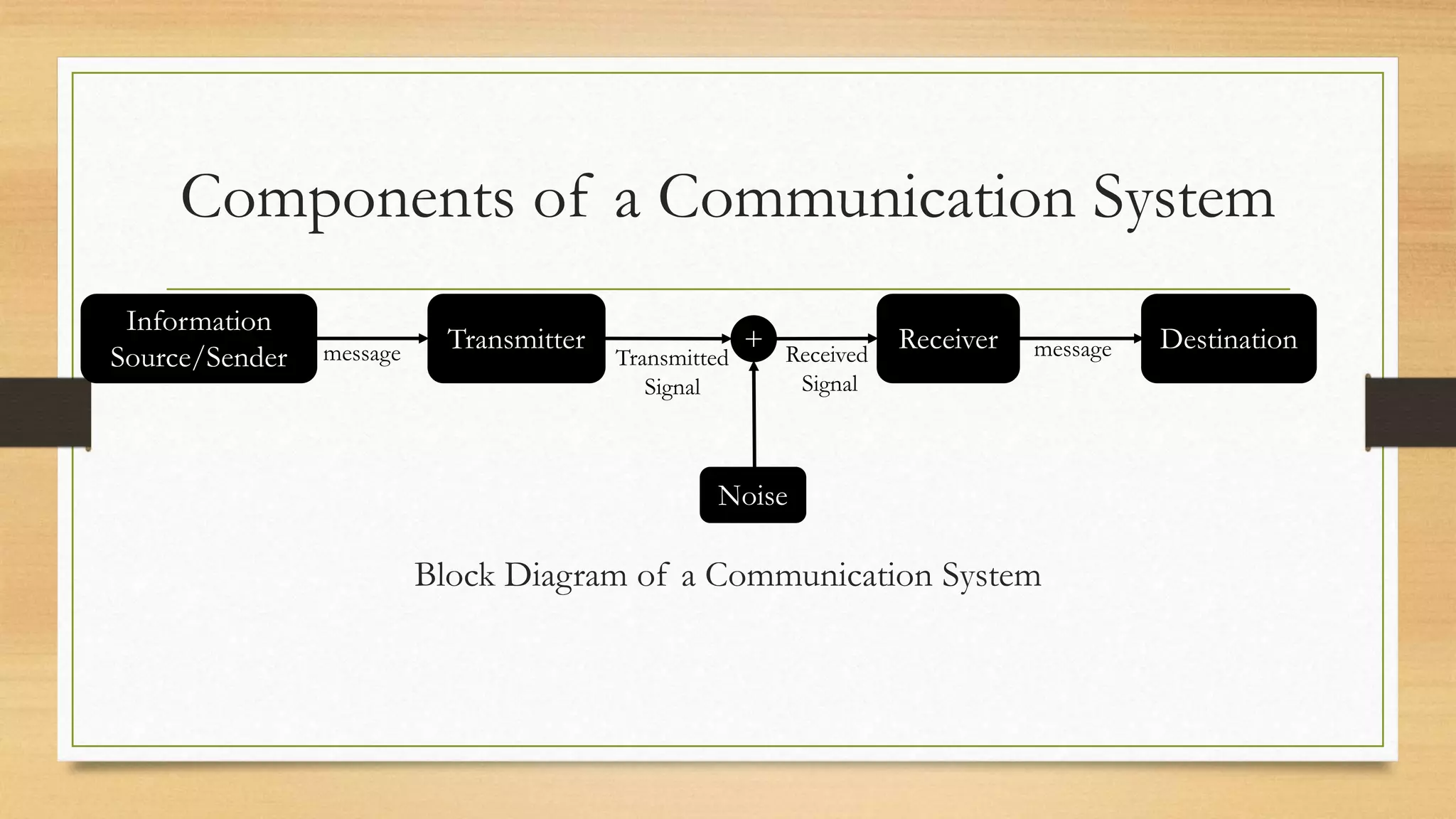
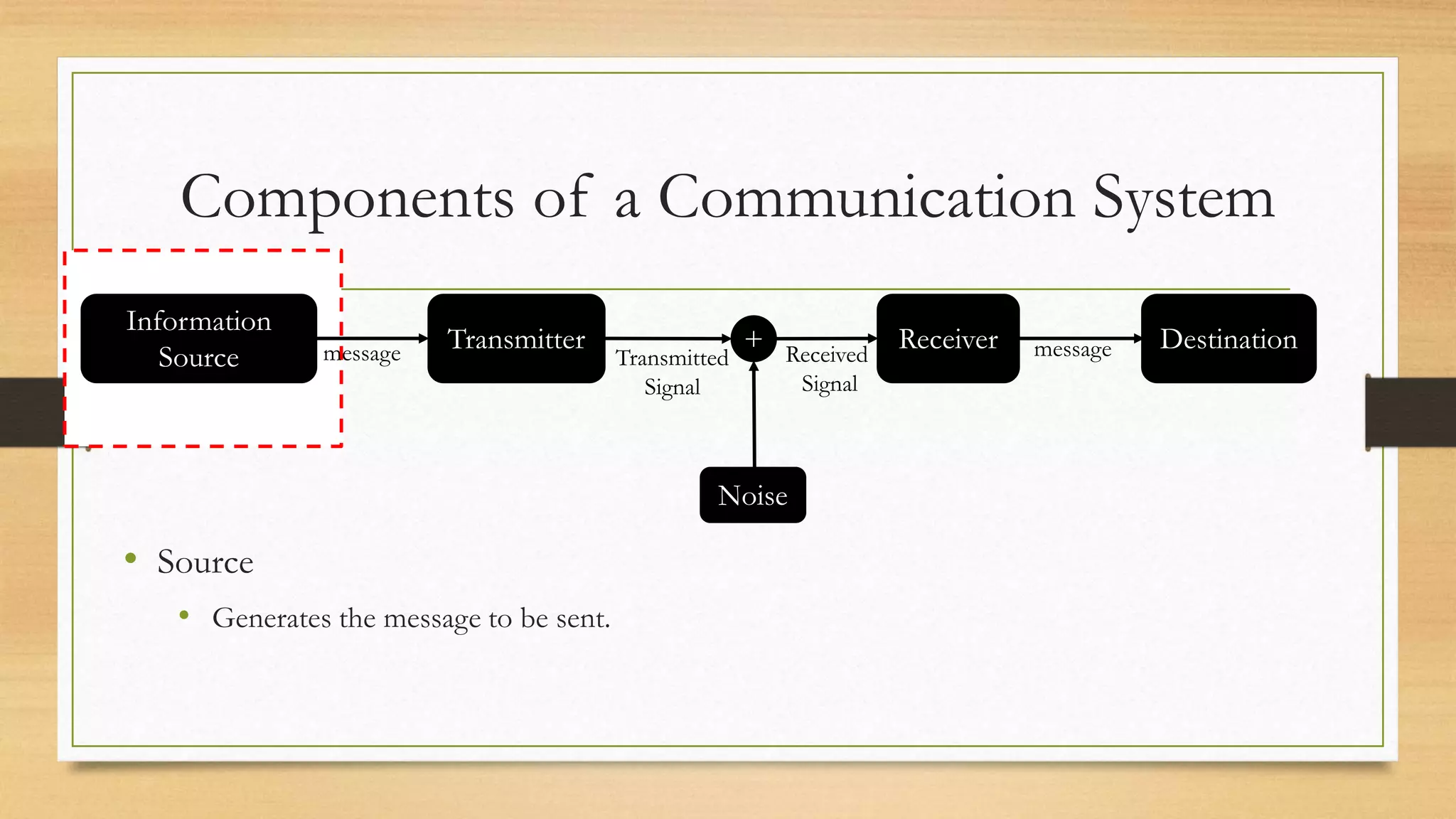
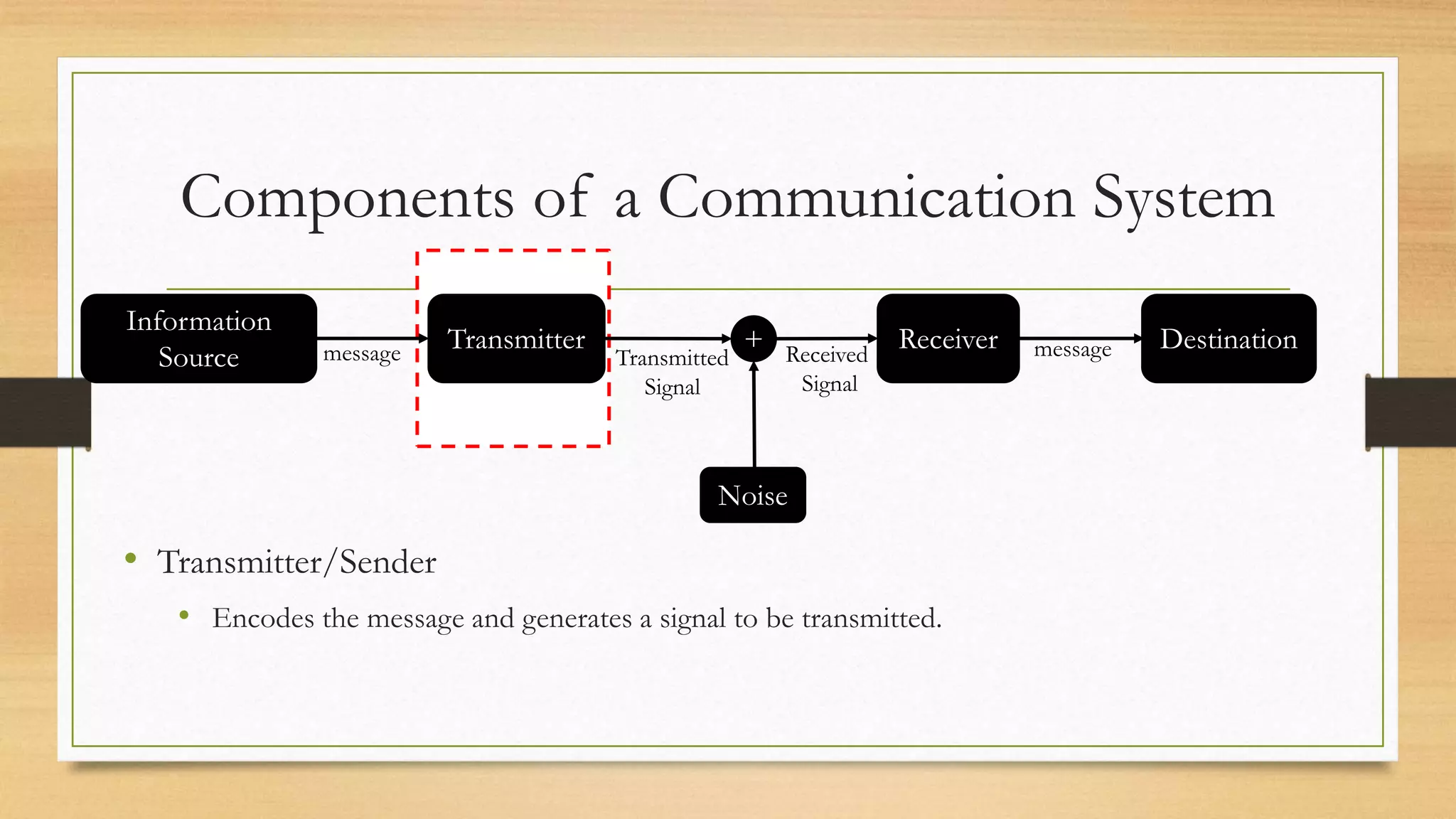
