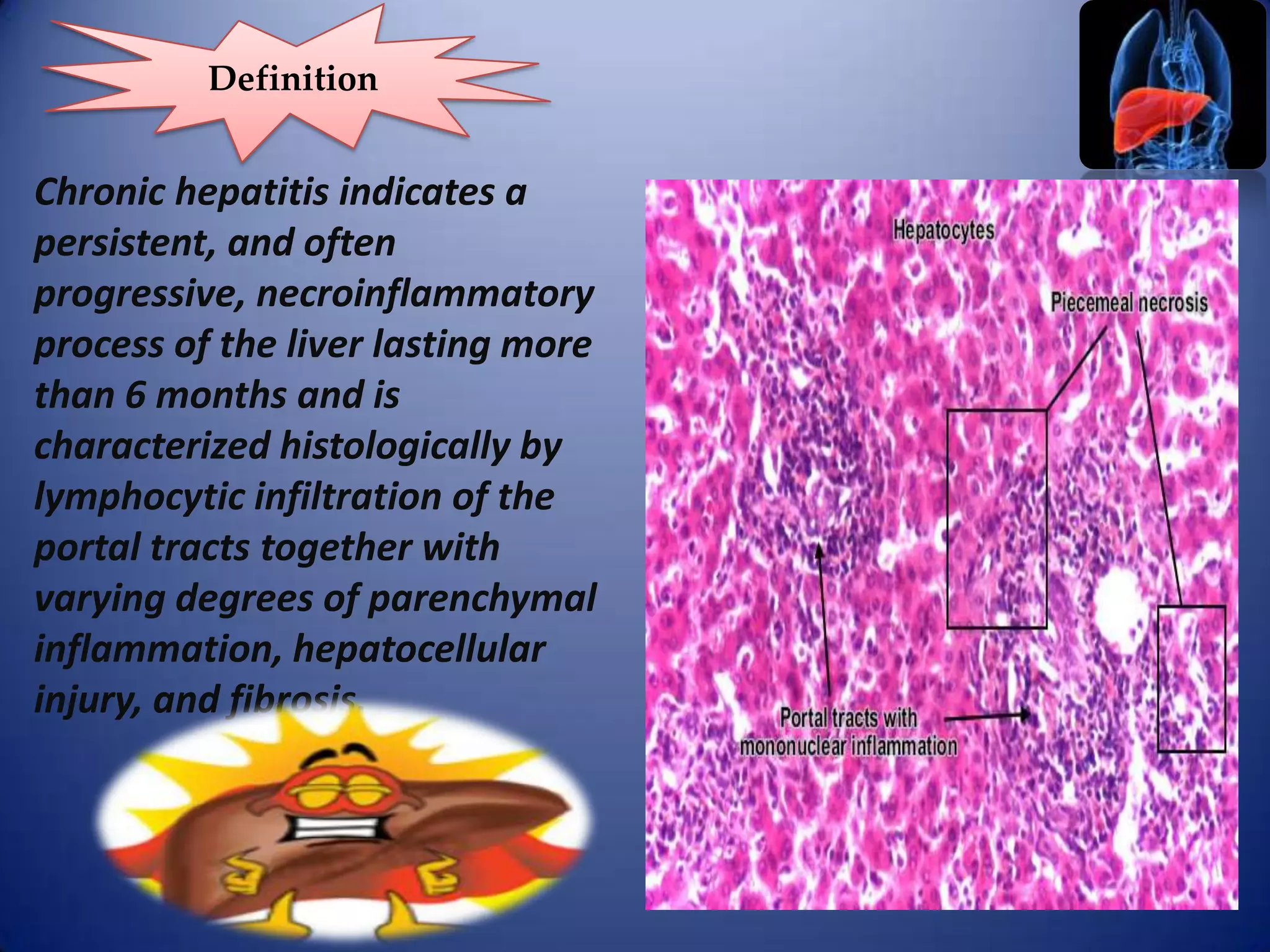
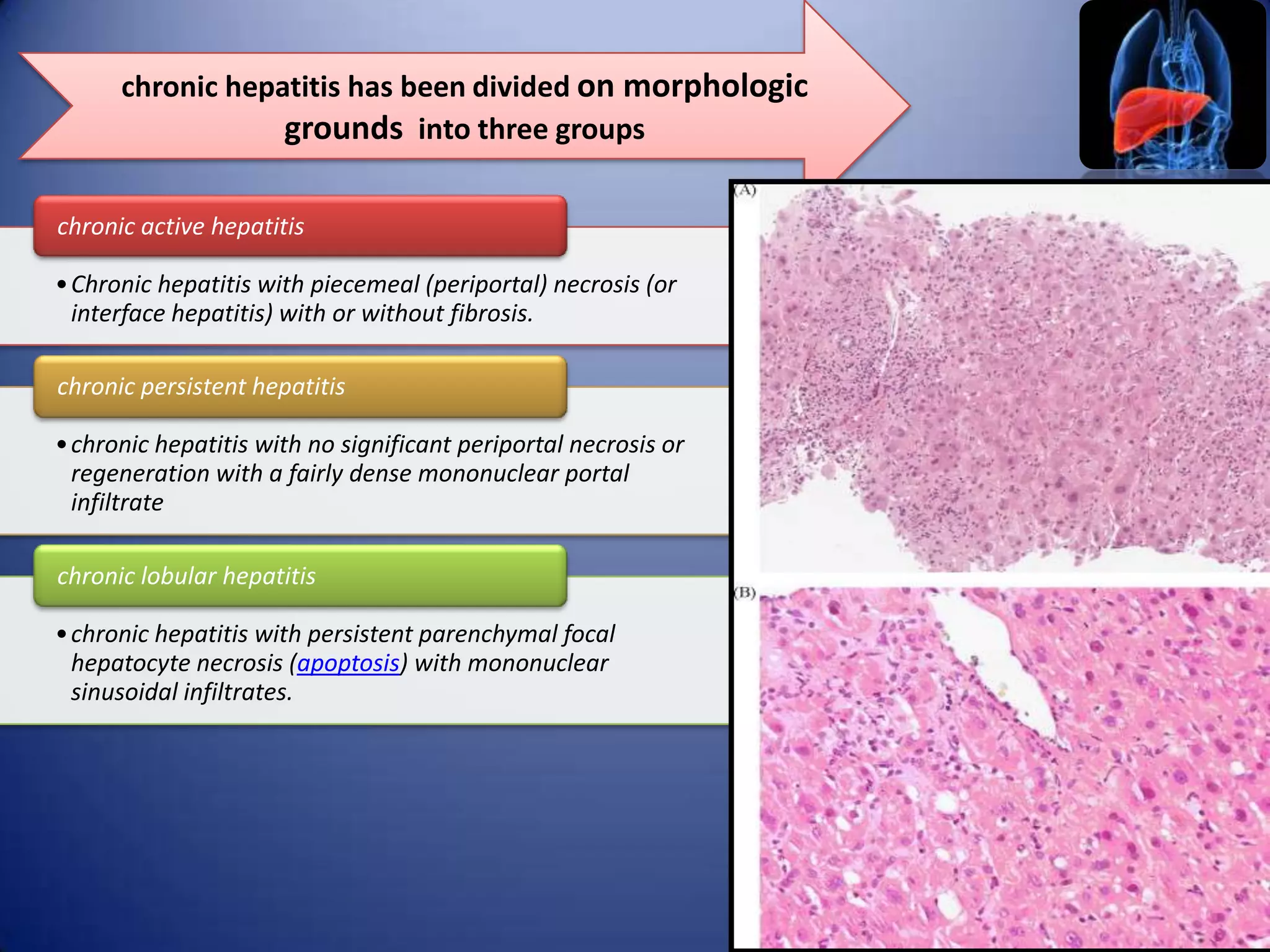
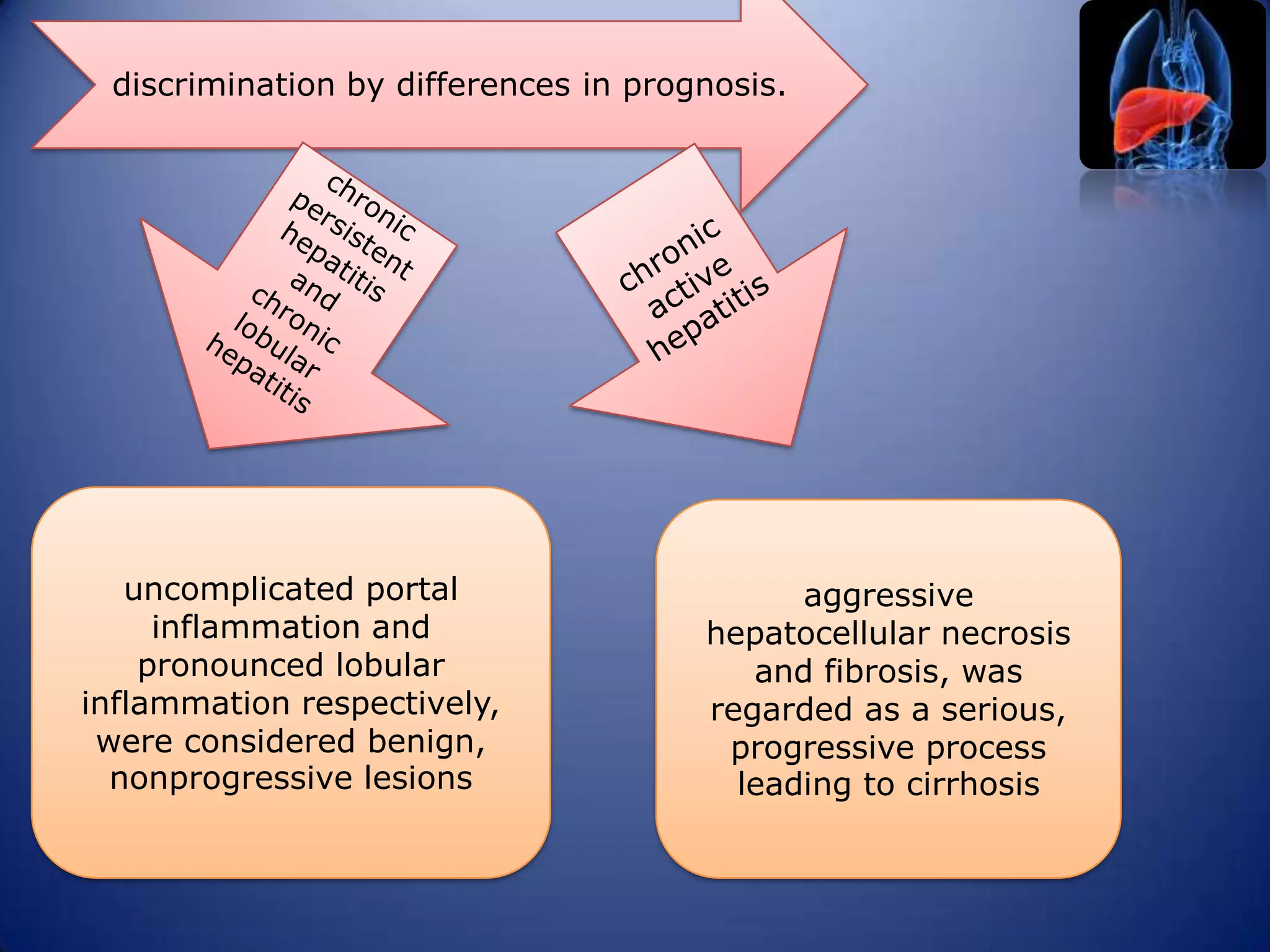
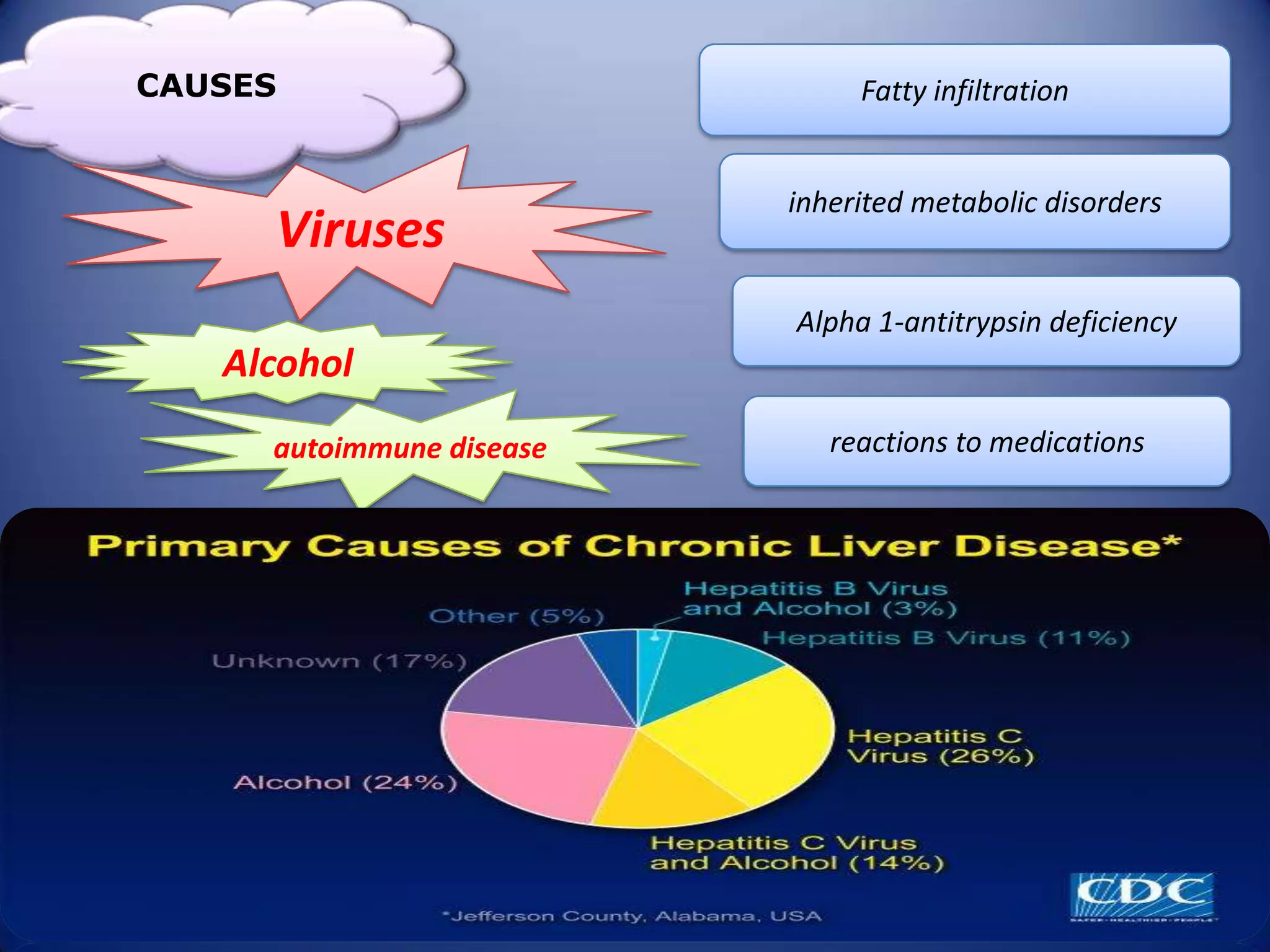
