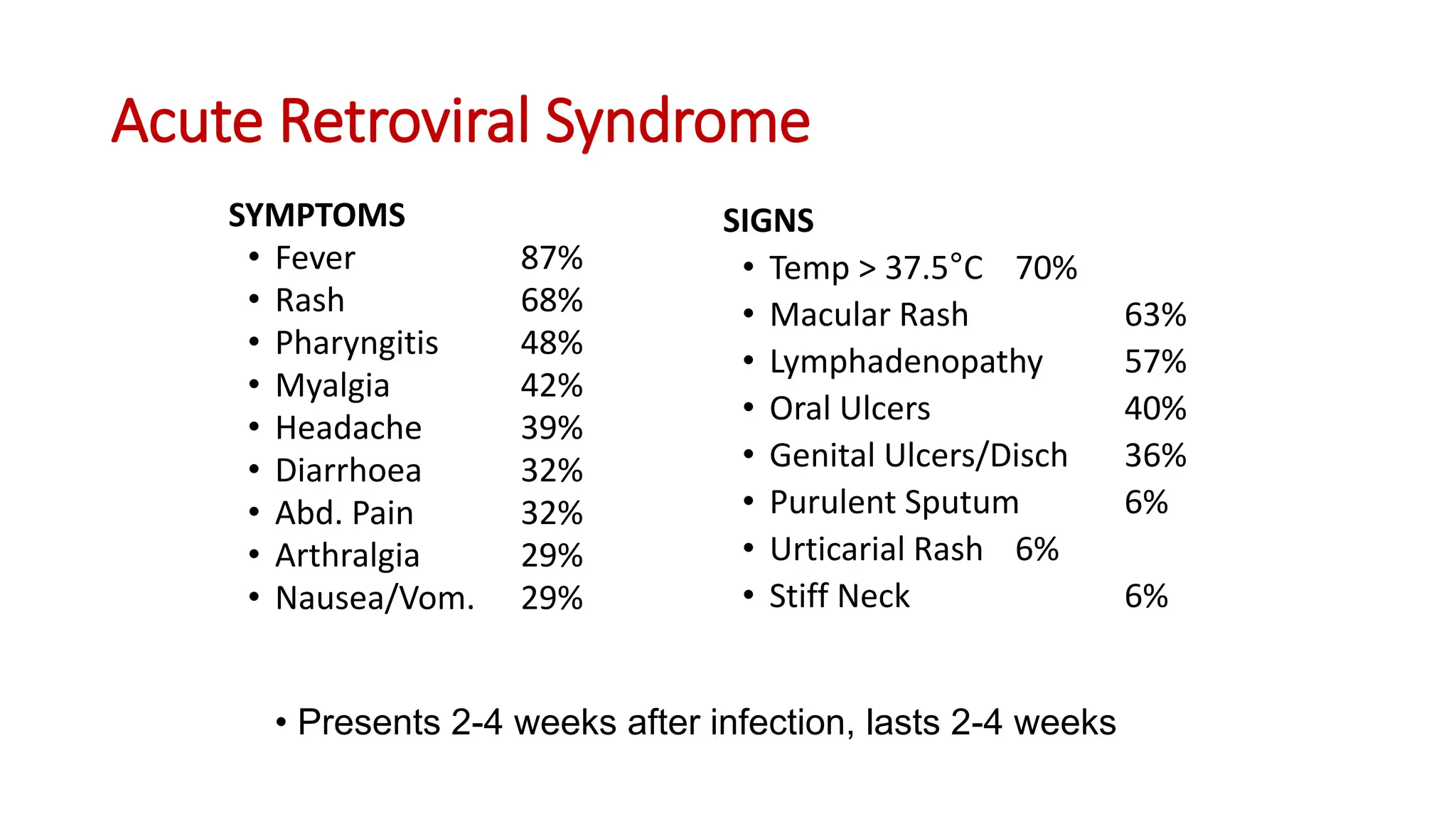
The document provides an overview of key topics related to HIV/AIDS in Namibia, including:
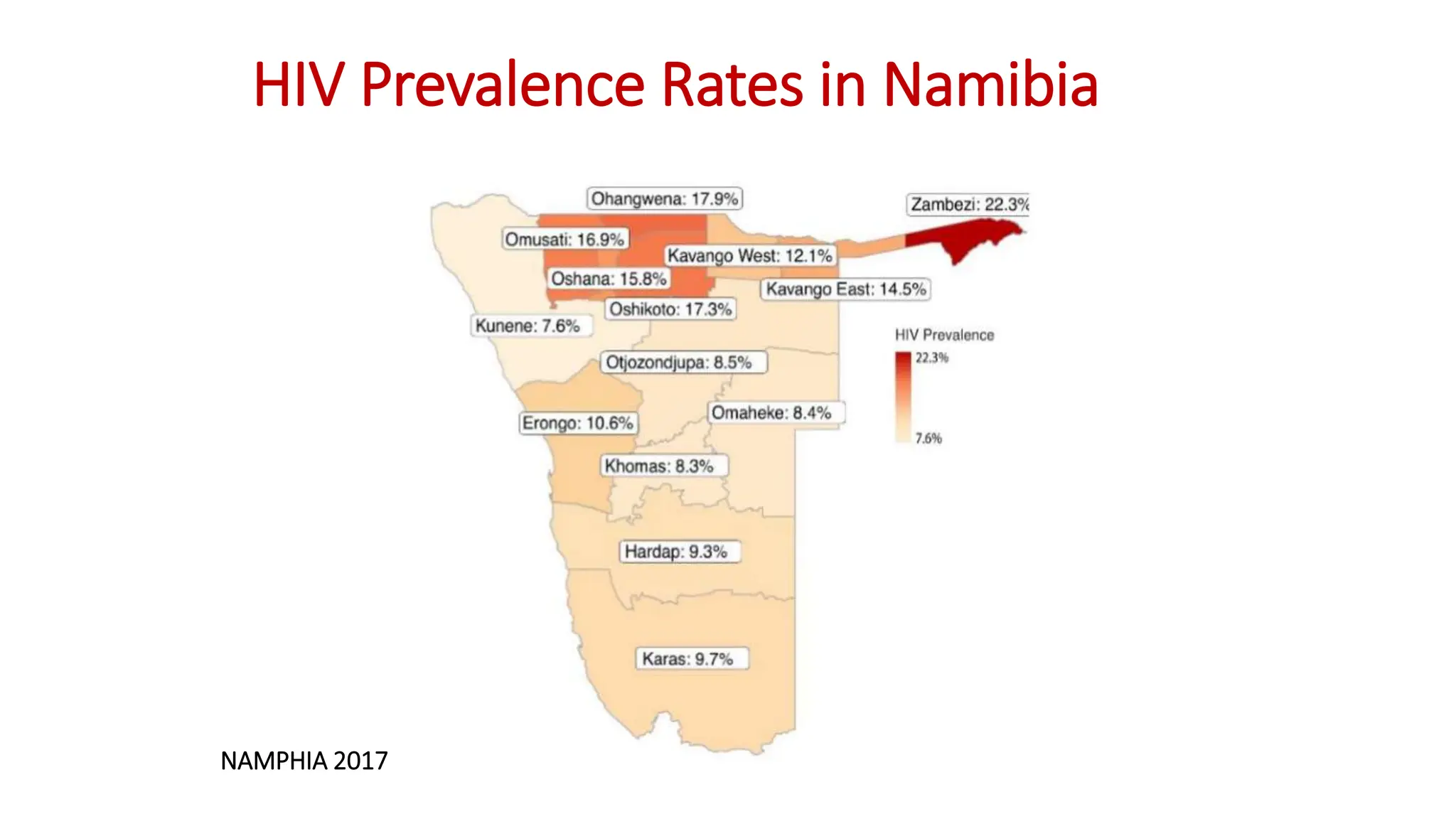
