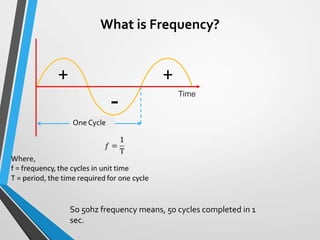
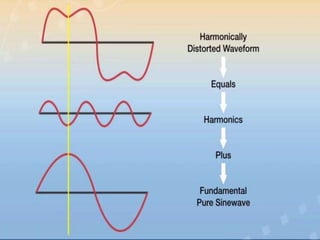
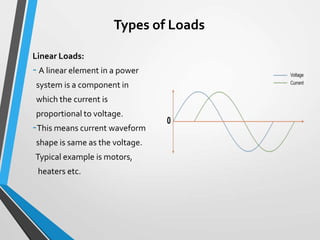
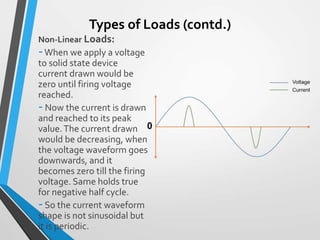
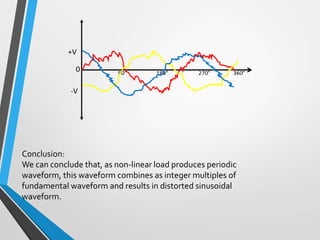
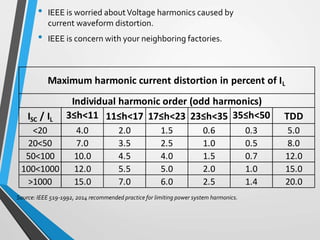
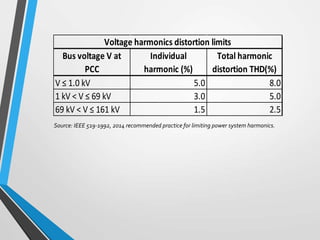
The document is a seminar introduction to power system harmonics, outlining the seminar's learning objectives and benefits, including increased awareness of harmonics and their effects on electrical systems. It discusses the definition, origin, and types of harmonics, particularly focusing on linear and non-linear loads, along with their adverse effects on equipment and power systems. The document also references IEEE 519 standards for limiting harmonics, addressing their impact from both engineering and business perspectives.