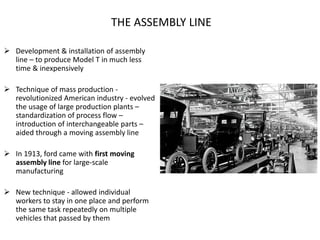
Henry Ford was an American industrialist and founder of Ford Motor Company. In 1908, he introduced the Model T, which became the first affordable automobile for middle-class Americans due to Ford's use of the assembly line for mass production. Ford developed the moving assembly line where workers remained stationary while parts moved down the line, allowing each worker to specialize in a single repeated task. This revolutionary technique dramatically reduced production costs and time, increasing profits. By 1914, Ford could produce a car every 93 minutes and pay workers $5 per day, more than doubling the company's profits.