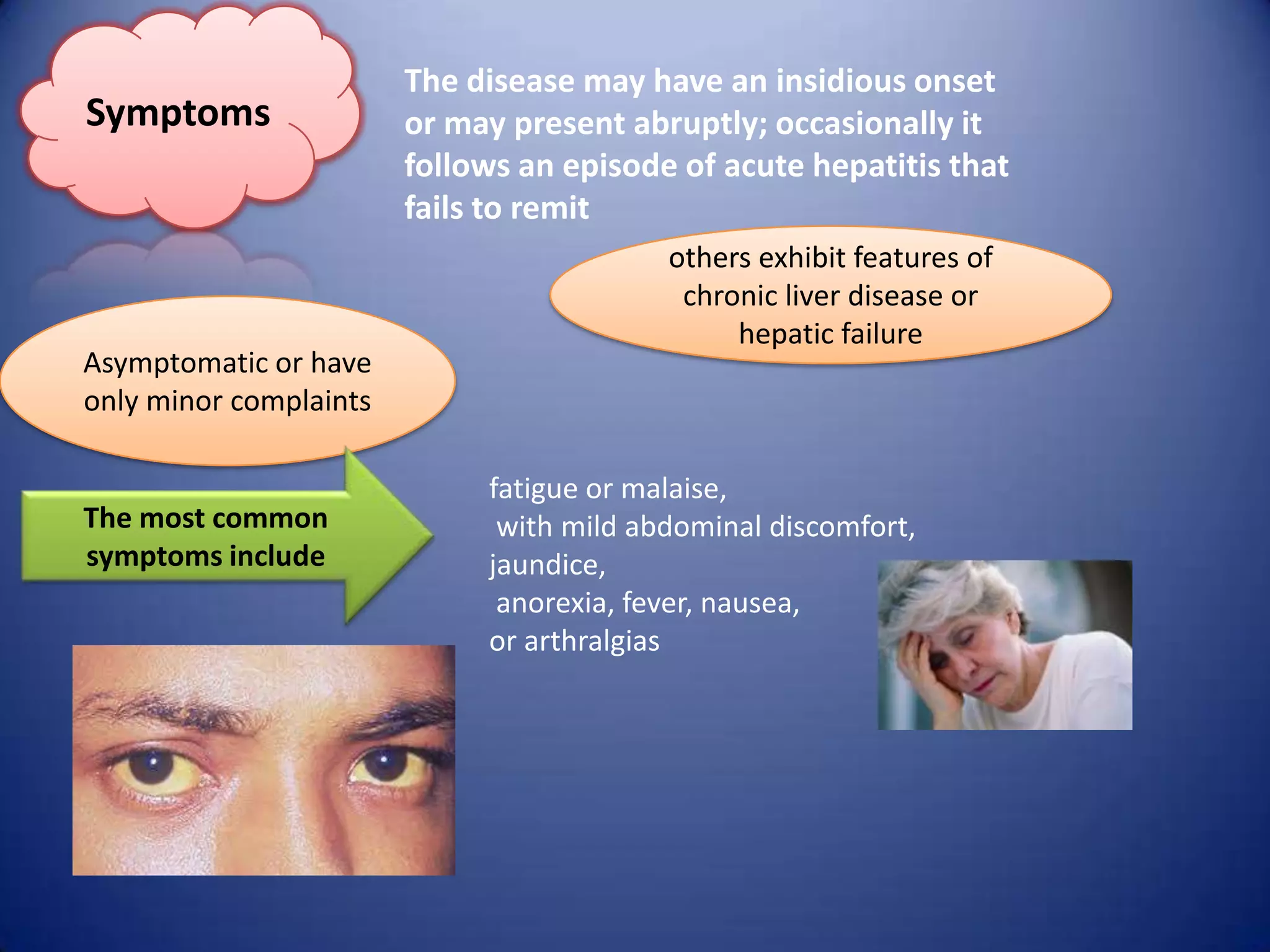
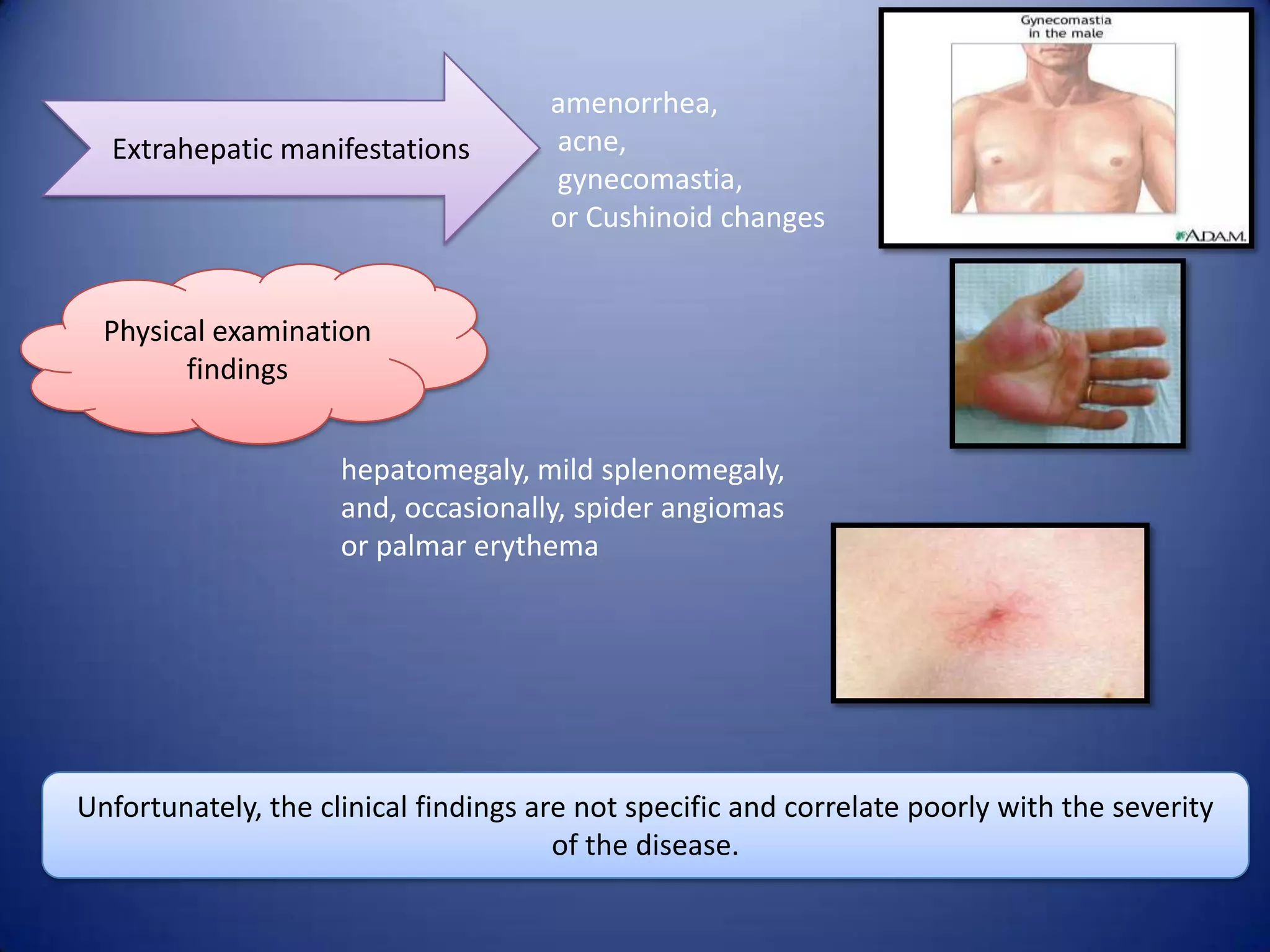
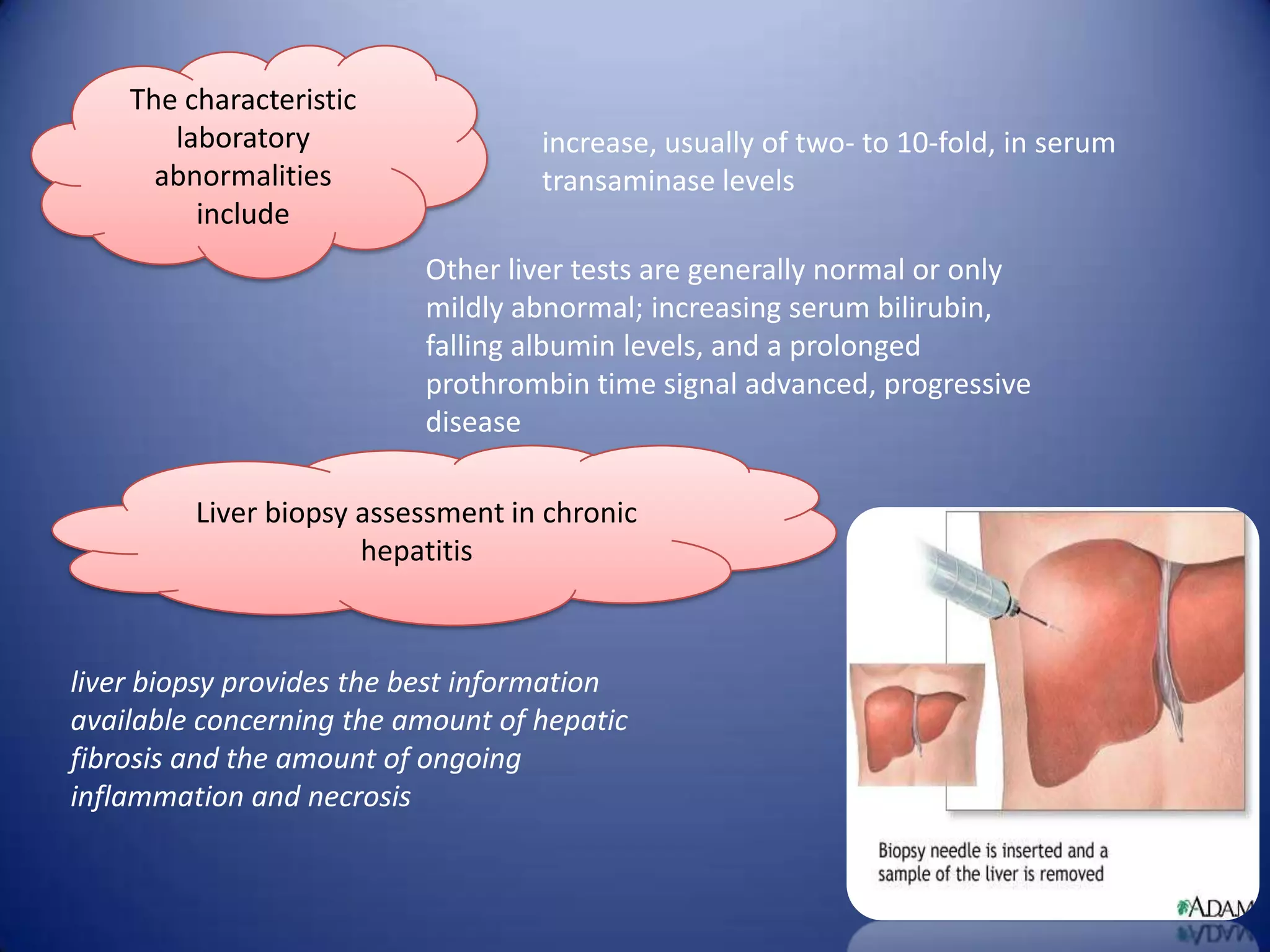
