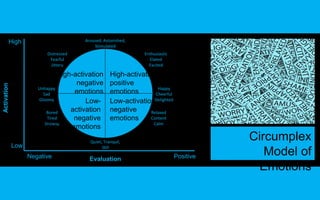
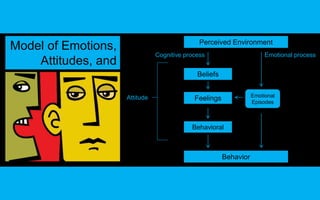
This document discusses emotions, attitudes, and their relationship to the workplace. It defines emotions as brief psychological episodes directed at objects or events that create a state of readiness. Attitudes are evaluations consisting of beliefs, feelings, and behavioral intentions. A model is presented showing how the perceived environment influences cognitive and emotional processes, which impact feelings, attitudes, and behaviors. The document also discusses concepts like emotional intelligence, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, psychological contracts, and how emotions can impact these workplace attitudes.