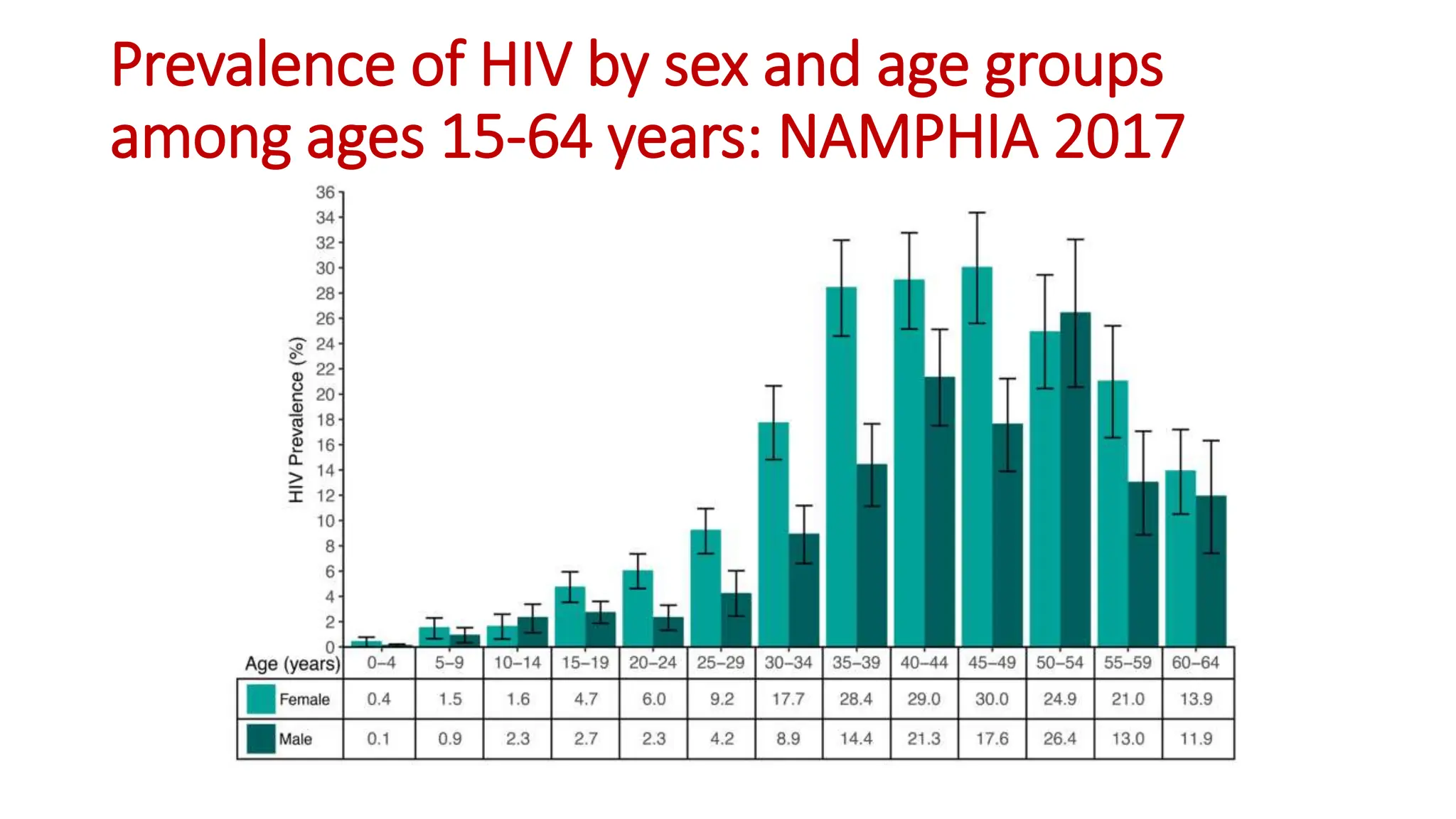
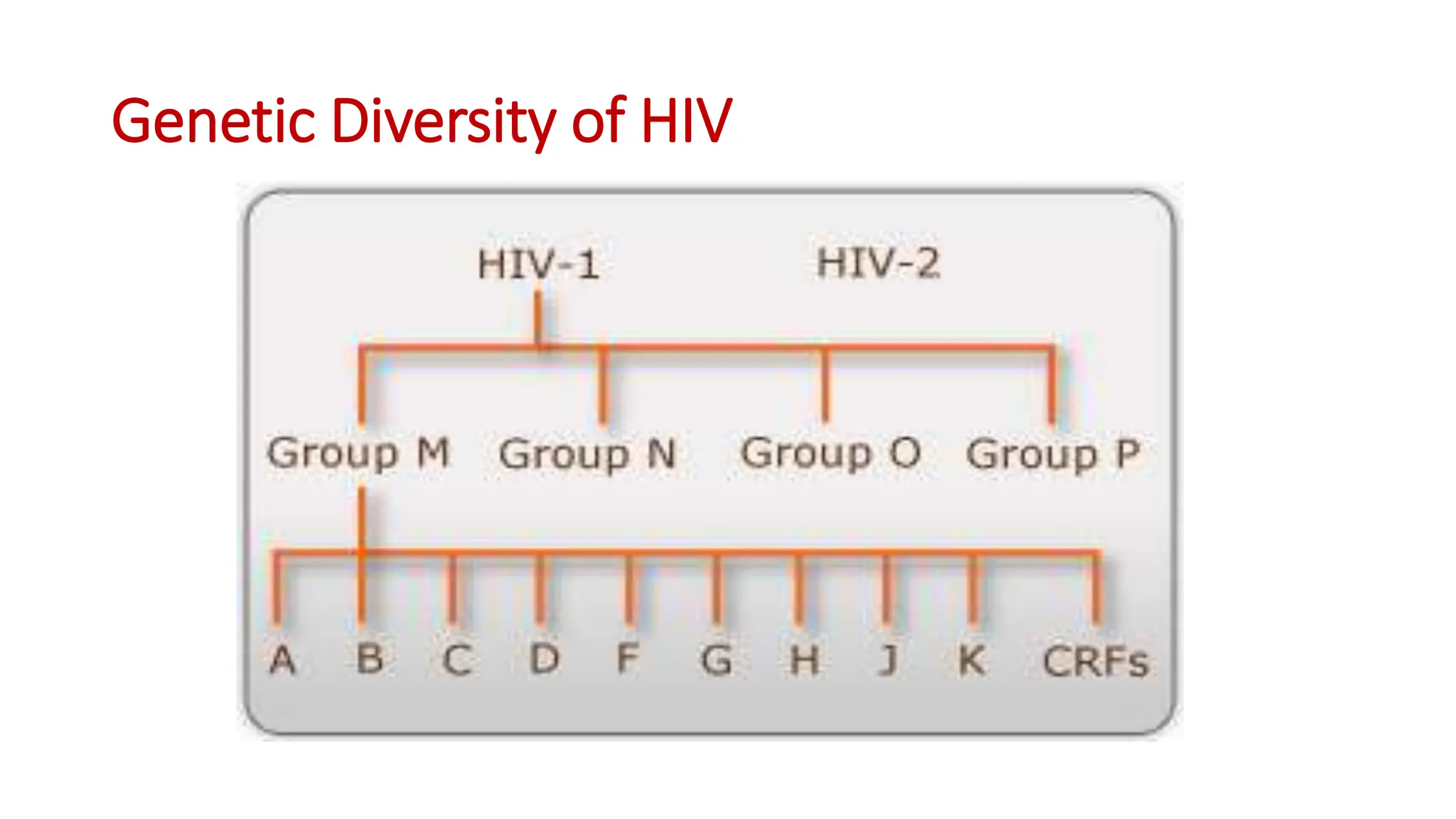
1) HIV prevalence rates in Namibia are reported from the 2017 NAMPHIA study. The predominant strain in Namibia is HIV-1 type C, which is more virulent and associated with faster disease progression than other subtypes like B.
