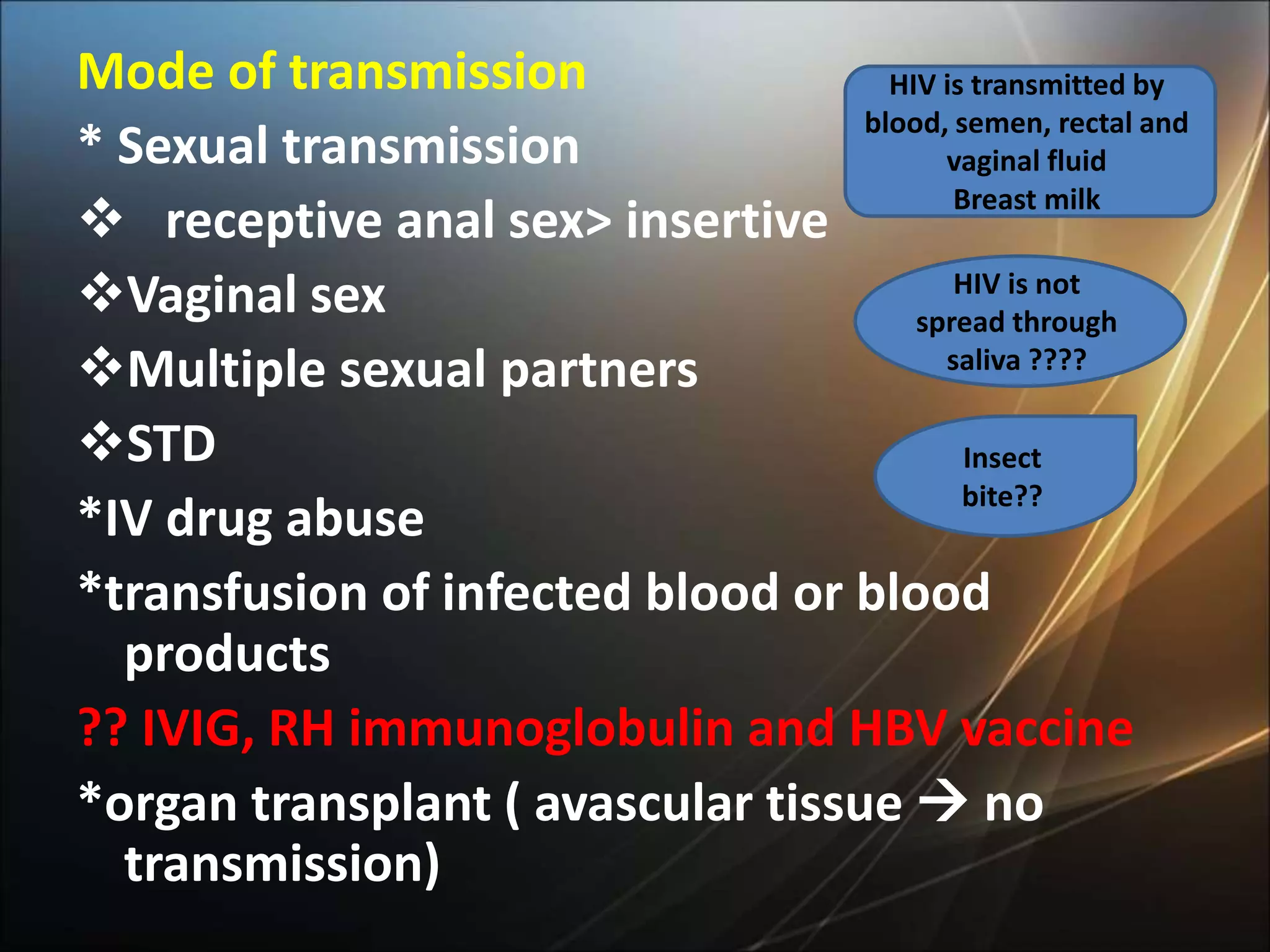


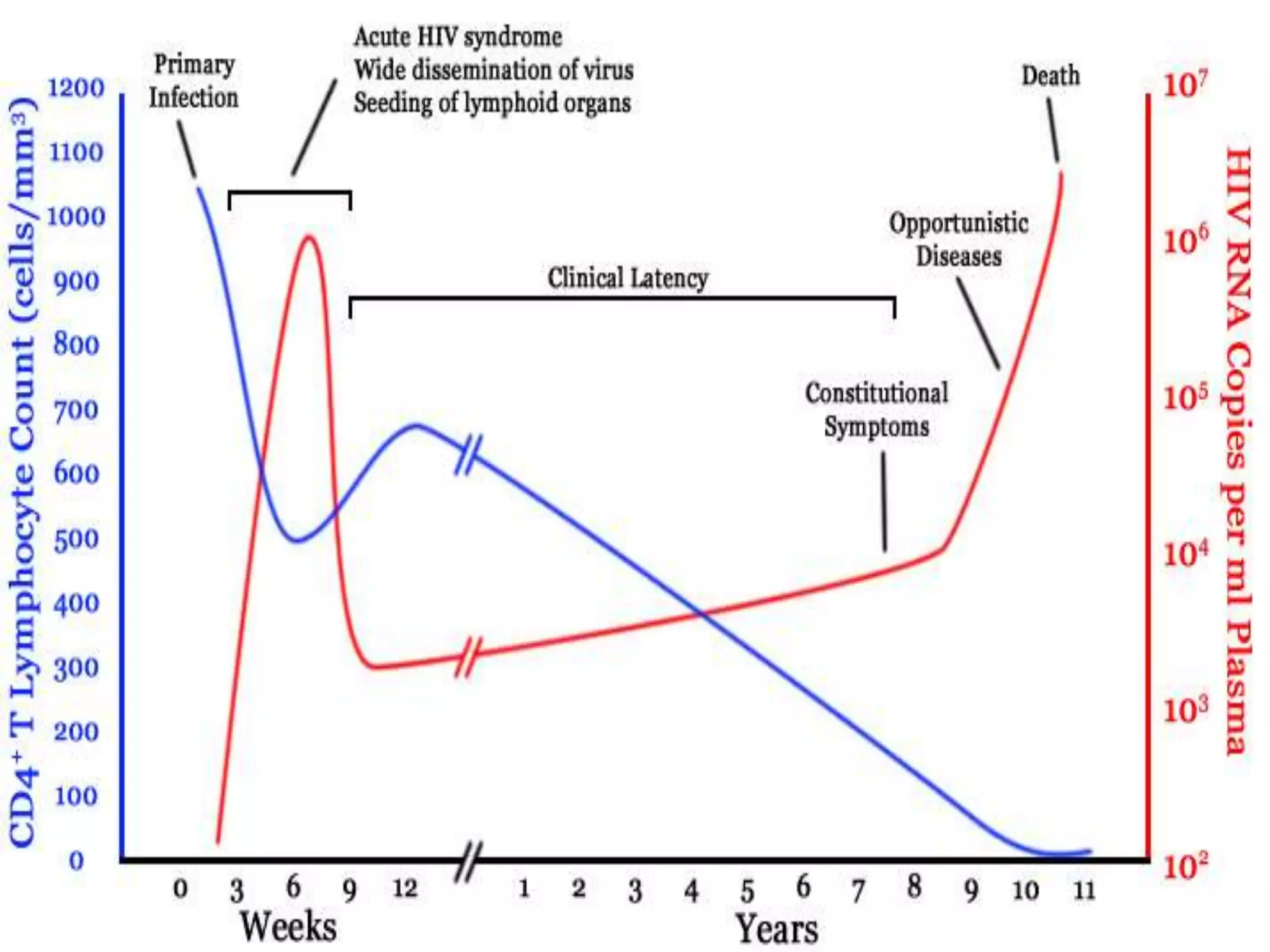





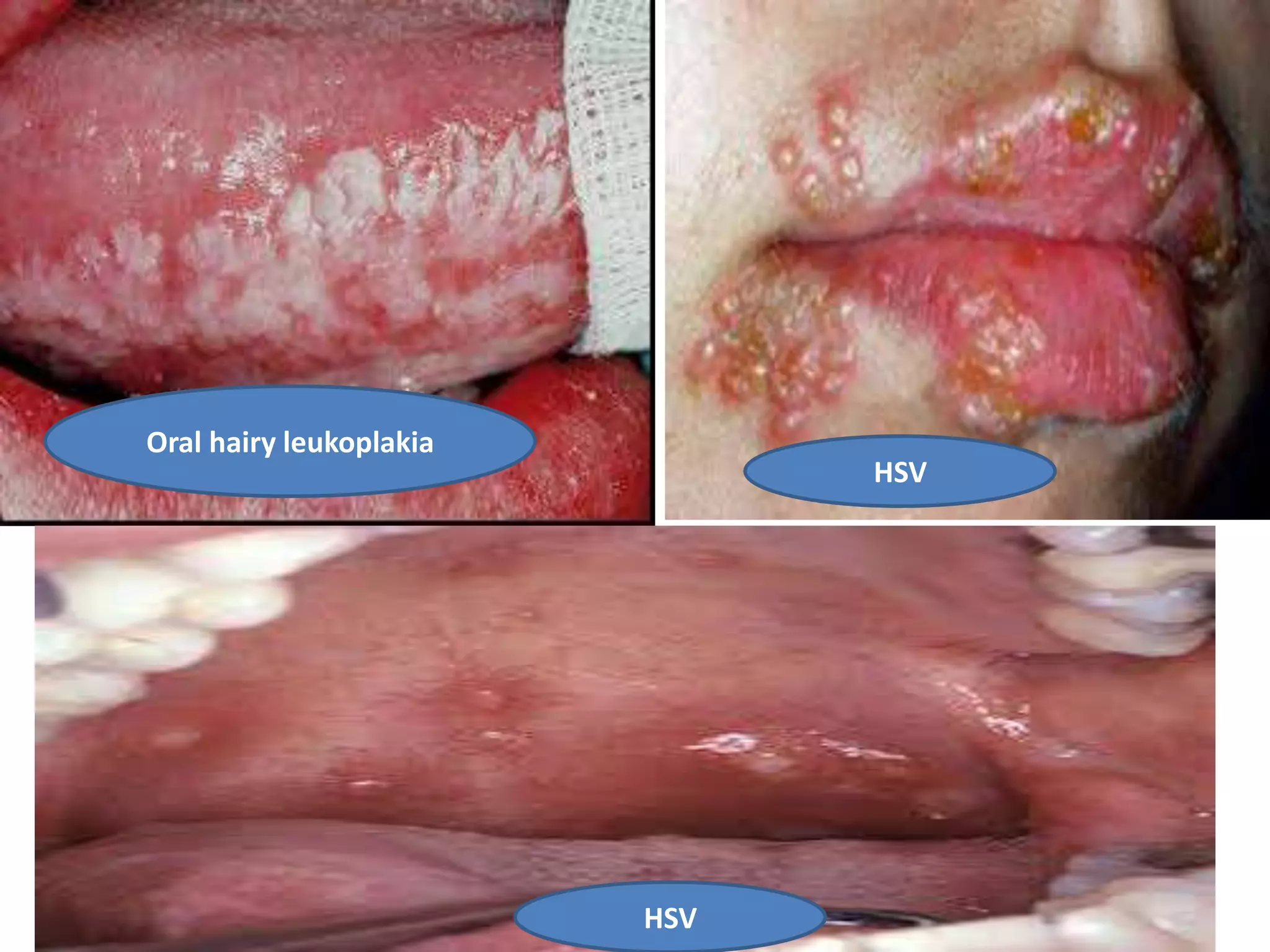
