Embed presentation
Downloaded 26 times


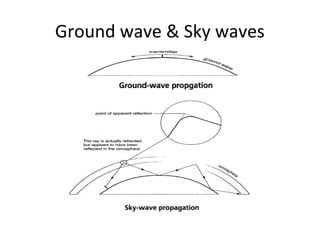


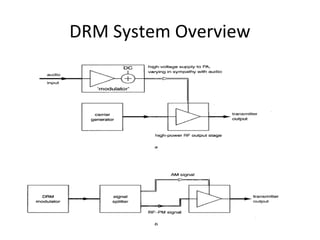
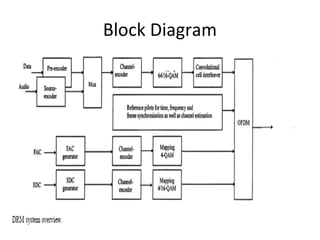
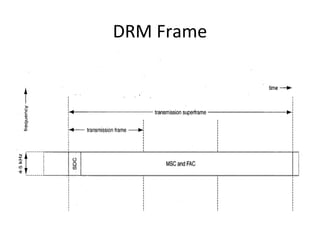


Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM) is a global open digital radio standard developed as an improvement over analog AM broadcasting which suffers from low audio quality, interference, fading, and high operating costs. DRM converts audio to digital, multiplexes it with other data, applies channel coding for transmission robustness, and modulates the coded data onto radio frequencies, offering better audio quality, signal-to-noise ratio, and less distortion than analog AM radio.










