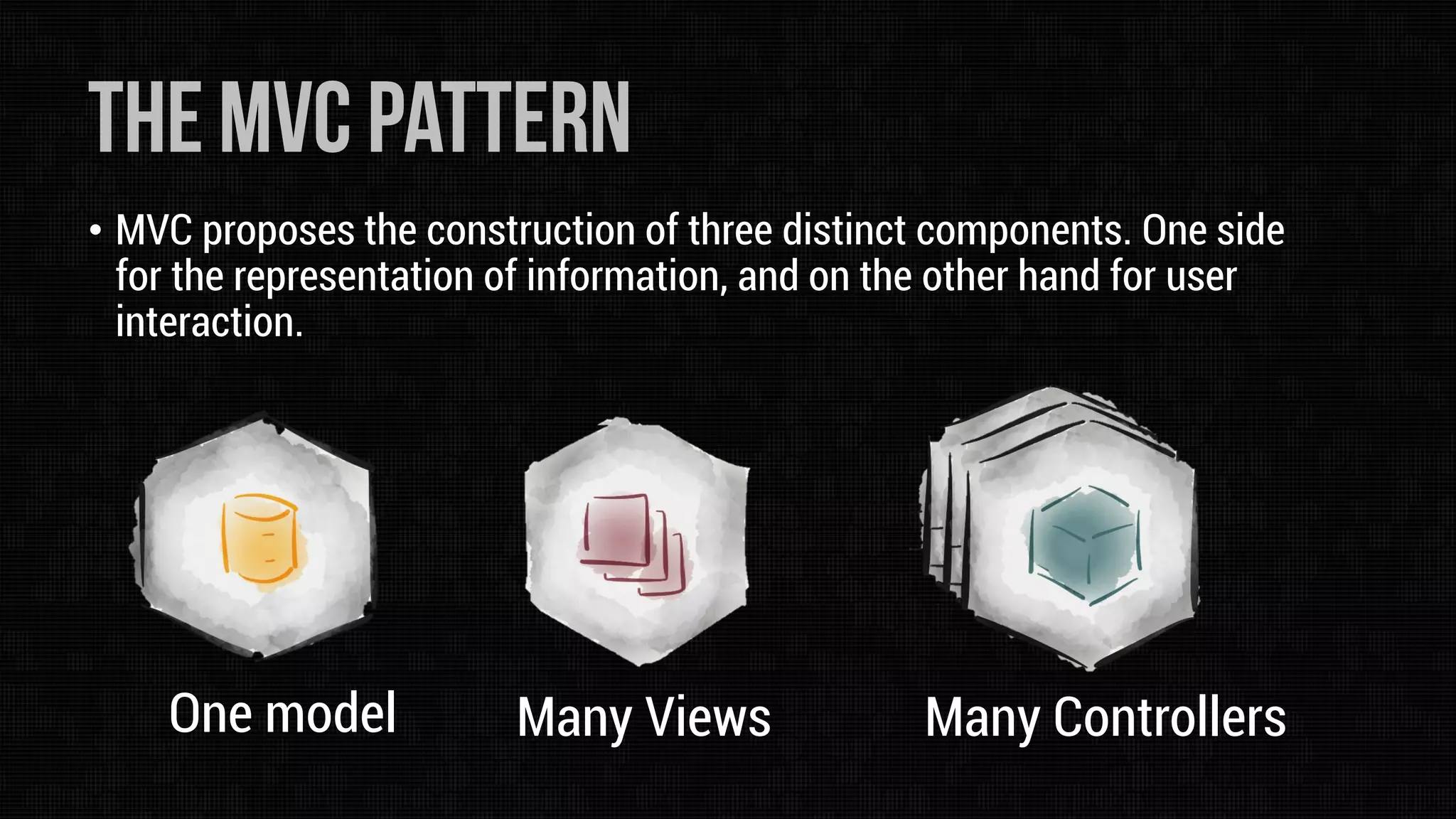
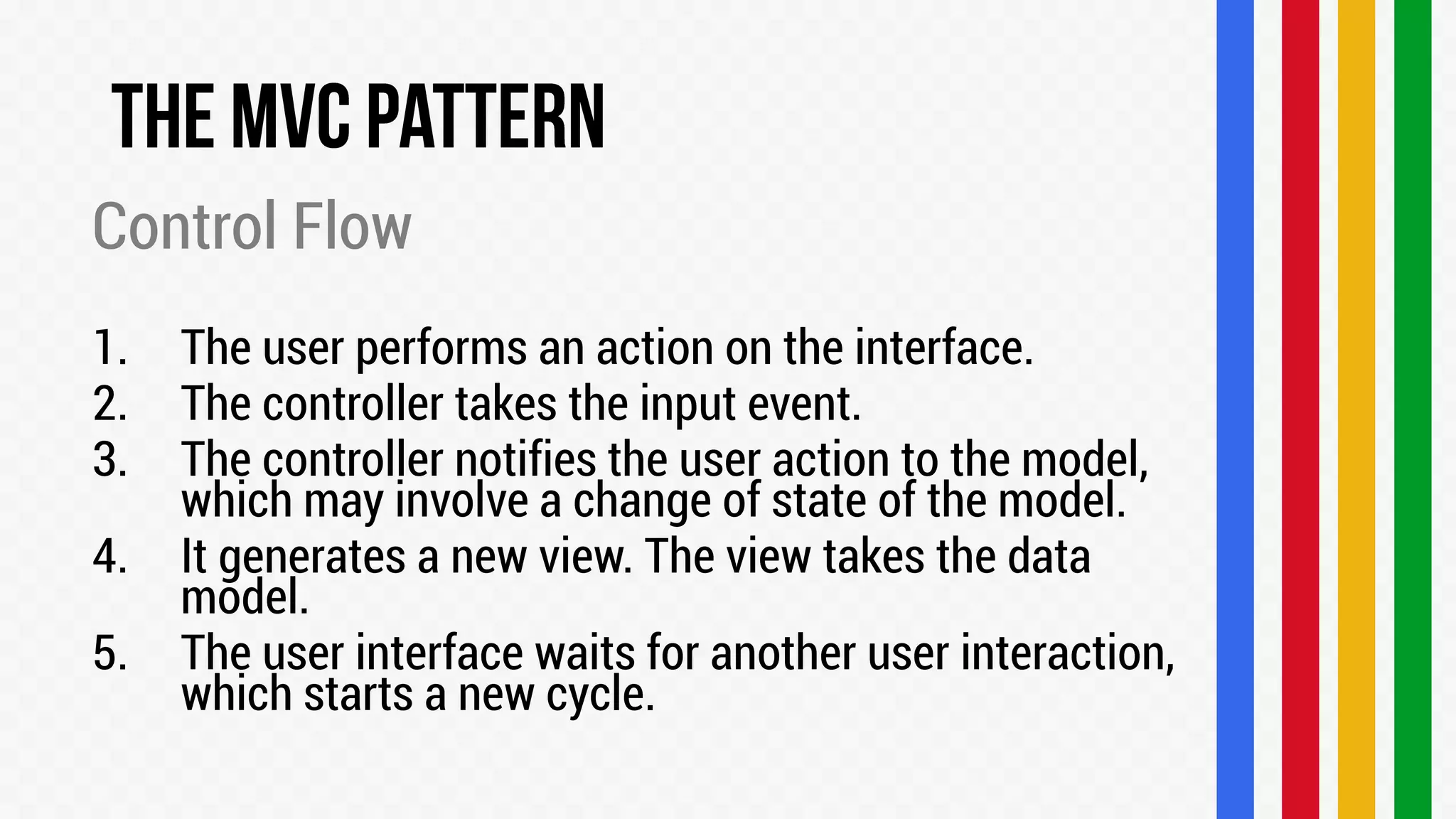
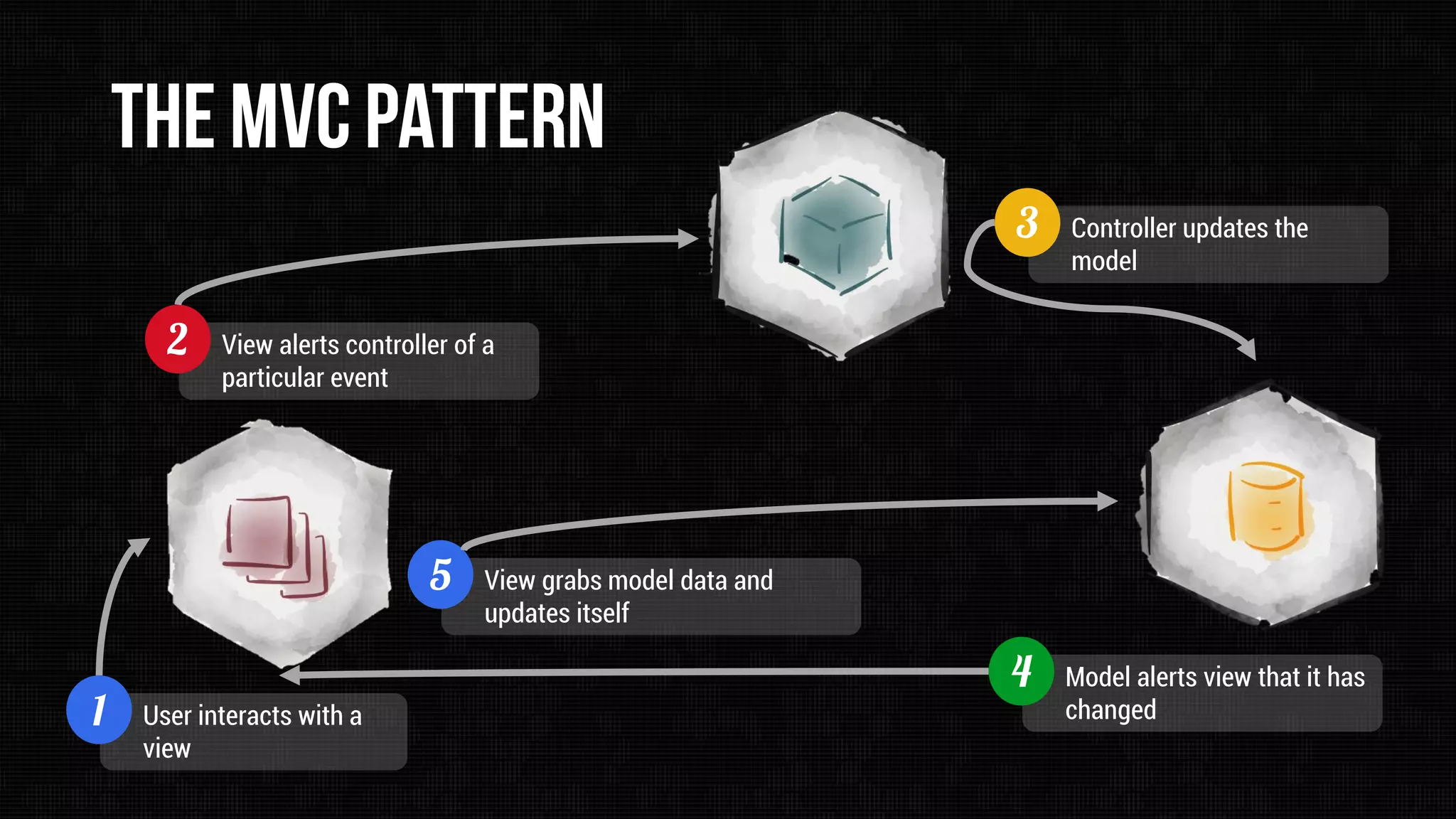
The document describes the Model-View-Controller (MVC) software architectural pattern. MVC separates an application into three main components: the model, the view, and the controller. The model manages the application's data and business logic. The view displays the model's information. The controller interprets inputs from the user and updates the model and/or view accordingly. This separation of concerns makes the application modular, reusable, and maintainable.