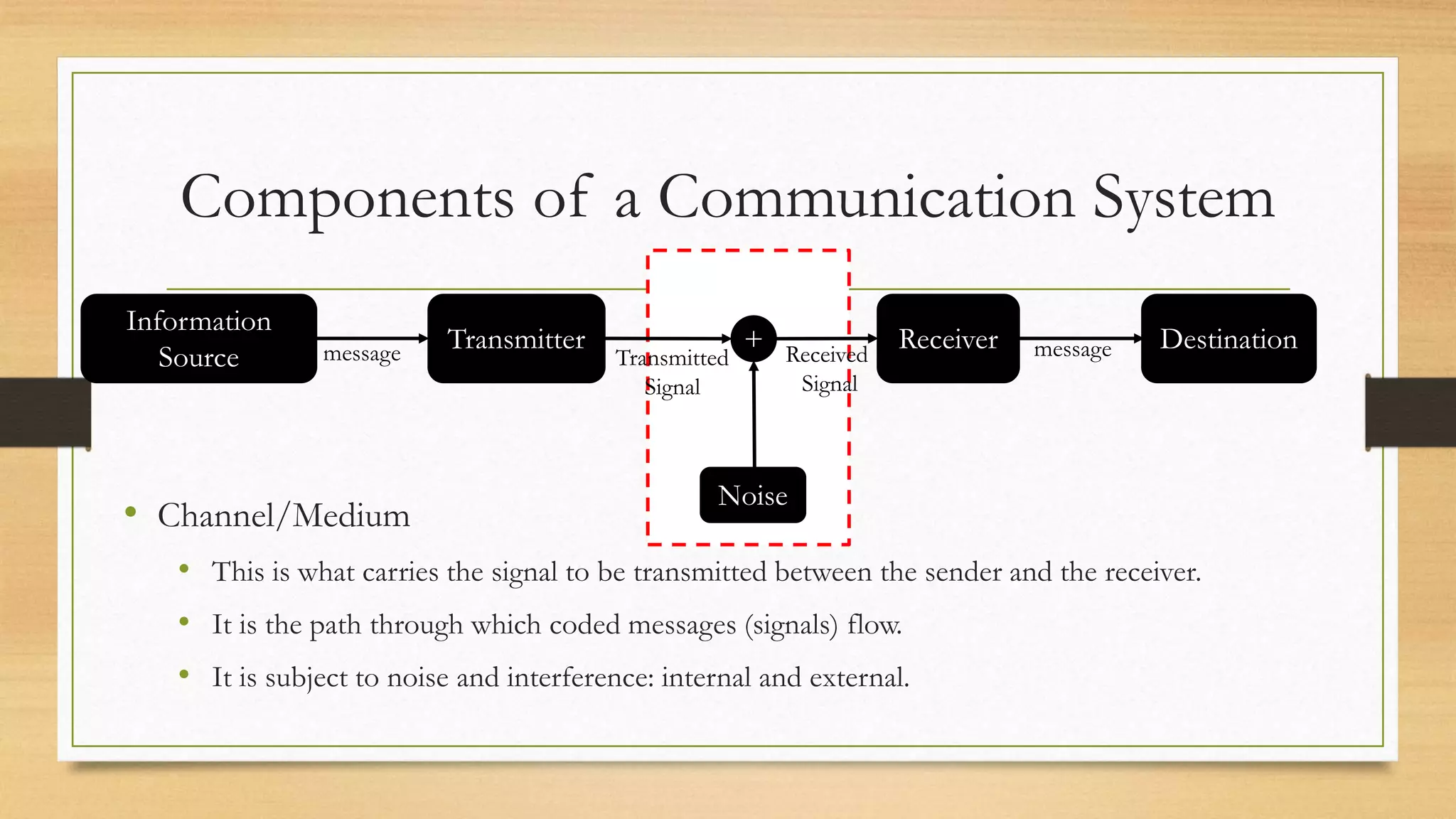
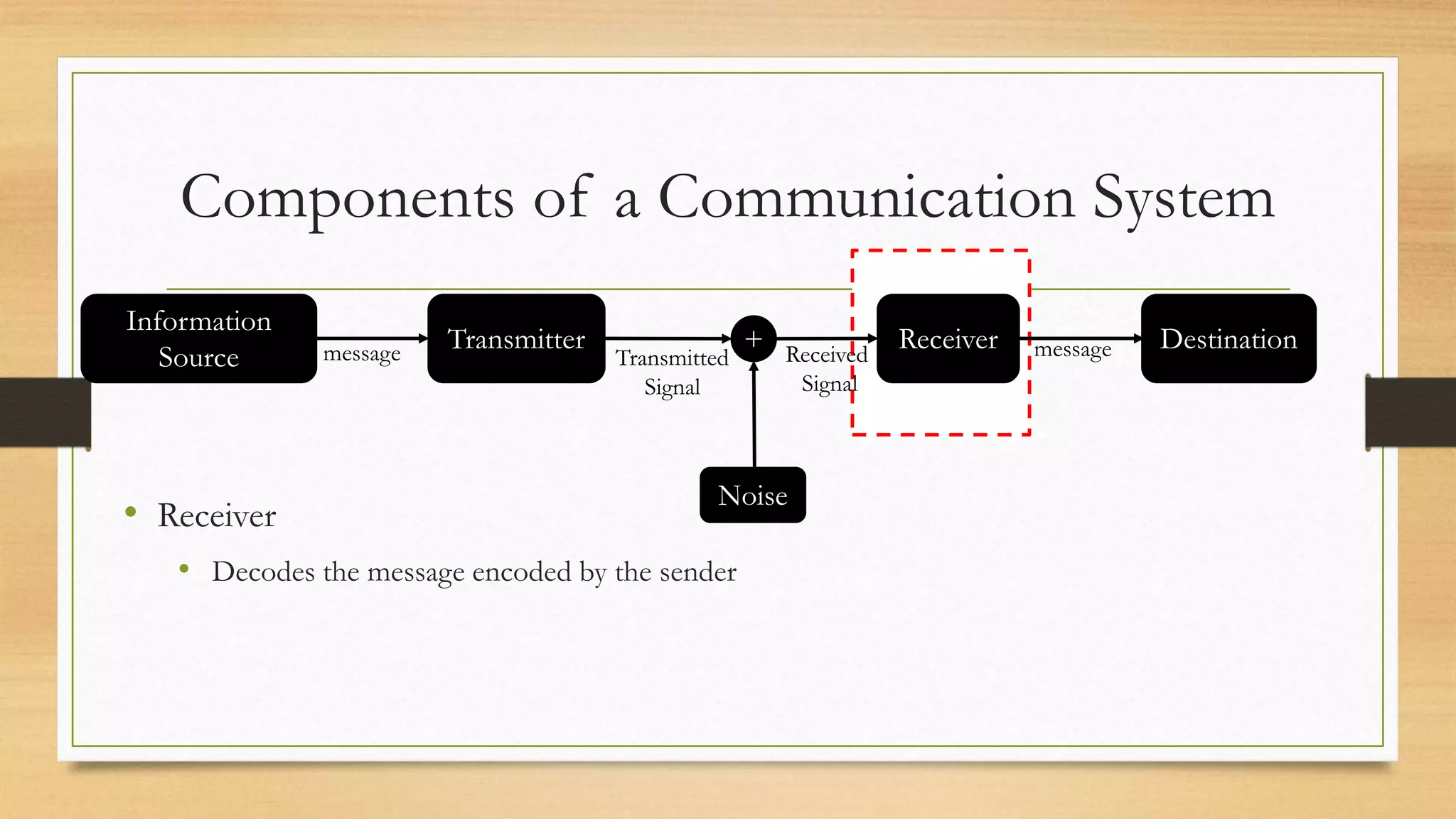
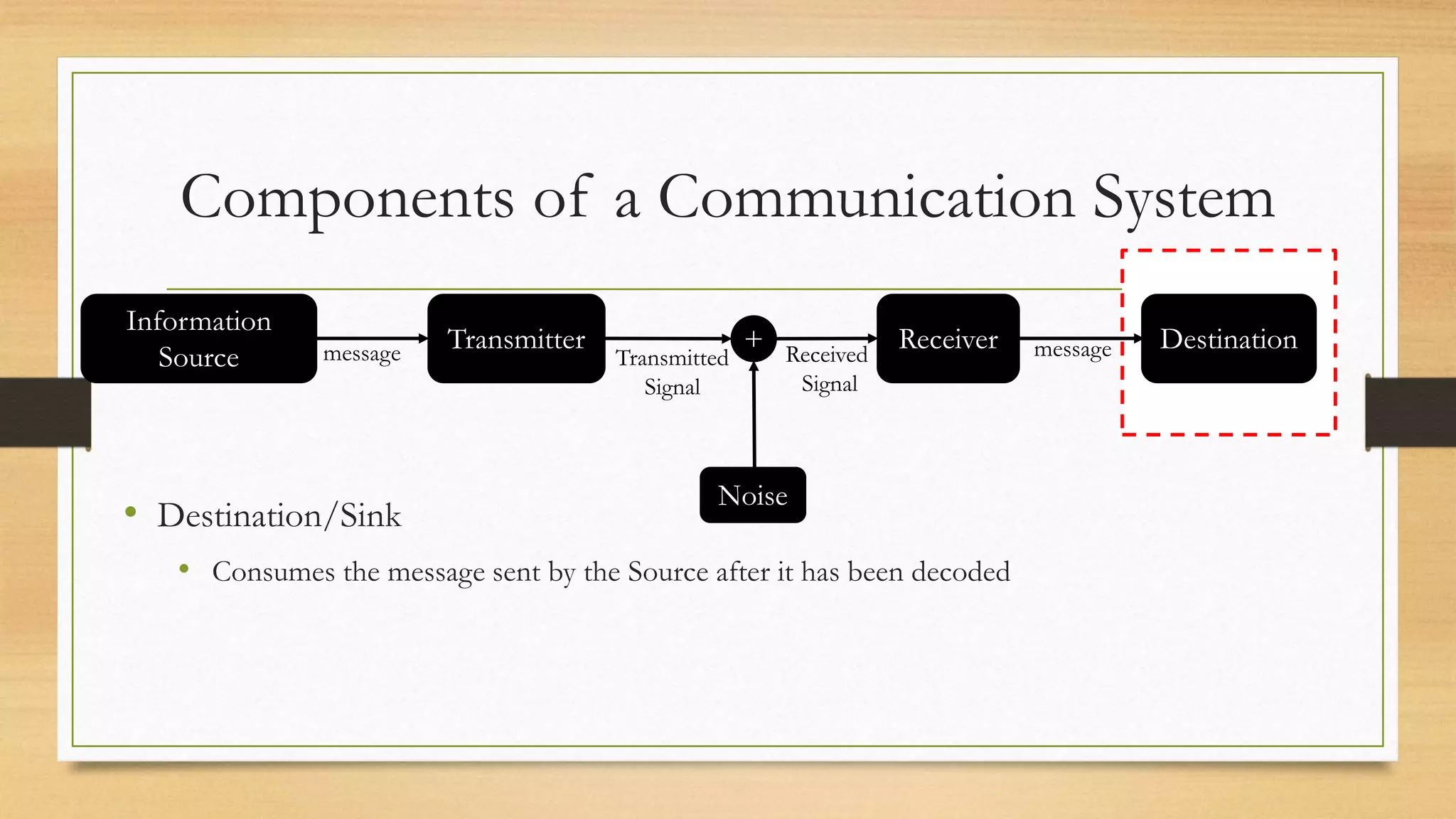
