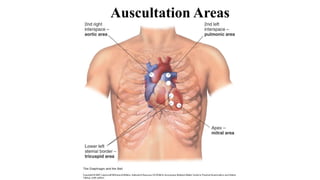
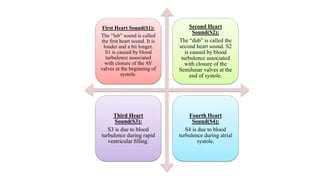
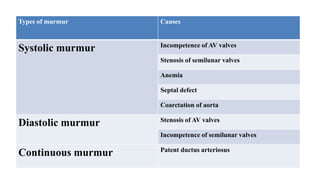
The document discusses heart sounds and murmurs. It describes the four normal heart sounds heard during the cardiac cycle known as S1, S2, S3, and S4. S1 and S2 are the loudest and resemble "lub" and "dub". S3 is softer and S4 is only audible in pathological conditions. Abnormal heart sounds called murmurs can be caused by various valve issues or septal defects. Murmurs are classified as systolic, diastolic, or continuous based on when they occur in the cardiac cycle.