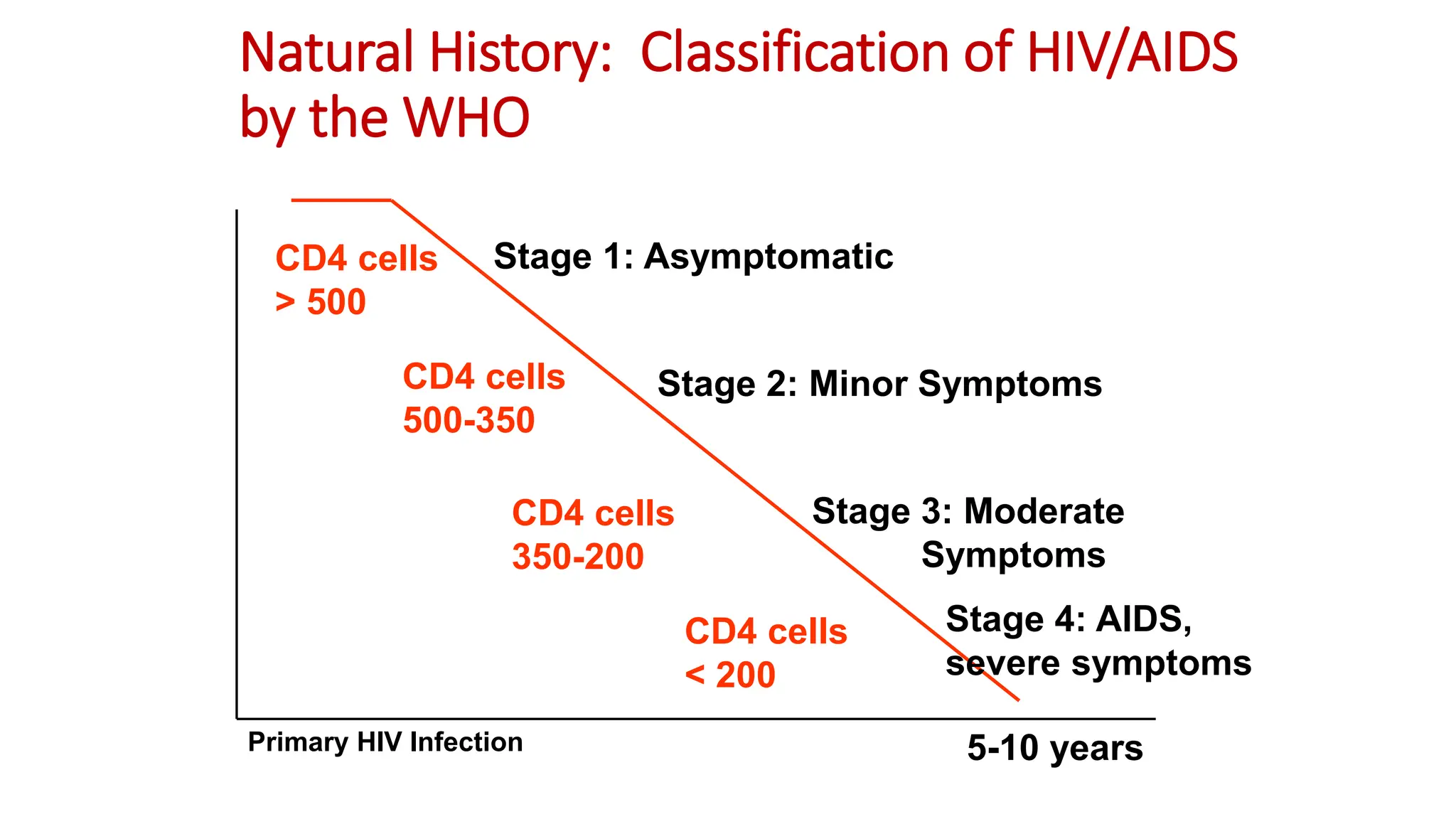
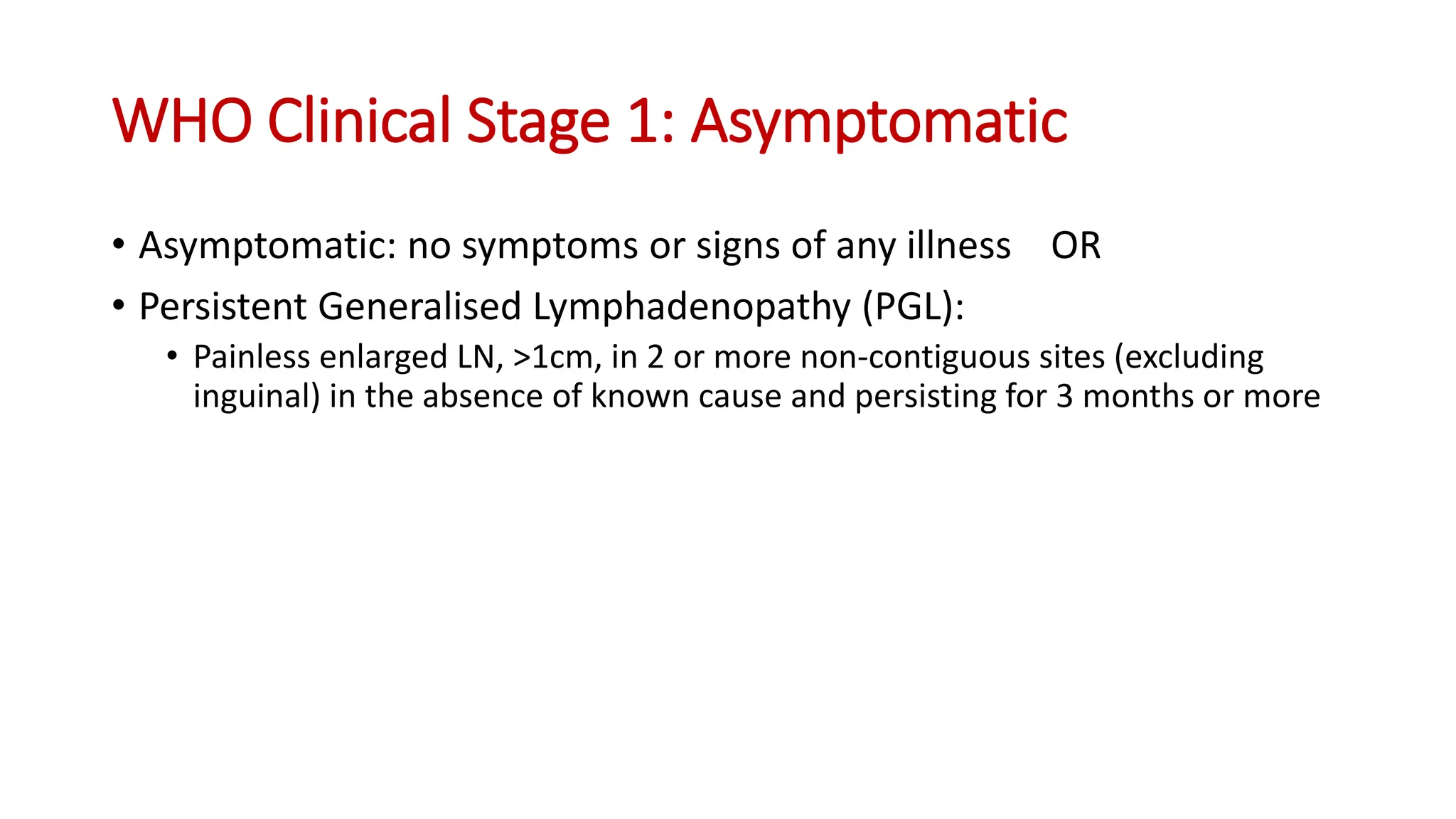
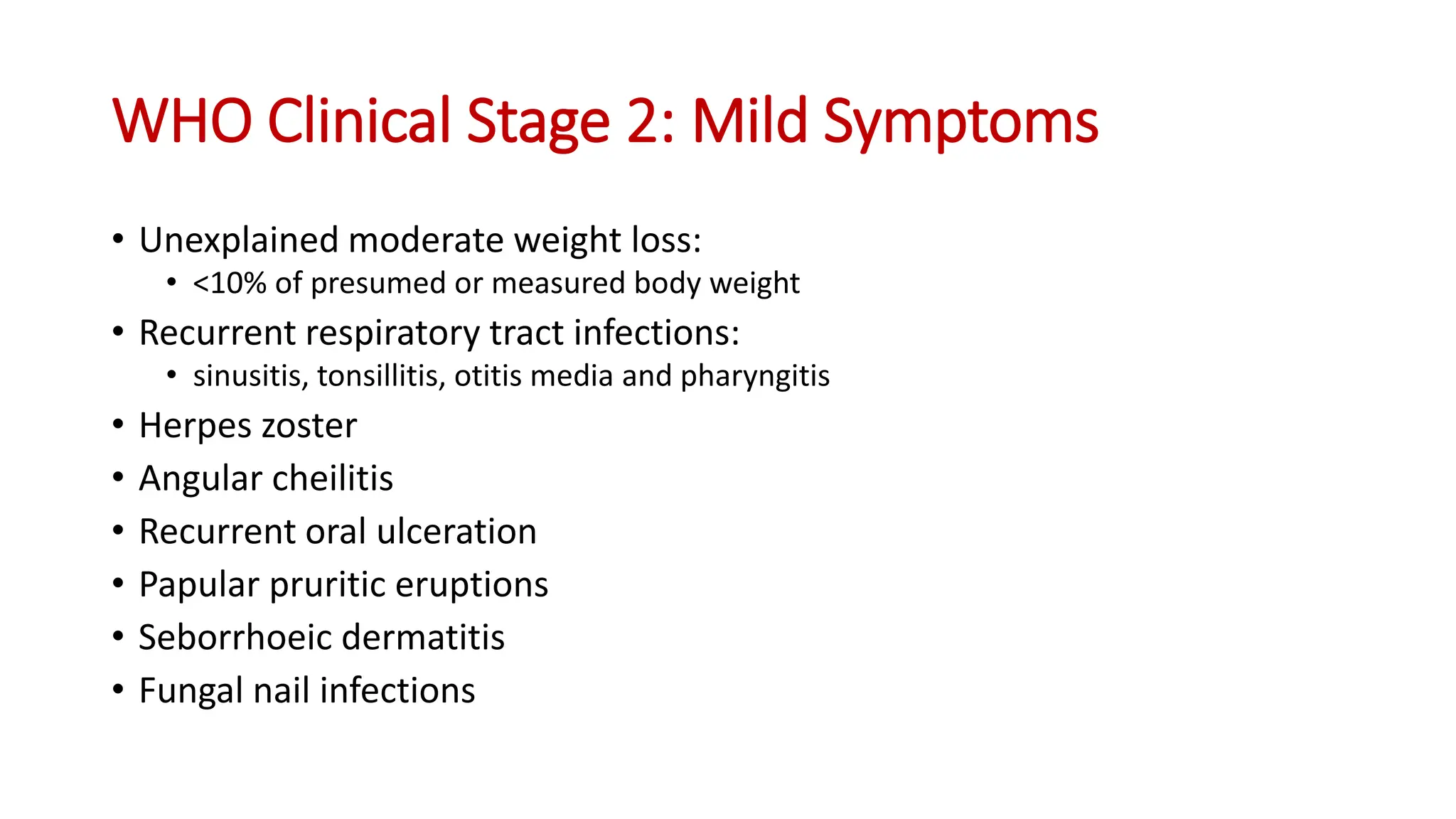
2) Clinical staging of HIV is described according to the WHO system from Stage 1 (asymptomatic) to Stage 4 (severe AIDS symptoms). Guidelines for use of co-trimoxazole preventive therapy, isoniazid preventive therapy, and criteria for initiating antiretroviral therapy are provided.
