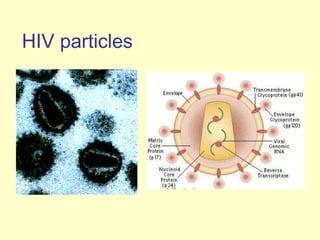
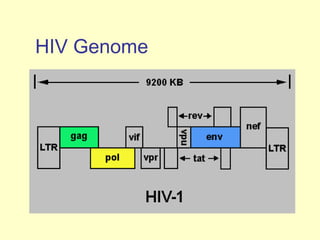
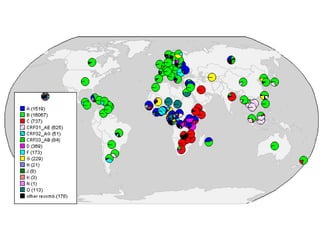
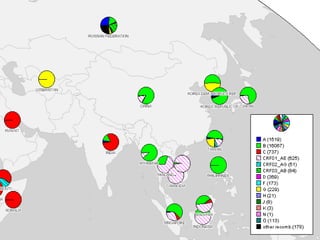
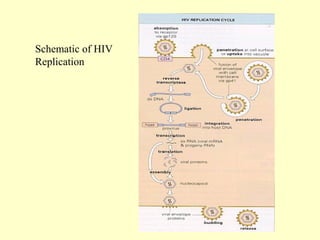
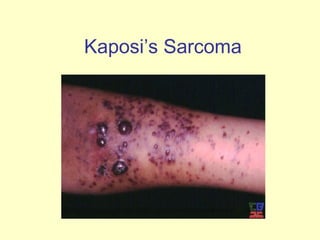
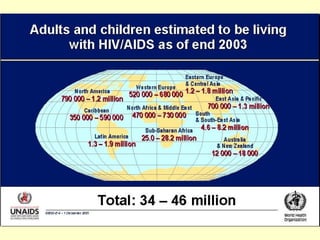
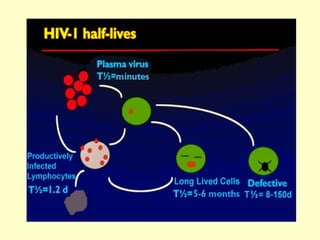
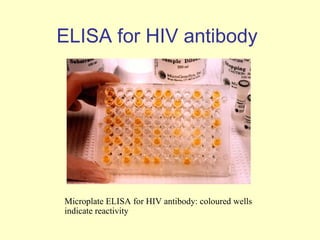
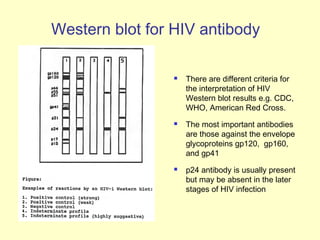
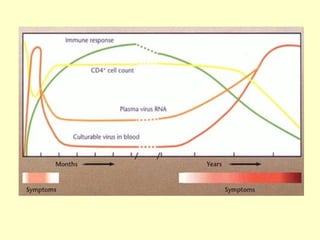
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is an enveloped RNA virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It belongs to the retrovirus family and there are two types, HIV-1 and HIV-2. HIV infects and destroys CD4+ T cells of the immune system, ultimately weakening the body's ability to fight infections and disease. Common routes of transmission include sexual contact, contaminated blood transfusions, and from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth or breastfeeding. While antiretroviral treatment can slow the progression of the disease, there is currently no cure for HIV/AIDS.