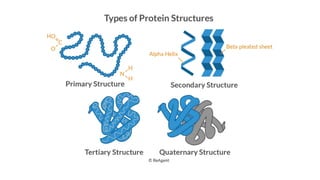
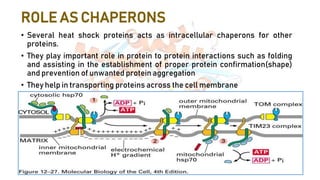
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) are crucial in cellular processes, produced in response to stress, and assist in protein folding and degradation. Classified by molecular weight, HSPs are involved in the cellular stress response and function as chaperons to maintain protein integrity. They also play a role in immunity by alerting the immune system to abnormal proteins in cancerous or infected cells.