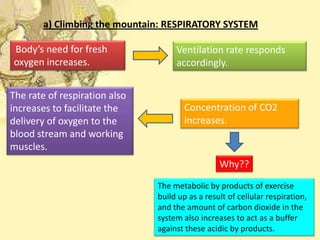
When climbing Mount Everest, the man's circulatory and respiratory systems undergo several changes to provide oxygen to his working muscles:
His heart rate increases to pump more oxygen-rich blood while diastolic blood pressure drops and systolic pressure and blood volume rise. His breathing also deepens and his ventilation rate increases to deliver more oxygen to his bloodstream.
Upon reaching the peak, tissue hypoxia occurs due to less oxygen in the thin air. His heart works harder, pumping more blood, while lung conditions involve faster, deeper breathing and increased pulmonary artery pressure to compensate for the lower oxygen levels.