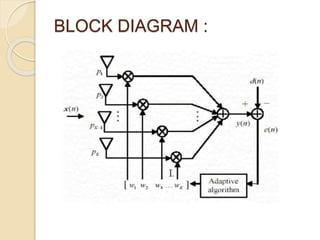
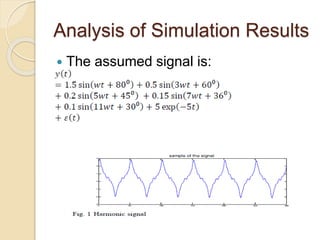
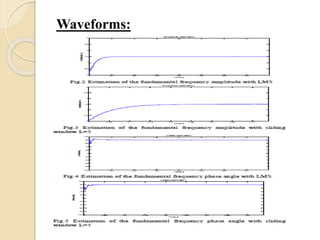
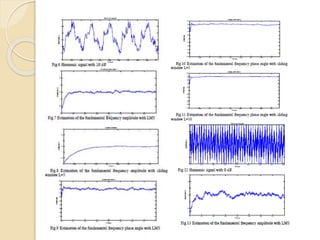
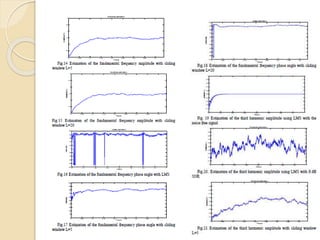
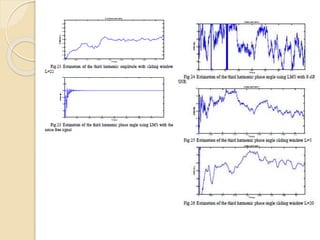
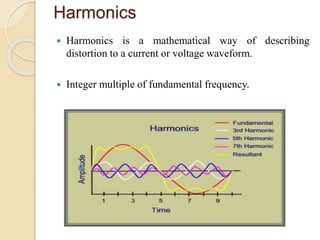
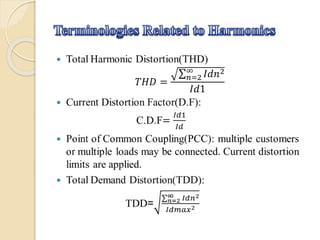
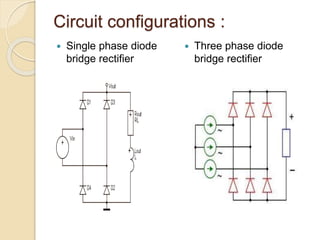
This document discusses harmonic estimation using the sliding window least mean square (SW-LMS) algorithm. It introduces harmonics and their effects, as well as traditional Fourier transform and LMS algorithms for analysis. The SW-LMS algorithm is presented as improving on LMS by using a sliding window to exclude oscillations and work better in noisy signals. Simulation results show the SW-LMS algorithm can effectively estimate harmonics even at high noise levels. In conclusion, SW-LMS provides an effective technique for harmonic estimation.







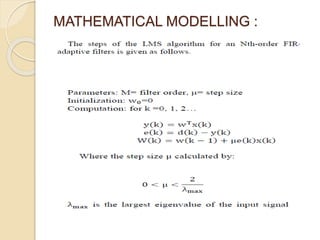


![ Where the weight and the constants are updated as folows
:
USING SLIDING WINDOW :
SW training algorithms also known as high order training algorithms
use a sliding window of system input/output observations to perform
instantaneous learning.It can be applied when the data is highly
noisy.Typically the model weights are updated using information
obtained from store of [L ]previous training vectors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/harmonicestimationbylmsalgorithm-141011000910-conversion-gate01/85/Harmonic-estimation-by-lms-algorithm-16-320.jpg)
![ Given [L] vector data store and current data point 푥푡,this
algorithm computes a moving average search direction
for LMS as follows :
The weighting factor 훼 controls the contribution of the
current vector to the search direction. The weights are
updated as follows :
The store S for harmonic estimation includes only input
given as :
S=[ x1 x2 … xL]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/harmonicestimationbylmsalgorithm-141011000910-conversion-gate01/85/Harmonic-estimation-by-lms-algorithm-17-320.jpg)