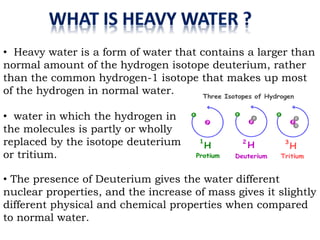
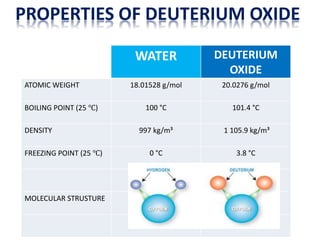
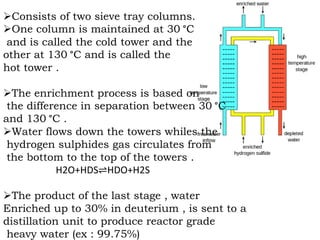
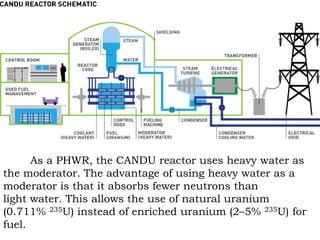
Heavy water, also known as deuterium oxide, contains a larger amount of the hydrogen isotope deuterium than regular water. It has slightly different physical and chemical properties than water due to deuterium making it slightly heavier. Heavy water is produced mainly through hydrogen sulfide-water chemical exchange and has a variety of uses including as a moderator in CANDU nuclear reactors. While it is not toxic to humans in low doses, high concentrations can be harmful to animals and plants by slowing chemical reactions and metabolic processes.