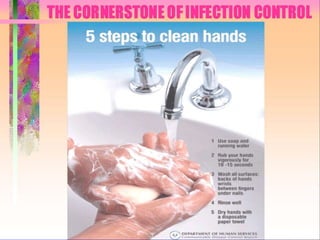
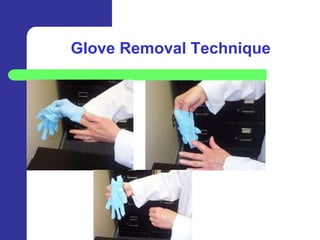
This document provides an overview of right-to-know and hazard communication training. It discusses employer and employee responsibilities regarding chemical awareness and safety. Key topics covered include chemical labels, material safety data sheets (MSDS), routes of chemical entry, hazards, emergency procedures, and bloodborne pathogens exposure control. The training emphasizes familiarizing employees with chemicals in their work areas, consulting labels and MSDS, and following safety precautions such as wearing proper personal protective equipment.