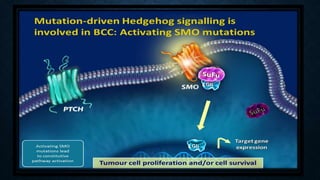
The hedgehog signalling pathway plays a fundamental role in embryonic development and regulates processes like organ formation and tissue patterning. It involves hedgehog ligands that bind to patched receptors, relieving suppression of smoothened. This activates Gli transcription factors that drive expression of target genes. Abnormal activation of this pathway through mutations in key genes like patched or smoothened can lead to basal cell carcinoma and other cancers by inappropriately activating downstream signalling. Germline mutations in patched that cause Gorlin syndrome predispose individuals to developing multiple basal cell carcinomas through deregulated hedgehog signalling.