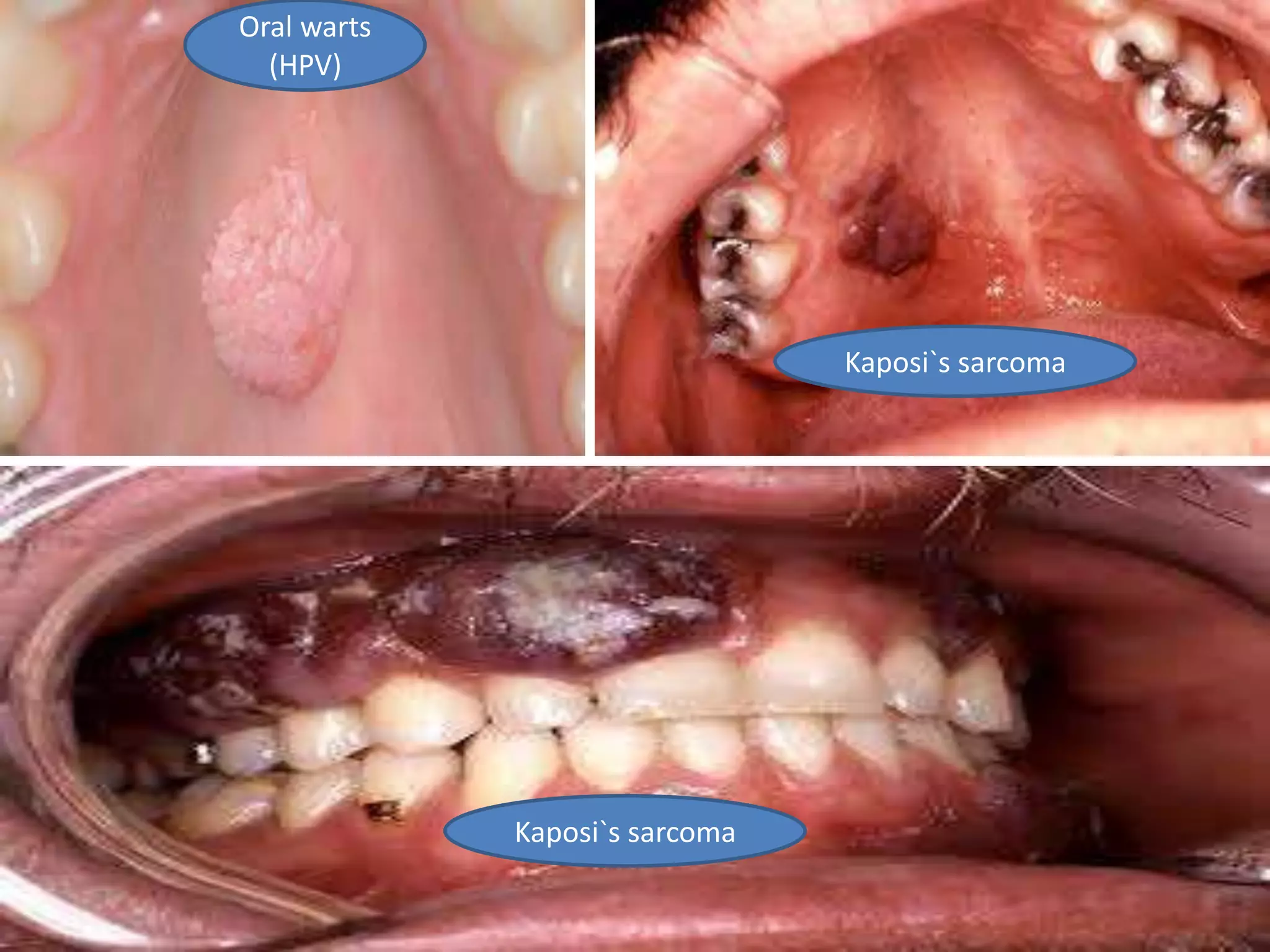
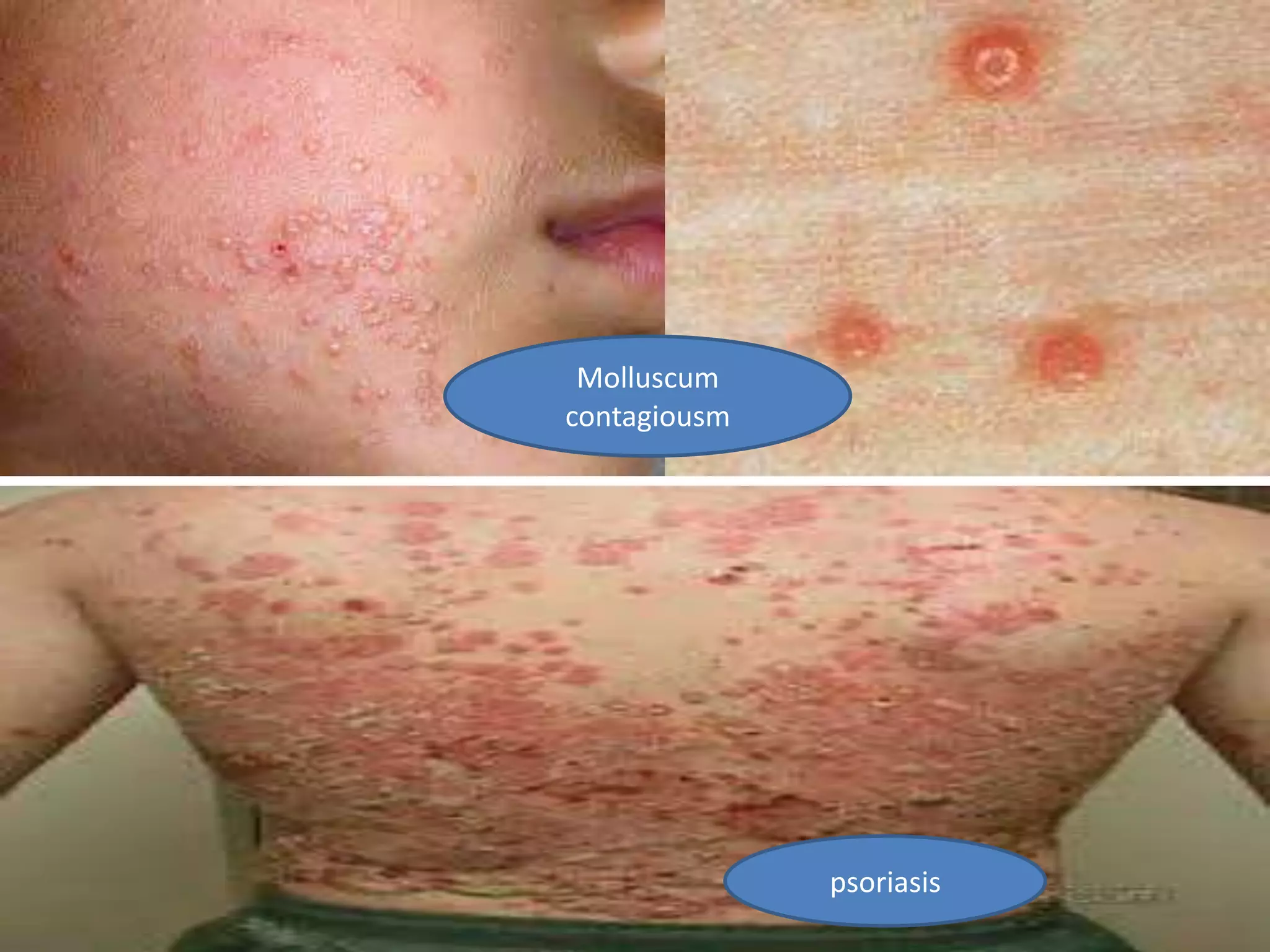