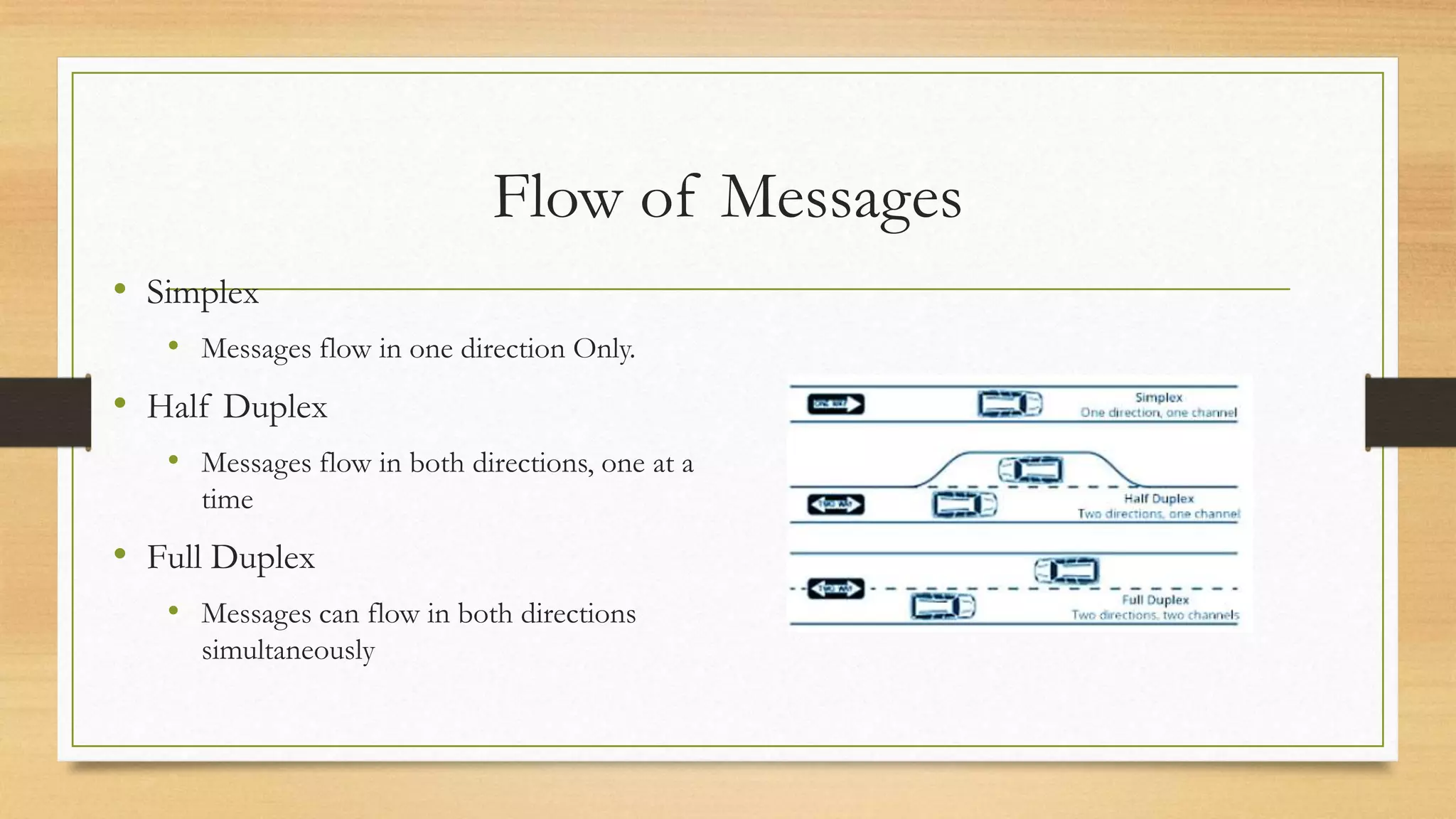
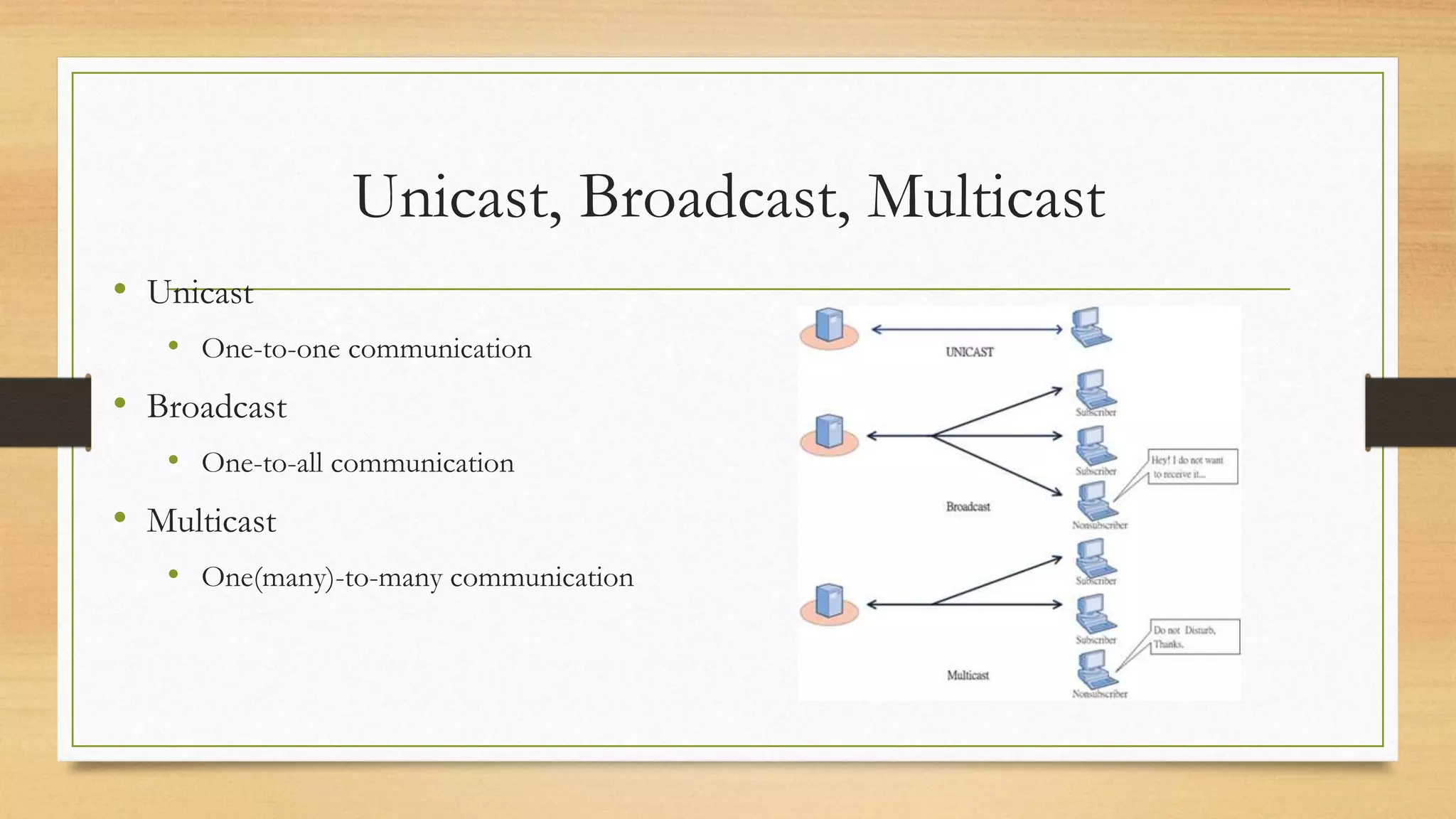
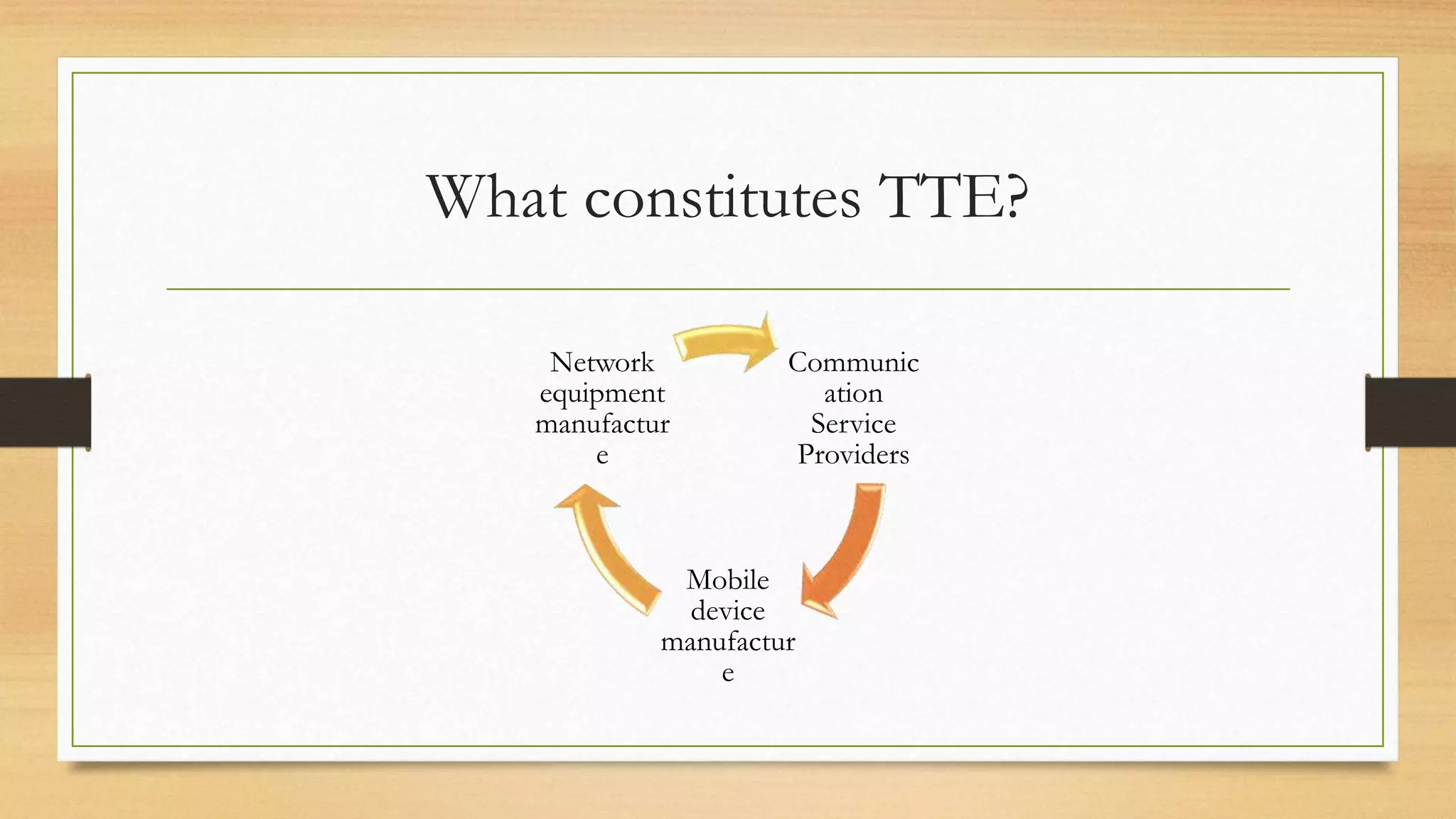
The document defines key elements of a communication system including information sources, transmitters, receivers, destinations, and different modes of transmission. It then describes the components of a telecommunication system including users, access networks to connect users to telecom networks, transport networks to carry signals between access networks, and data centers that house servers and storage. Finally, it defines a telecommunication ecosystem as a community of different players like users, technology providers, network operators, content providers, and regulators that work together in telecommunications.