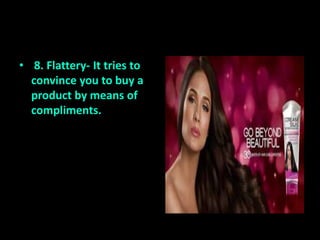
Health consumerism refers to the wise selection of health-related products, agencies, and goods by consumers. Consumers obtain information from various sources like family, advertisements, labels, folklore, testimonials, and the media. Advertisements use techniques like testimonials, appealing to status, bandwagon effects, false images, humor, rewards, scientific evidence, and flattery to influence consumers. Consumers have rights like access to basic needs, safety, information, choice, representation, redress, education, and a healthy environment. As consumers, individuals also have responsibilities like being critically aware, taking action, considering social and environmental impacts, and organizing with other consumers.