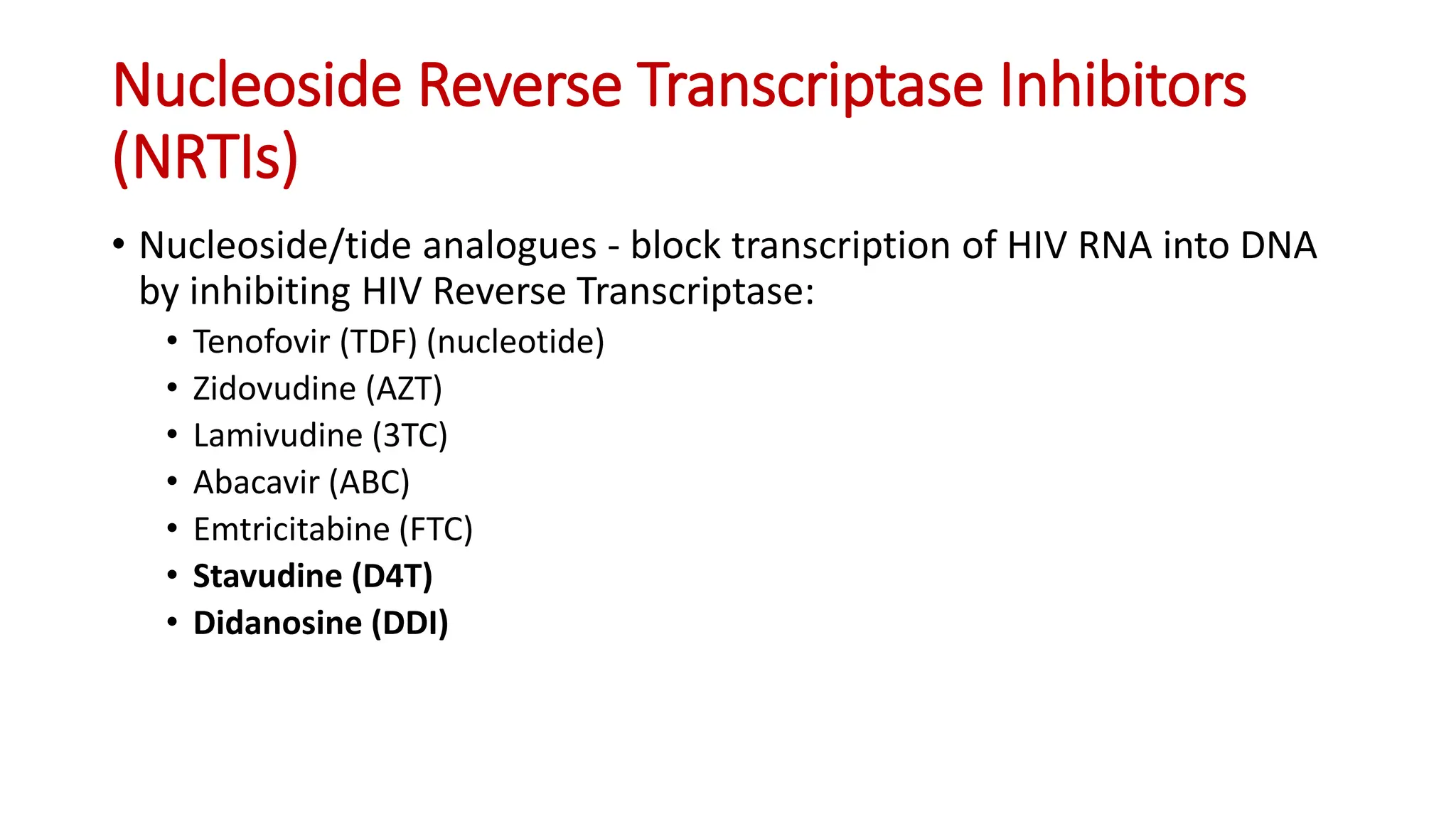
