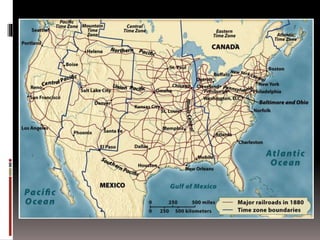
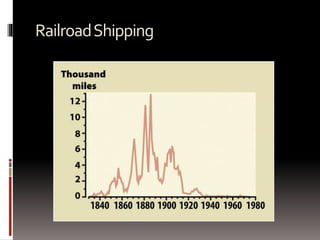
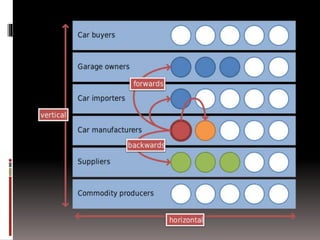
The document summarizes key aspects of the Second Industrial Revolution period in the United States from 1870-1890, known as the Gilded Age. It describes how railroads drove industrialization and economic growth. New mass production techniques led to factory jobs becoming the primary employment. Inventions like the telephone and light bulb transformed society. Large monopolistic corporations like Standard Oil dominated industries. Working conditions were difficult and dangerous. Large economic inequality grew between the wealthy industrialists and working class. The West was transformed by farming, mining, and conflicts with Native Americans. Politics were corrupt and dominated by Republicans. New social ideologies like Social Darwinism emerged to explain inequality. Labor unrest grew but was suppressed after events like the Haymarket Affair.