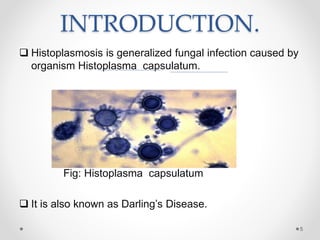
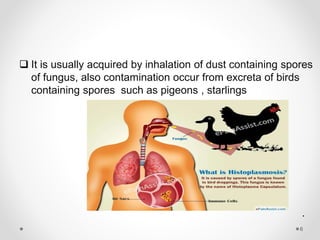
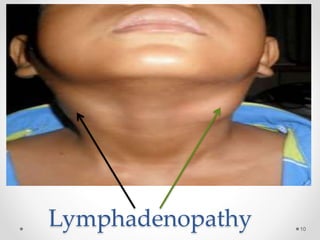
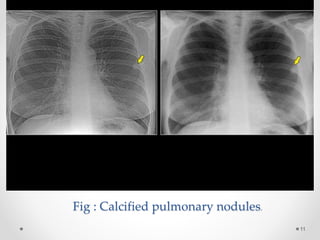
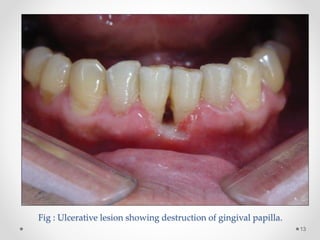
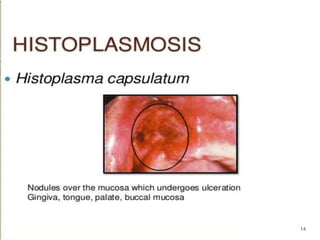
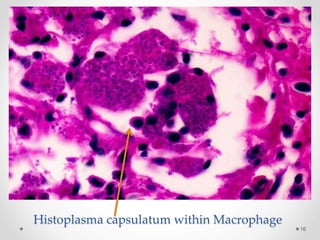
This document discusses histoplasmosis, a fungal infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatum. It is usually acquired through inhalation of spores from bird droppings and causes symptoms like fever, cough, enlarged spleen and liver, and lymph node swelling. Oral manifestations can include ulcerated or nodular lesions on the mouth and gums. Histologically, the fungus is found inside phagocytes. Laboratory tests can show elevated alkaline phosphatase and detect antibodies. Severe cases are treated with the antifungal medication Amphotericin B.