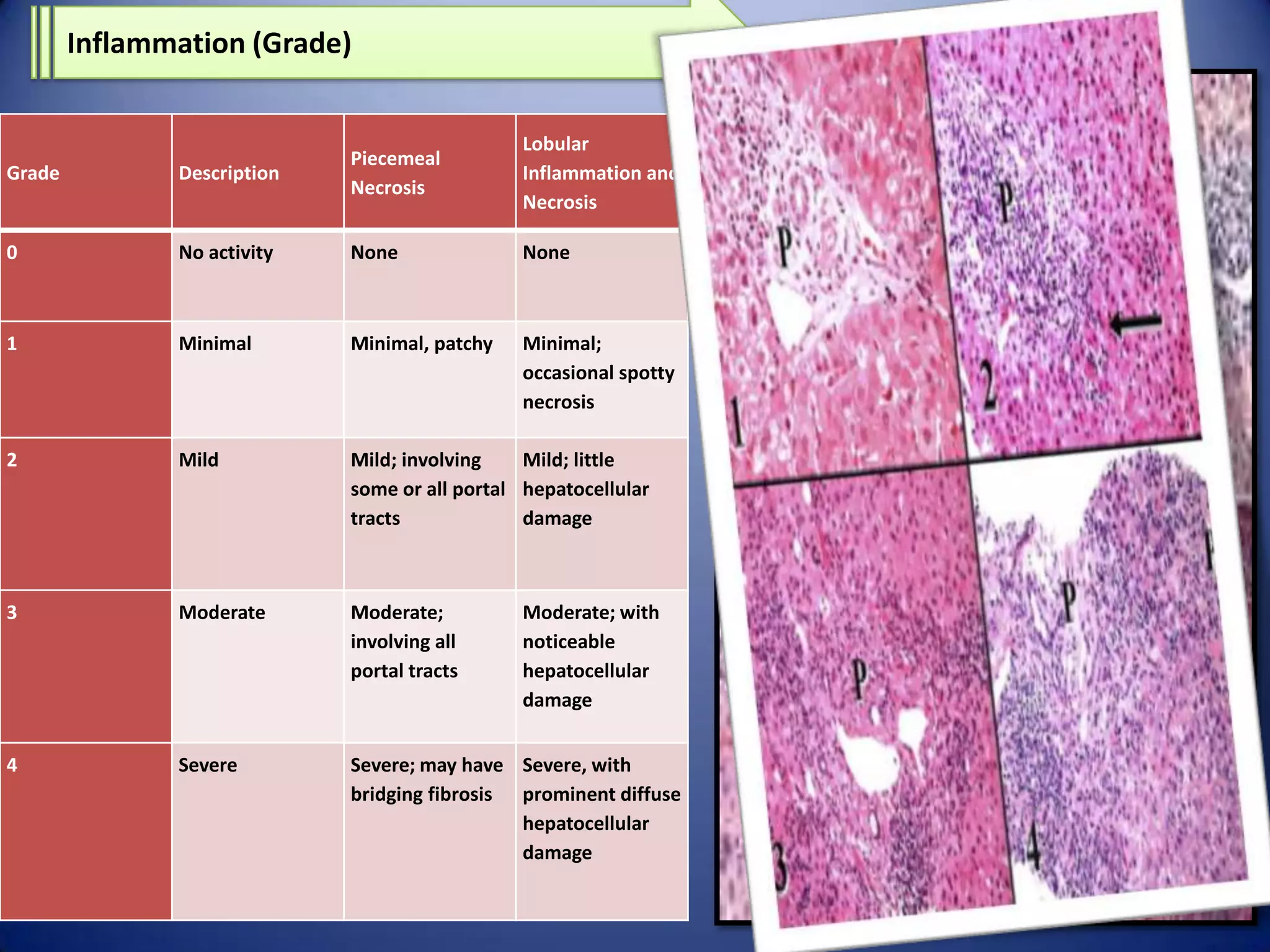
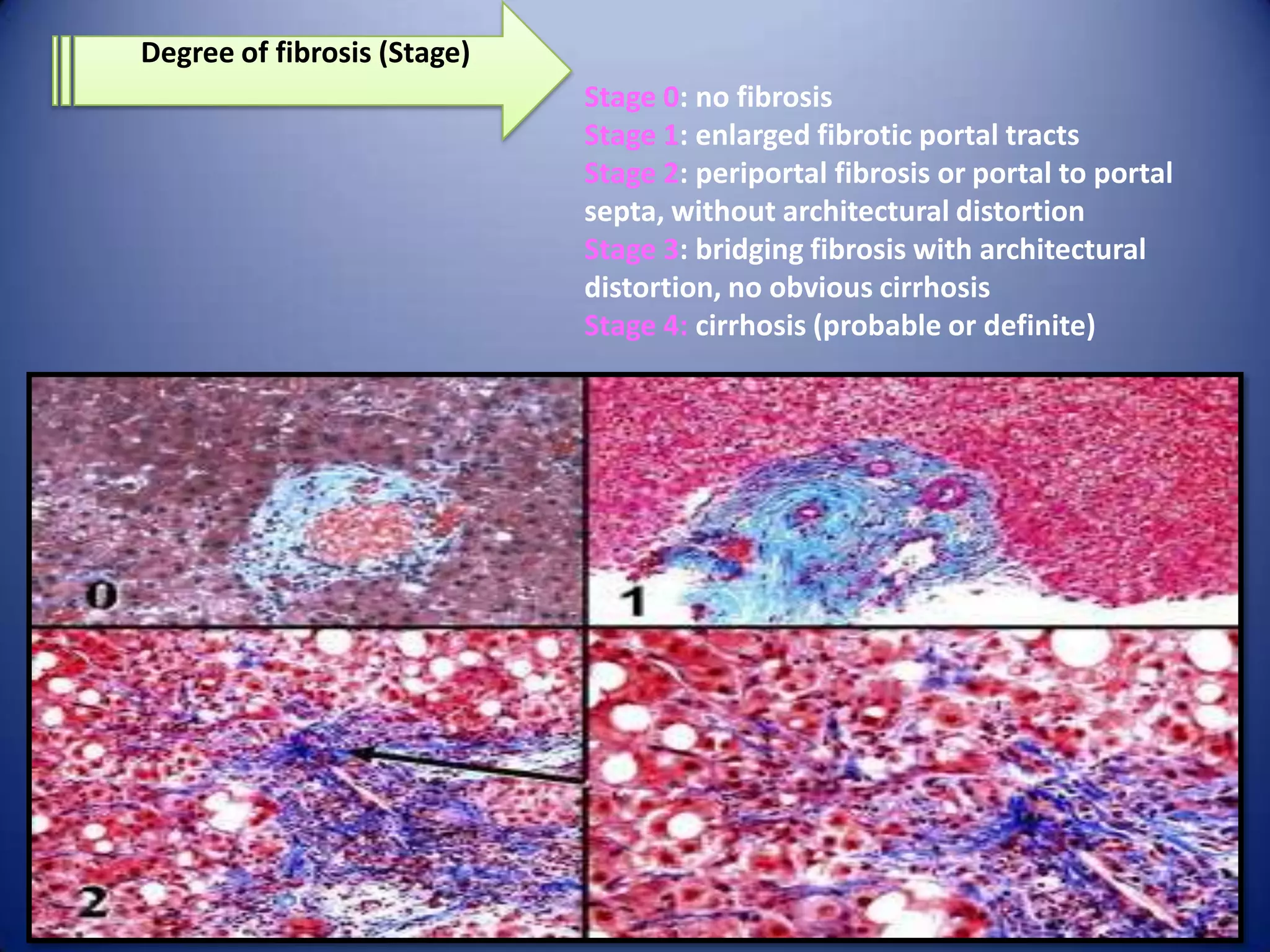
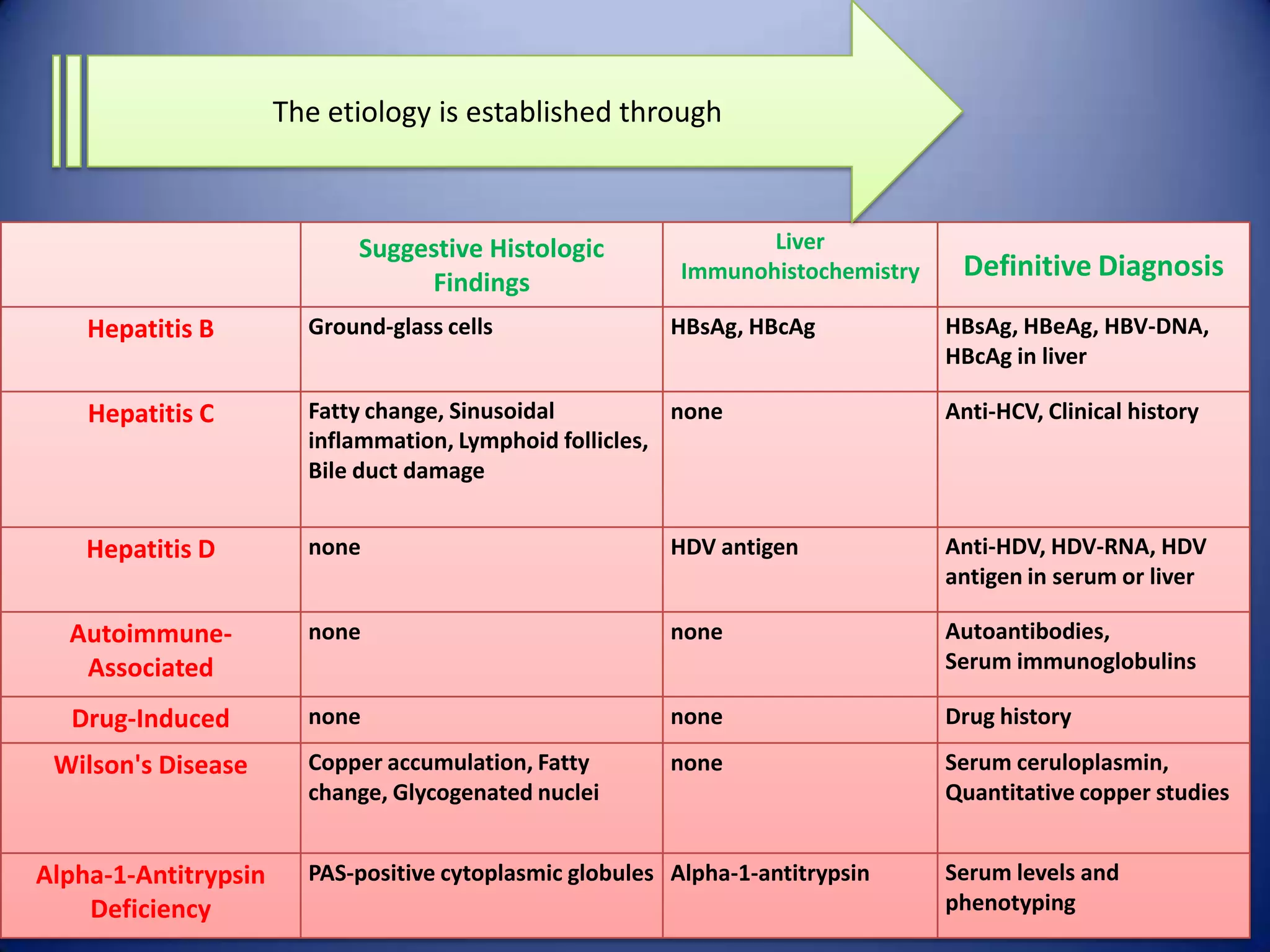
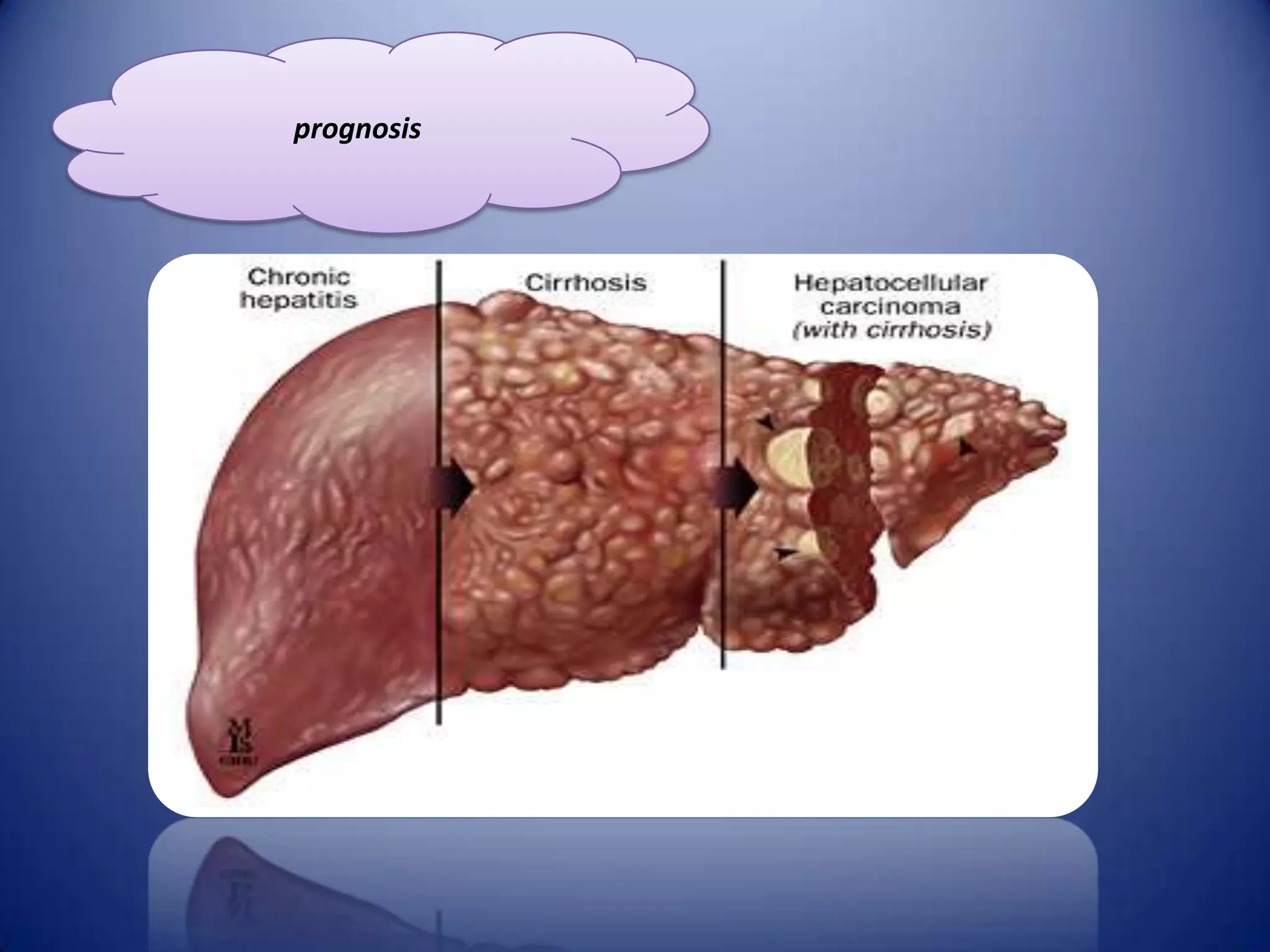
Chronic hepatitis is characterized by a persistent inflammatory process in the liver lasting over 6 months. It is classified into three types based on histological features: chronic active hepatitis marked by necrosis and fibrosis carrying the worst prognosis; chronic persistent hepatitis with portal inflammation but no significant necrosis; and chronic lobular hepatitis involving hepatocyte apoptosis. Chronic hepatitis can be caused by viruses, metabolic disorders, drugs, or autoimmune conditions. Patients may be asymptomatic or experience fatigue, abdominal pain, jaundice, or liver abnormalities. Liver biopsy examines inflammation grade and fibrosis stage and helps establish etiology through immunological testing.