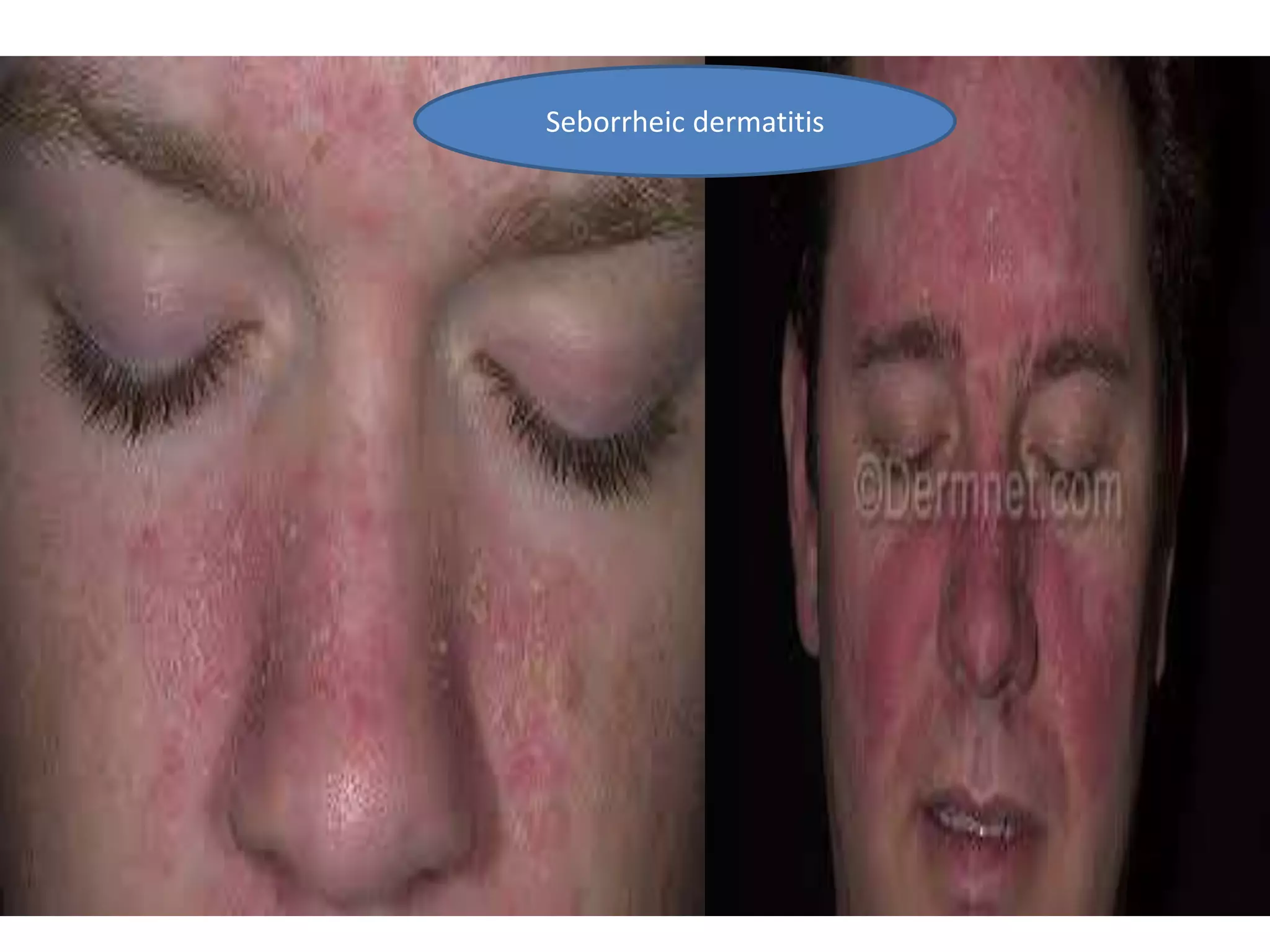













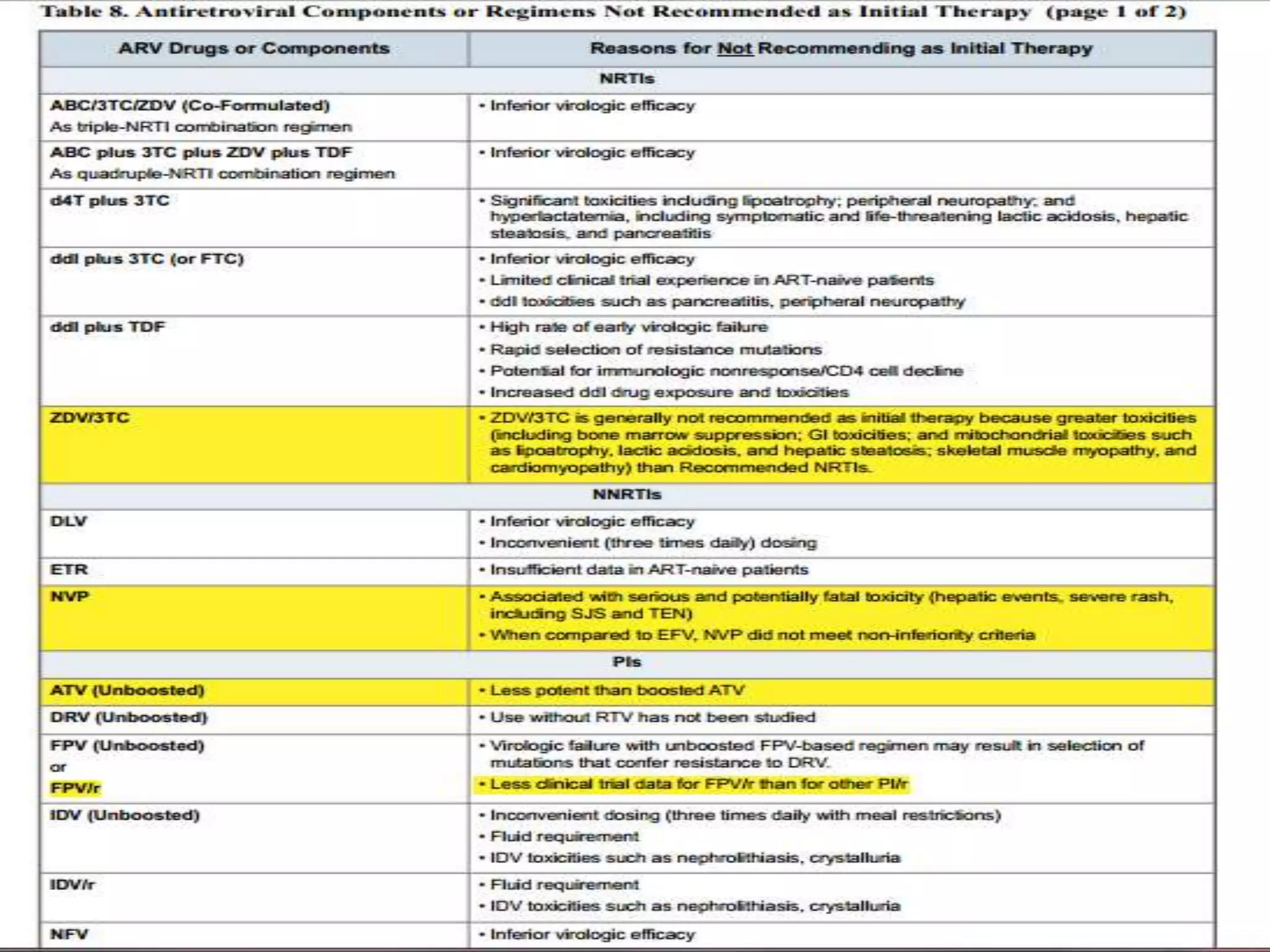
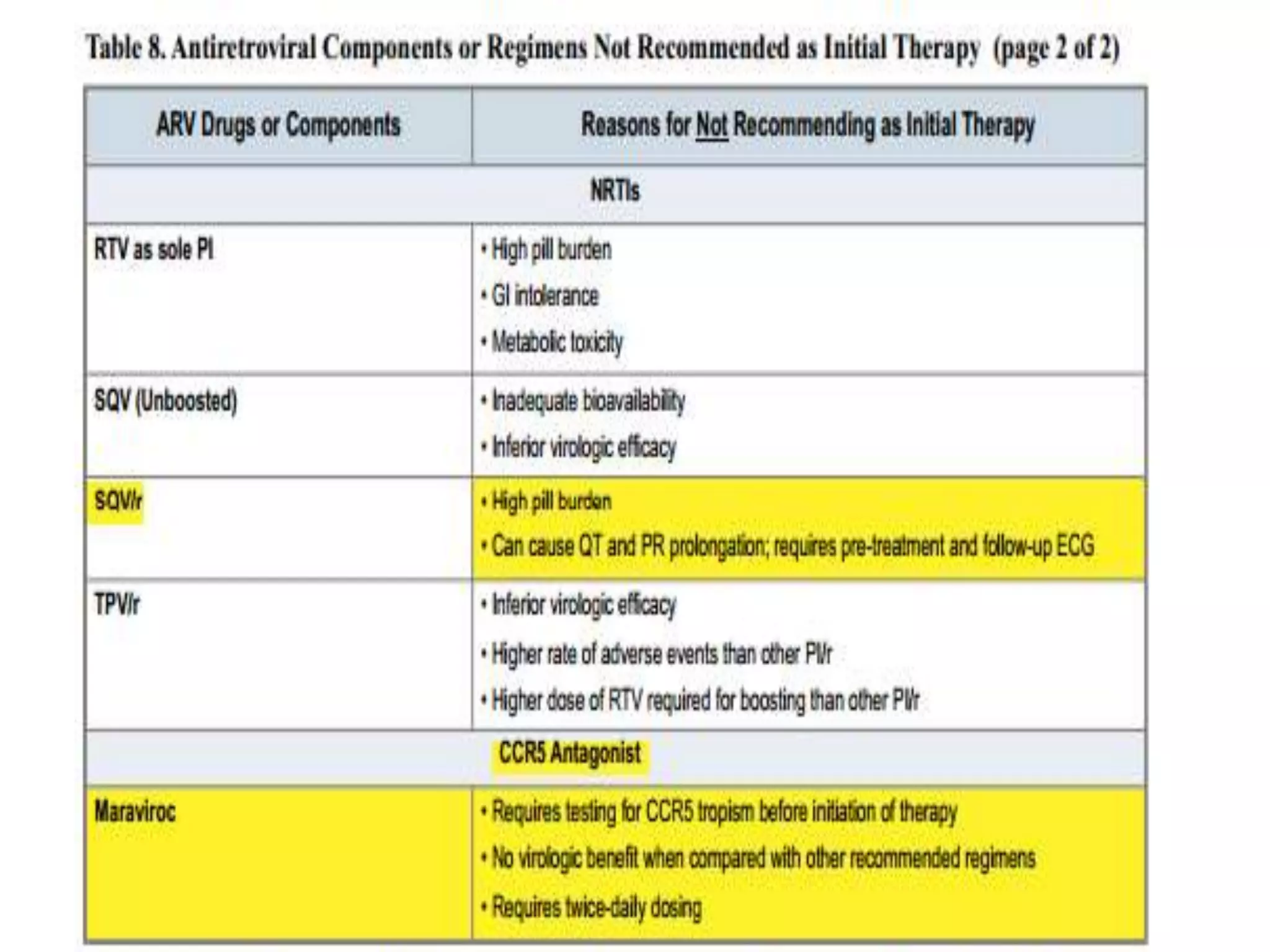
