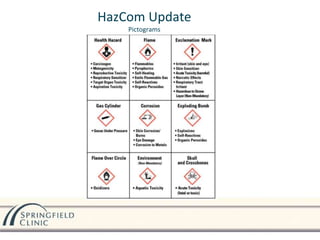
Springfield Clinic is committed to providing a safe work environment and has processes to manage chemical hazards and decrease injury risks. The clinic provides training on hazardous chemicals found in the workplace according to OSHA requirements. Labels and Safety Data Sheets are used to communicate hazards and first aid measures for chemicals. Personal protective equipment must be used for certain procedures, and spills and hazardous waste are disposed of properly according to guidelines. The clinic also takes precautions to prevent the spread of communicable diseases like tuberculosis and multi-drug resistant organisms.