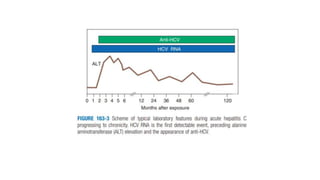
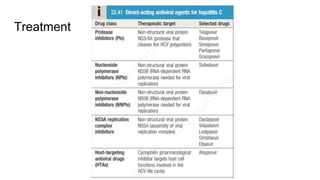
Hepatitis C is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV), primarily transmitted through parenteral routes like needle sharing and blood transfusions. Many individuals remain asymptomatic until cirrhosis develops over decades, with risk factors including male gender and immunosuppression. Diagnosis involves antibody tests, liver function tests, and imaging, while treatment options are available for chronic cases.