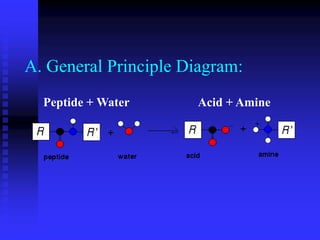
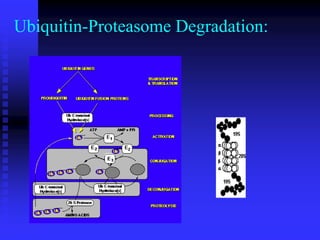
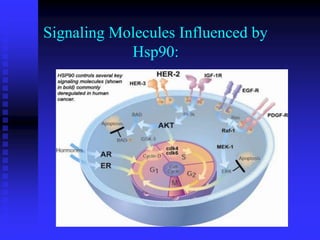
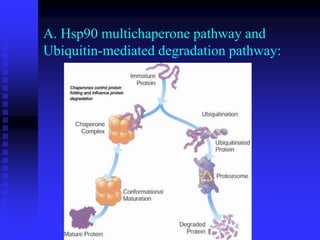
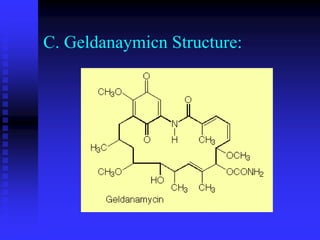
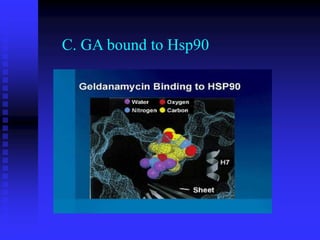
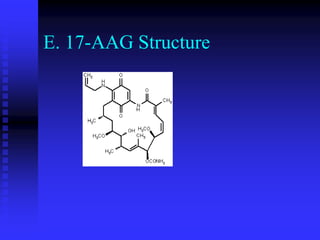
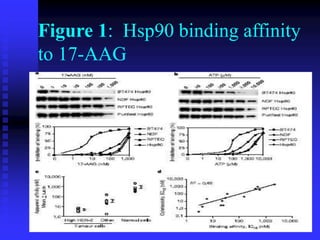
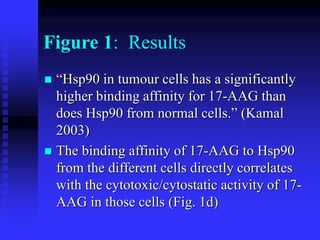
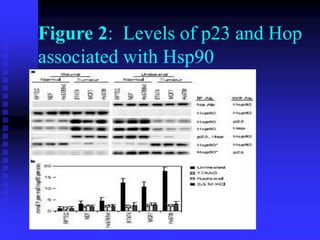
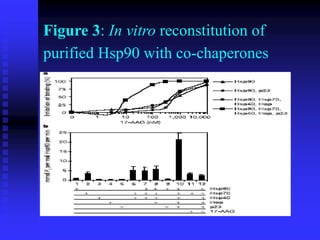
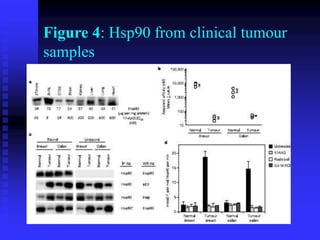
The document discusses heat shock proteins (Hsps), Hsp90 inhibitors, and protein degradation. It provides background on protein degradation mechanisms and heat shock proteins. Hsp90 plays a key role in cancer cell survival by regulating oncogenic signaling proteins. Hsp90 inhibitors like geldanamycin and 17-AAG bind Hsp90's ATP binding site, altering its function and inducing degradation of client proteins, stopping cancer cell growth. The paper found that tumor Hsp90 exclusively exists in active multichaperone complexes, conferring higher binding affinity for 17-AAG compared to normal cell Hsp90. This activated conformation in tumor cells represents a unique drug target.