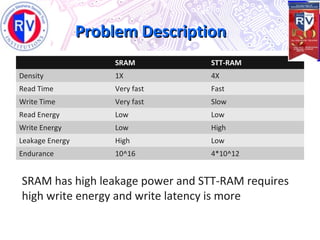
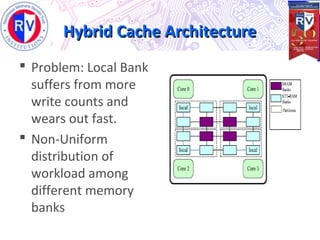
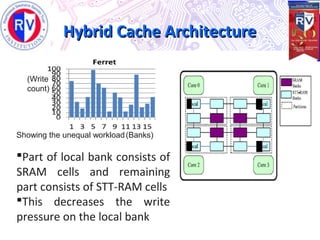
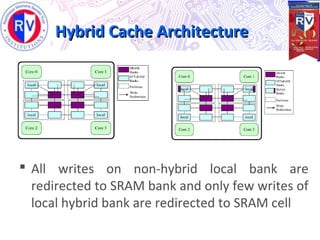
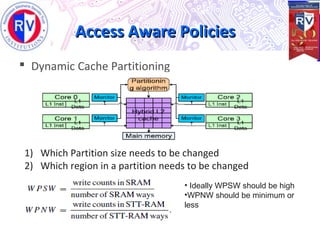
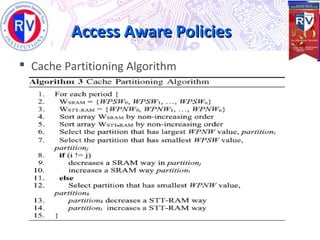
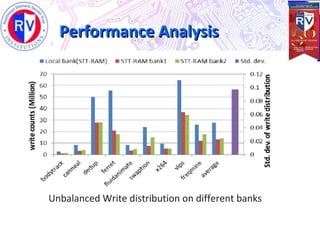
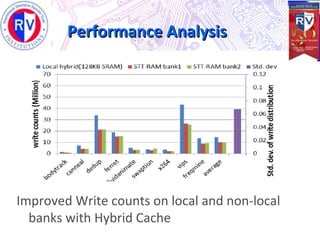
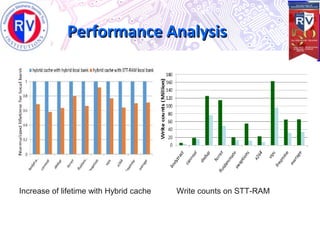
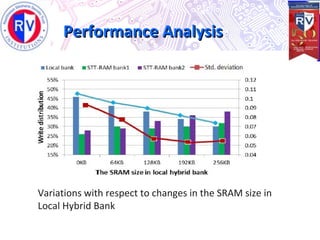
This document proposes a high endurance hybrid cache design with access aware policies and dynamic cache partitioning. It addresses the problems of high leakage power in SRAM caches and high write latency/energy in STT-RAM caches. The design uses a hybrid local cache with both SRAM and STT-RAM cells to reduce write pressure on any single bank. Access aware policies direct writes to the SRAM portion when possible to utilize its fast write speeds. Dynamic cache partitioning further balances the write distribution and reduces cache misses over time. Analysis shows this approach improves write counts, lifetime, and performance compared to a traditional cache design.