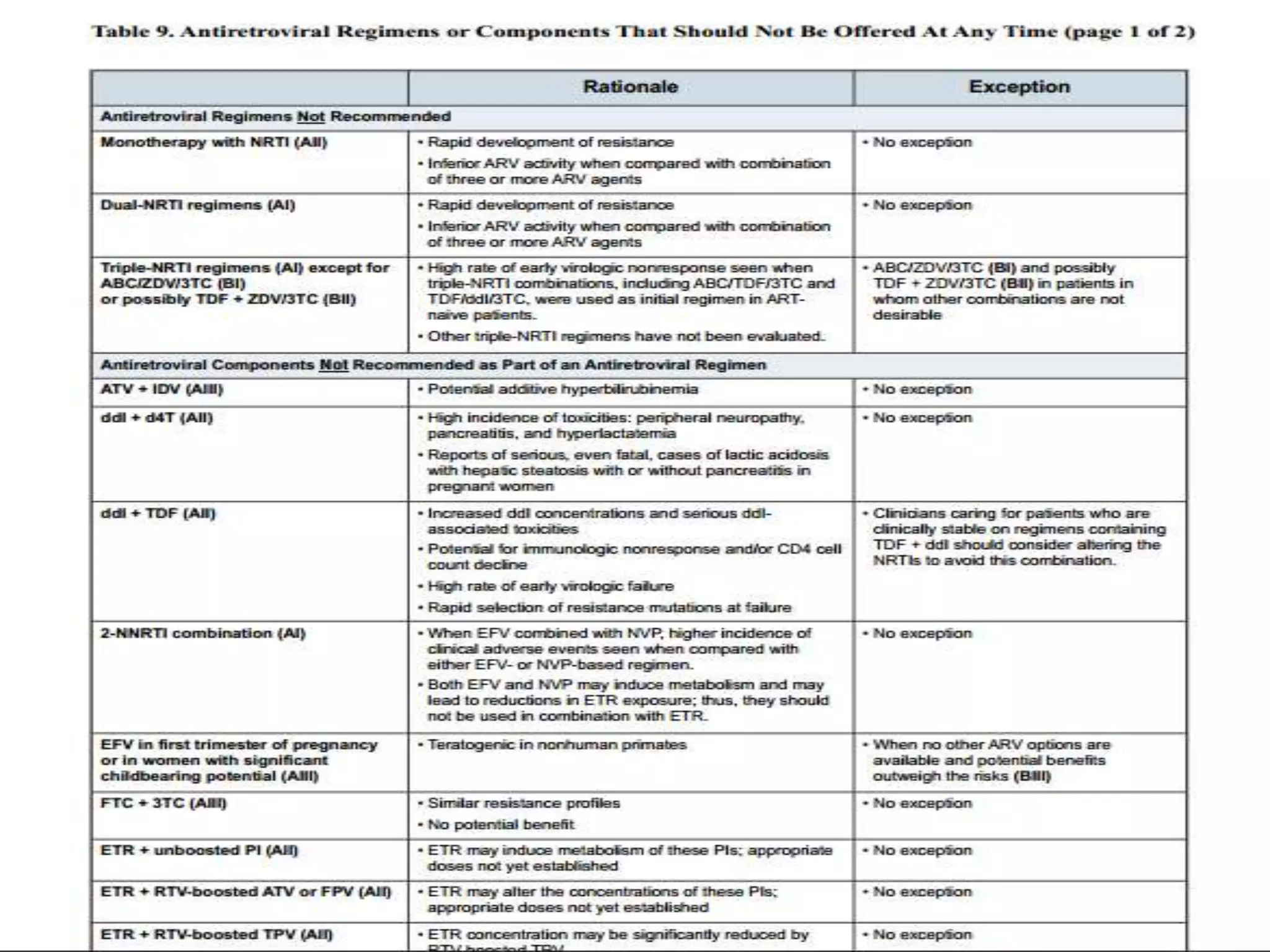
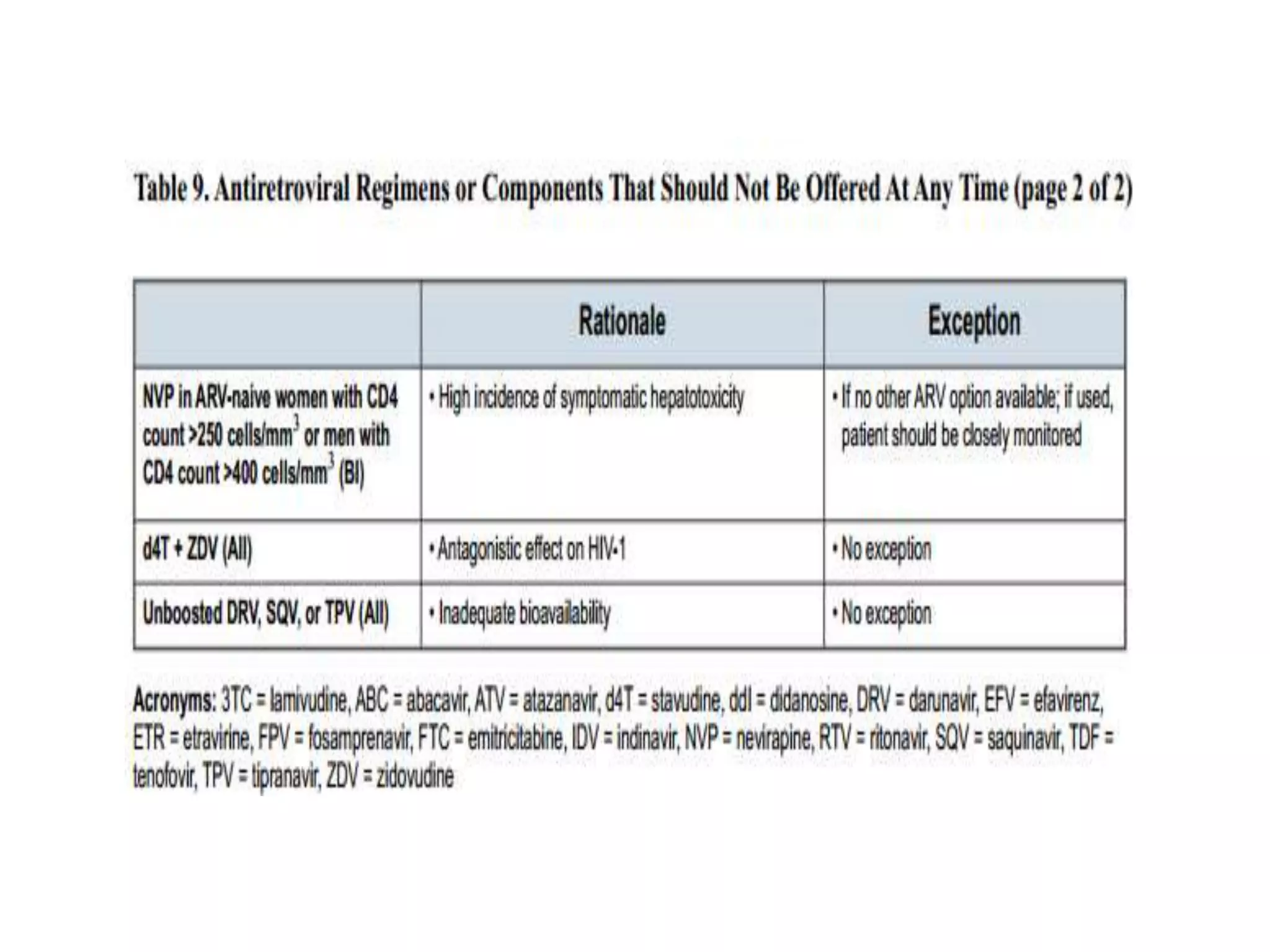





![Causes of immunologic failure
CD4 count <200/mm3 at initiation of ART
• Older age
• Coinfection (e.g., [HCV], HIV-2,[HTLV-1], HTLV-2)
• ARVs (e.g., zidovudine [ZDV], tenofovir disoproxil
fumarate [TDF] + didanosine [ddI]) and other
medications
• Persistent immune activation
• Loss of regenerative potential of the immune
system
• Concomitant medical conditions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hivlecturefellow-151221082930/75/Hiv-lecture-68-2048.jpg)
