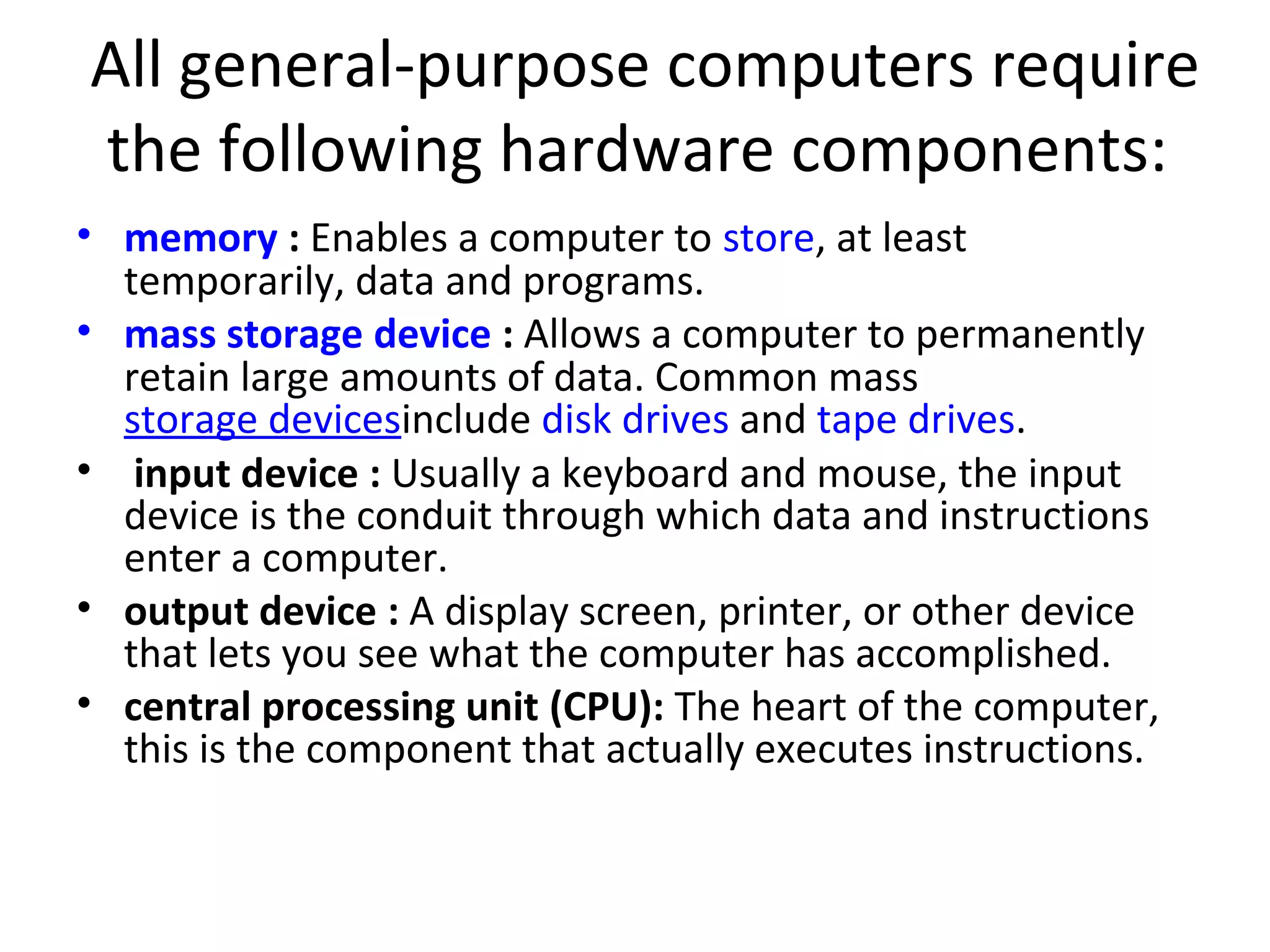
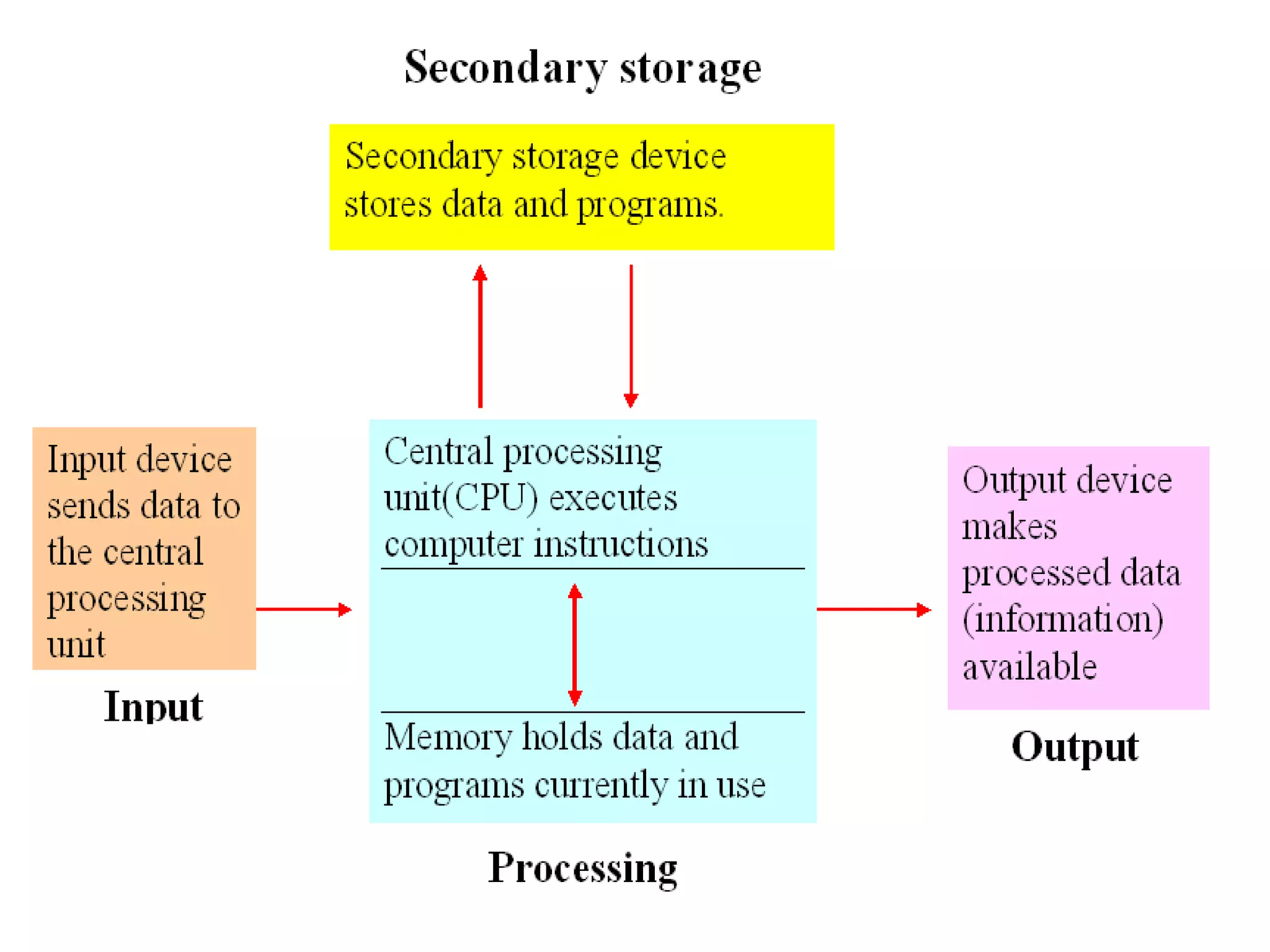
A computer is a programmable machine that receives input, stores and manipulates data, and provides output. It responds to specific instructions and can execute prerecorded lists of instructions (programs). All computers require hardware components like memory, mass storage devices, input devices, output devices, and a central processing unit (CPU). Computers can be classified based on their capabilities as personal computers, portable computers, servers, embedded computers, and supercomputers/mainframes.