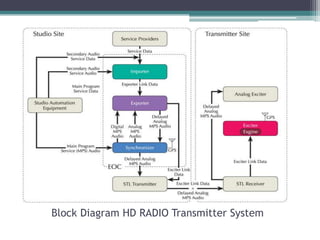
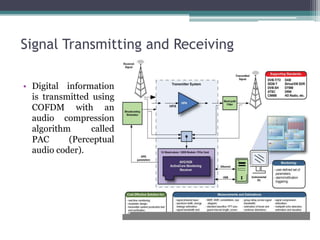
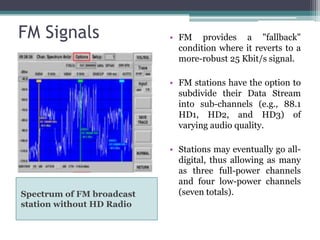
The document summarizes HD Radio technology which allows radio stations to broadcast both digital signals and analog signals simultaneously. It describes how HD Radio transmitters work by taking audio and data from studios and broadcasting the digital signals using COFDM modulation with audio compression, while also transmitting the analog signals. Receivers can then receive either signal type. The document outlines the key components of HD Radio transmitters including importers, exgines, exporters and synchronizers. It also discusses the differences between HD Radio implementation for AM and FM bands.