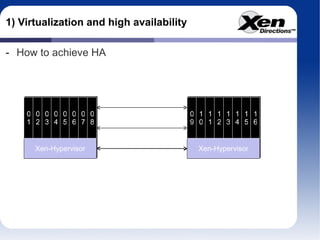
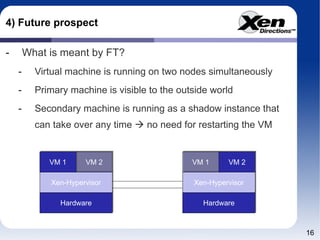
The document discusses using virtualization to build highly available infrastructures based on Xen. It covers virtualization and high availability, hardware requirements for planning redundant systems, available solutions today like XenServer, and future prospects like fault tolerance mechanisms. Fault tolerance will allow a virtual machine to run simultaneously on two nodes so the secondary can take over without restarting if the primary fails. Virtualization brings more complexity but also more flexibility to build highly available infrastructures.














![Thank you for your attention For further questions feel free to contact me at [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ha-xen-090629102518-phpapp01/85/High-Availability-and-Xen-20-320.jpg)