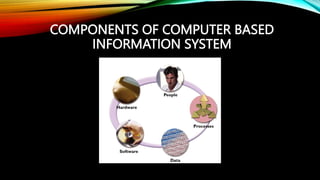
The document provides a comprehensive overview of information and communication technology (ICT), detailing its components such as hardware, software, data, people, and procedures. It explains the flow of information through different means including electrical signals, optical fibers, and radio waves, along with examples of telecommunication devices like telephones, fax machines, and the internet. Additionally, it covers various types of data storage devices and their principles of operation.