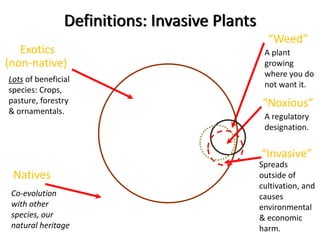
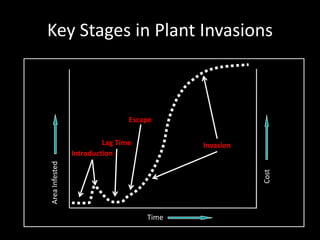
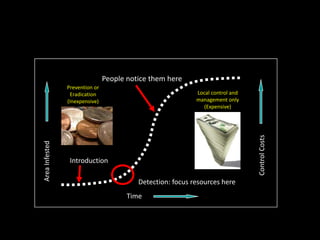
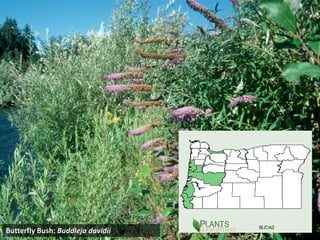
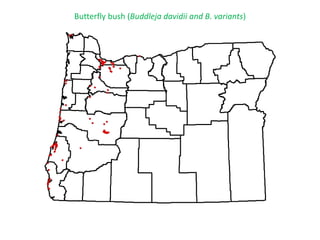
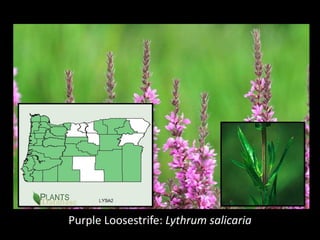
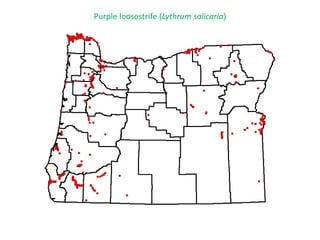
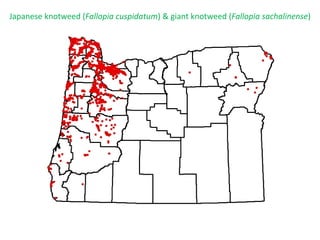
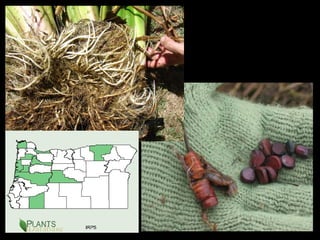
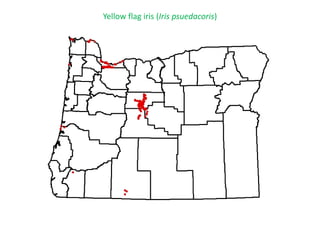
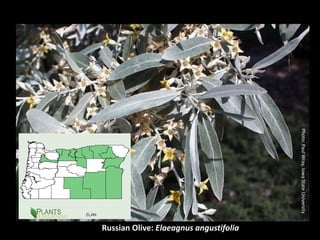
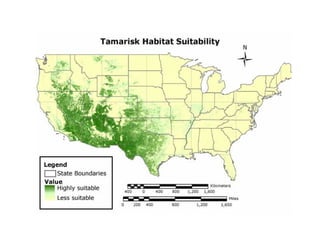
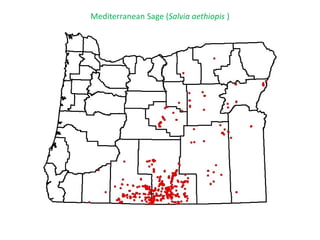
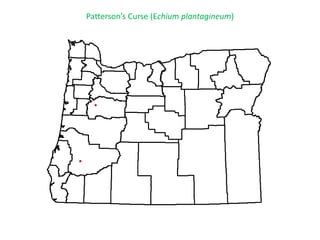
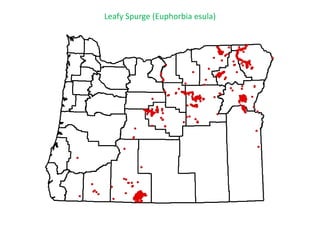
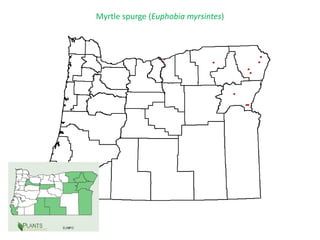
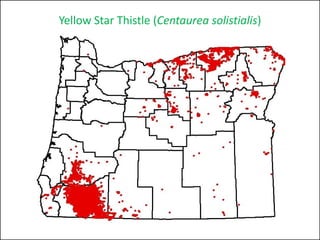
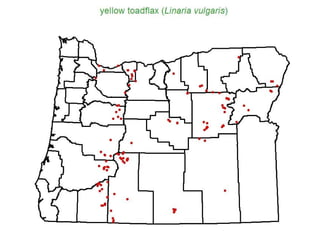
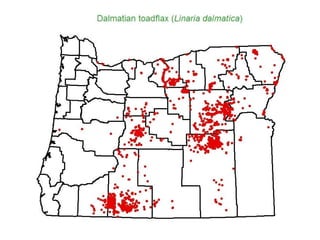
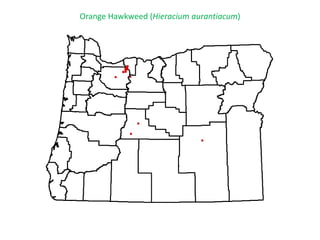
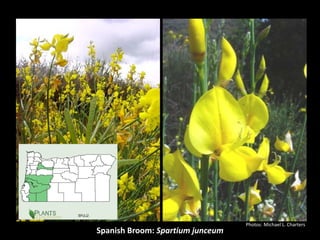
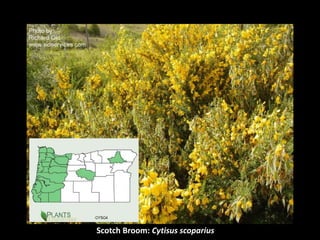
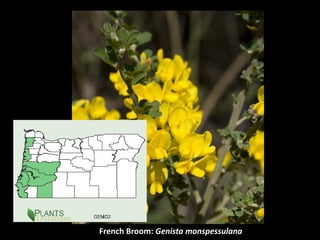
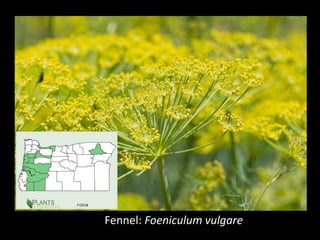
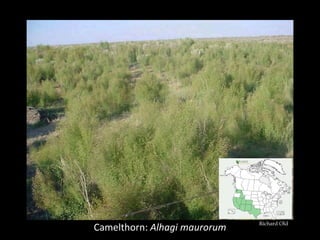
This document provides an overview of invasive species for green industry professionals. It begins with definitions of key terms like invasive, exotic, and noxious. It then discusses why invasive species are an issue, costing $143 billion per year in the US. The document covers the biology and management of invasives, including prevention, early detection, and control methods. It profiles several invasive plant species in Oregon like knotweed, butterfly bush, and yellow star thistle. Finally, it suggests actions professionals can take and lists resources for further information.