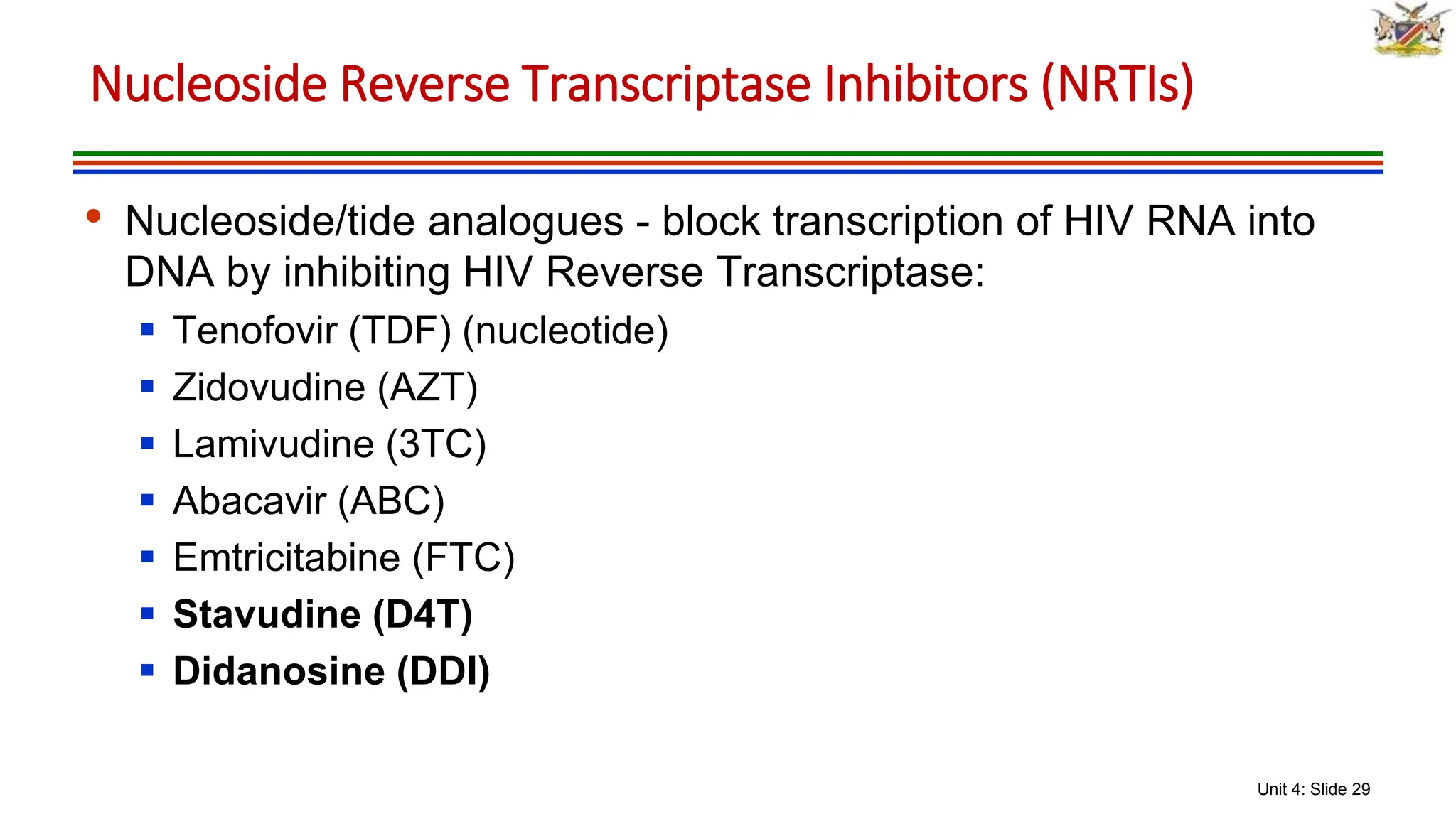
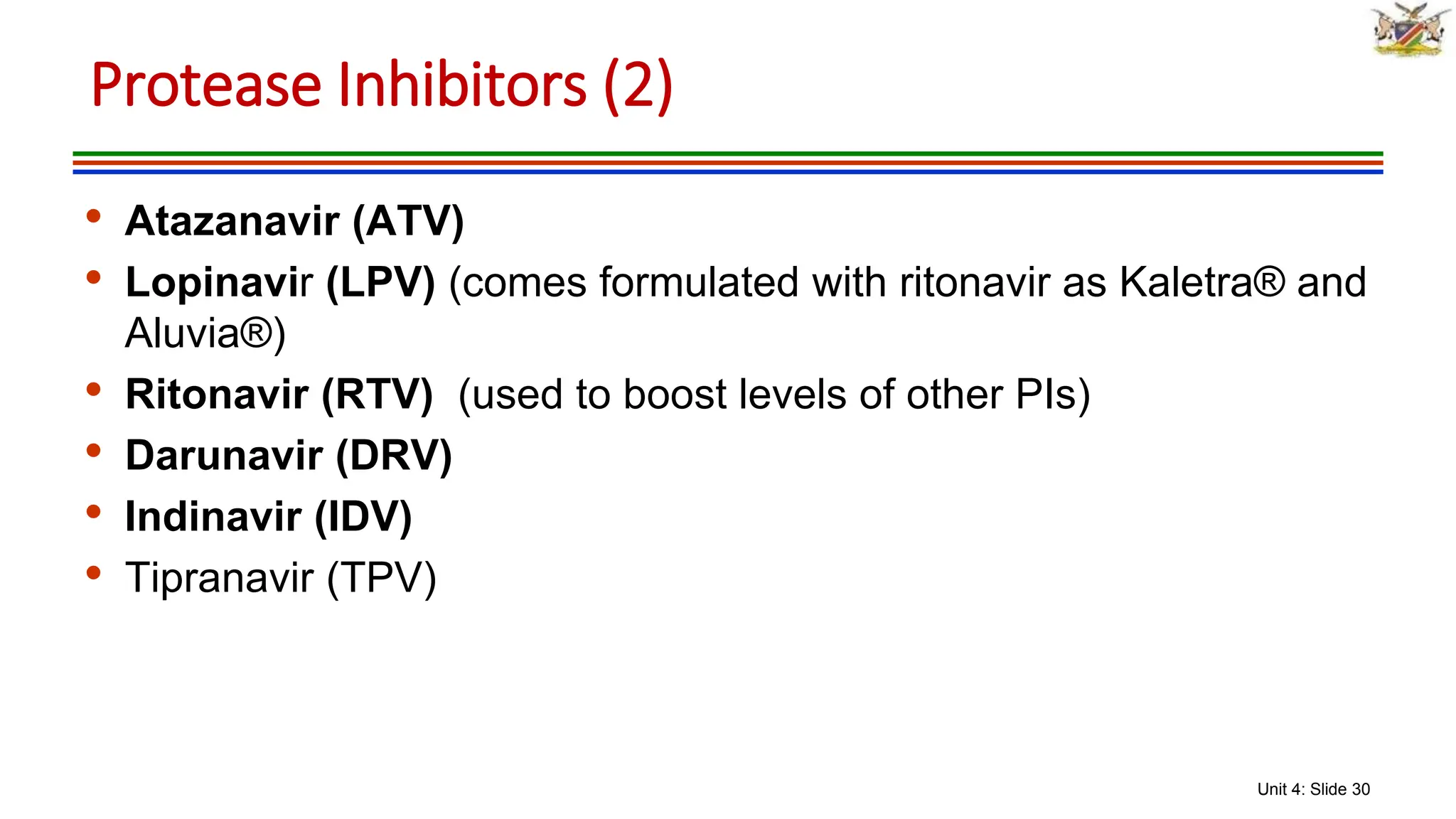
