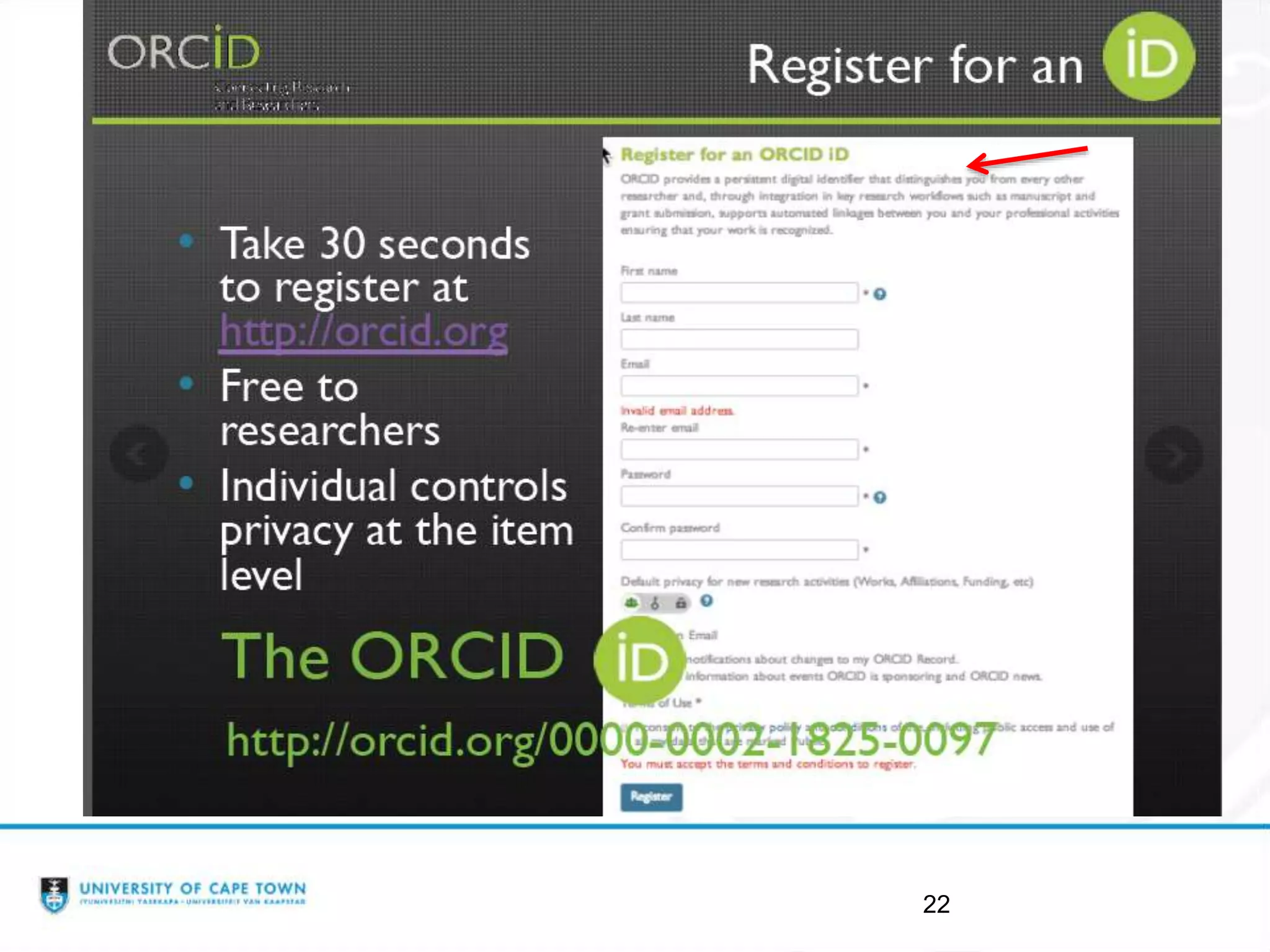
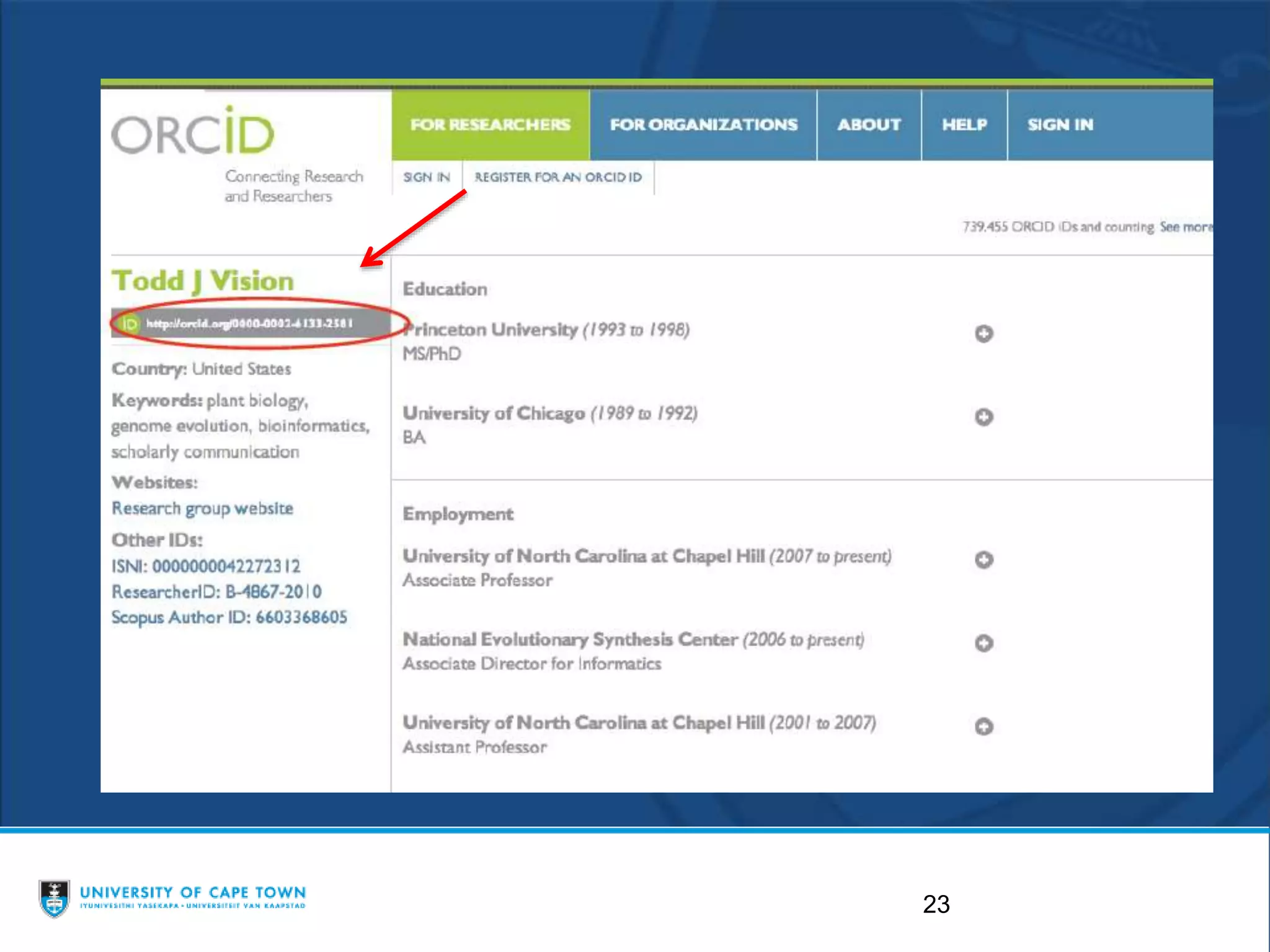
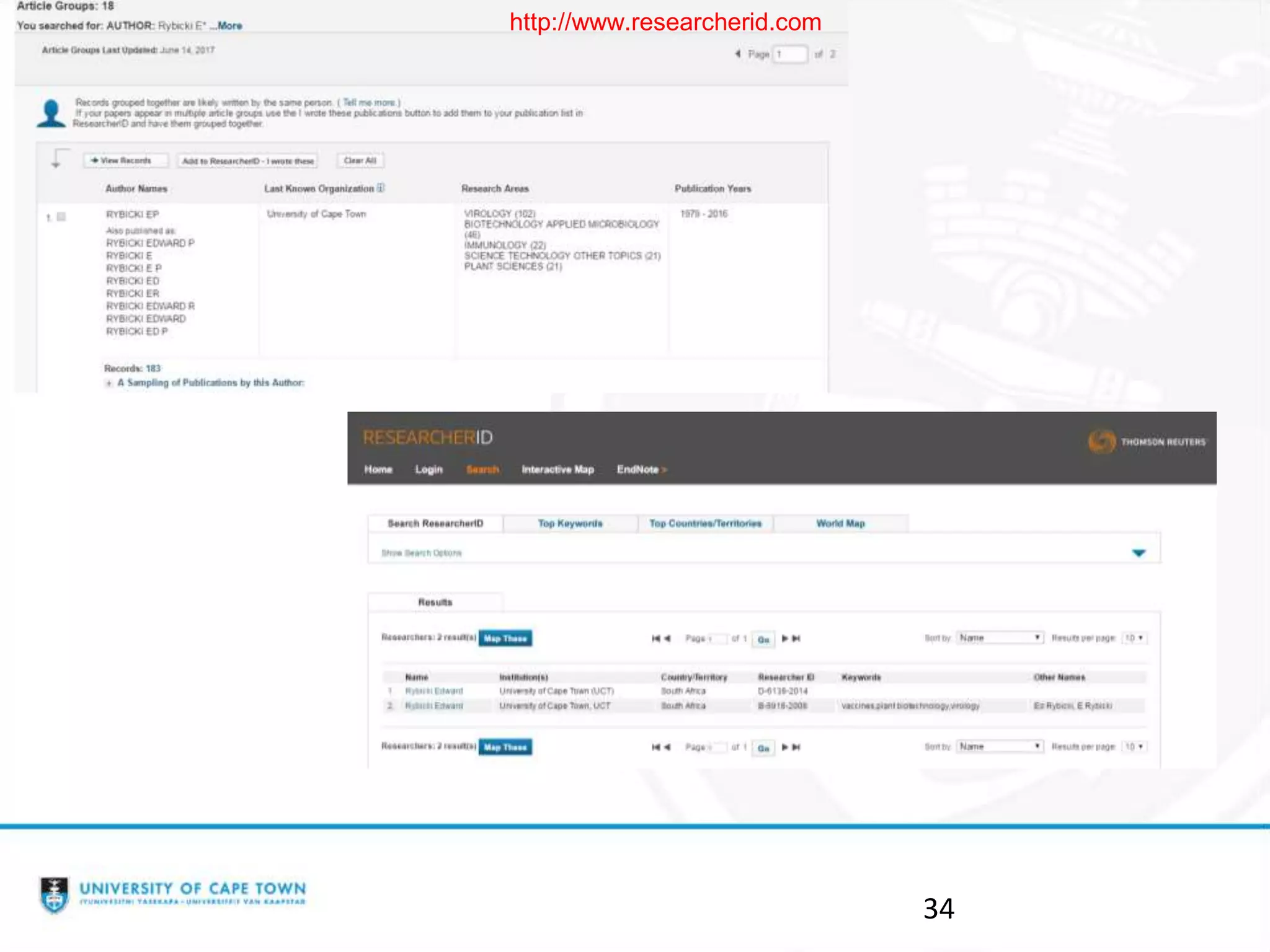
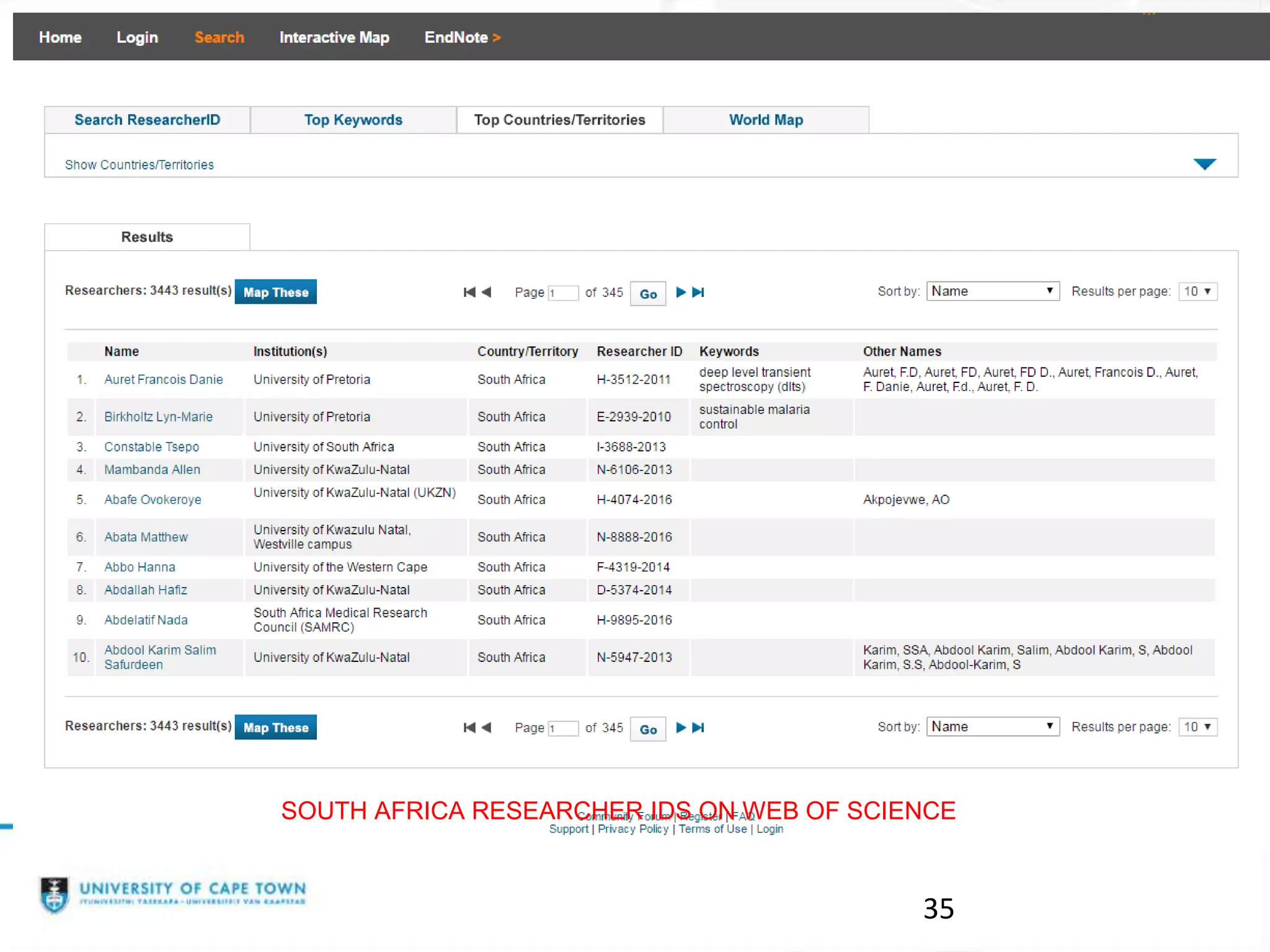
The document discusses researcher identities and profiles. It defines the h-index and how it is calculated. It emphasizes setting up profiles in ORCID, Google Scholar, Scopus, and ResearcherID to distinguish researchers from others with similar names and group all of their publications together. These profiles improve discoverability and metrics like citation counts. The document provides instructions on setting up ORCID and Google Scholar profiles.