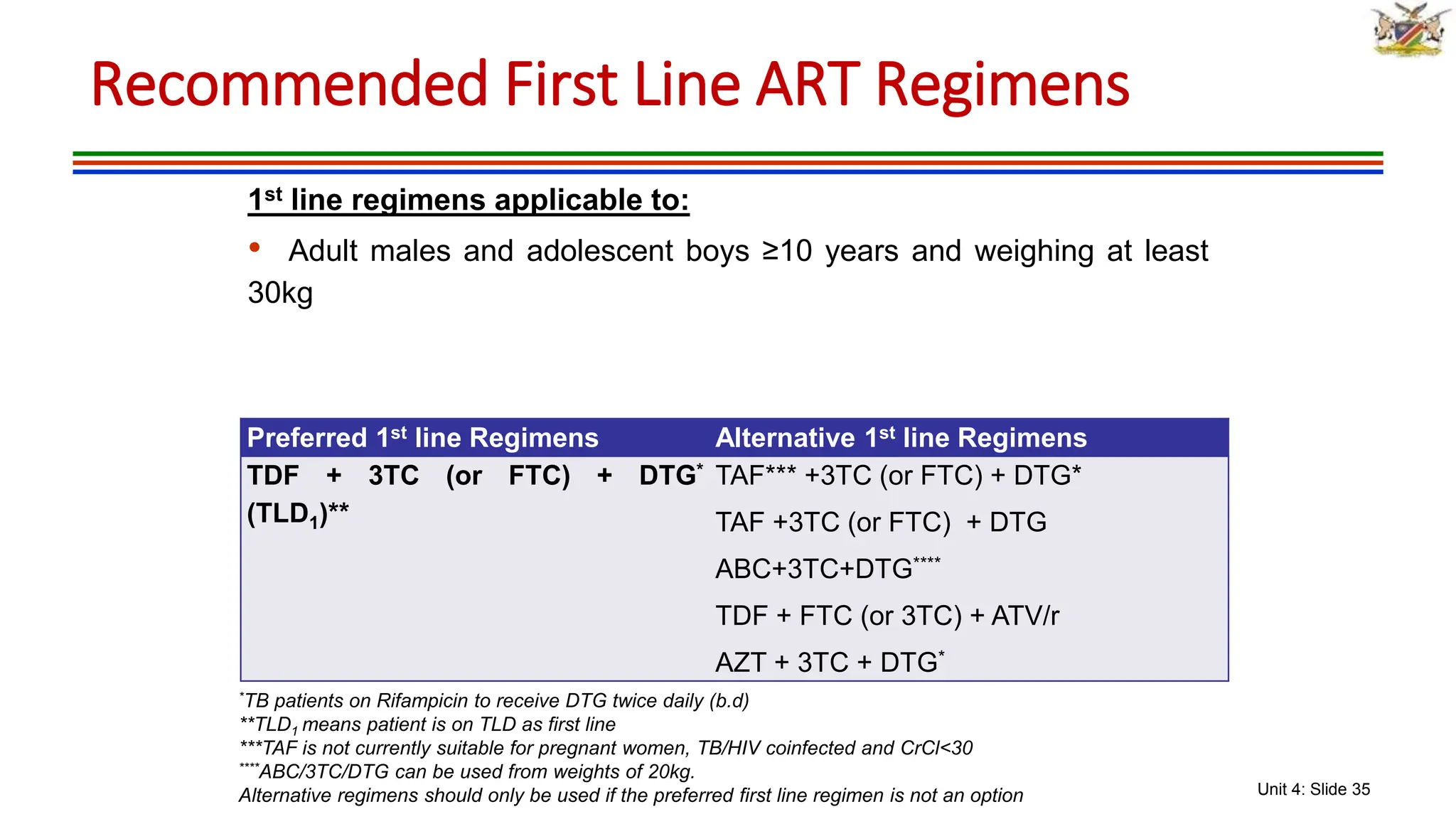
3) The classes