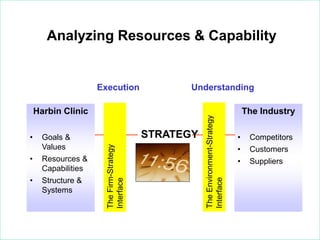
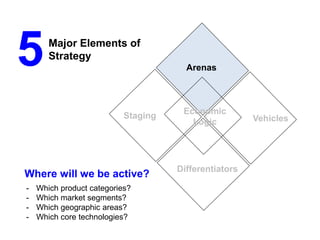
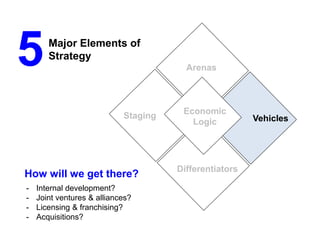
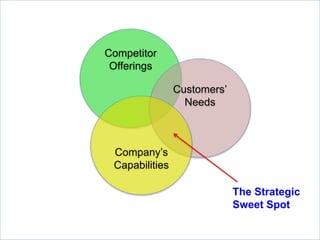
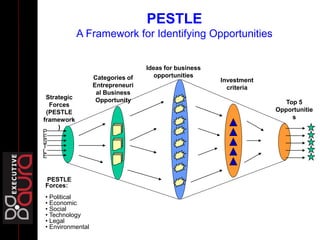
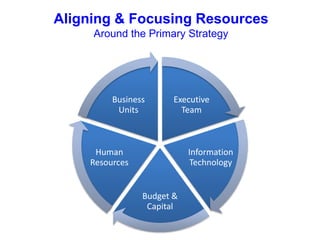
The document outlines strategies for growth within the Harbin Clinic, emphasizing the importance of a compelling vision, a clear roadmap, and effective resource management. Key components of strategic decision-making include high-quality data, technology access, sound judgment, trust, and flexibility, with a focus on understanding both internal capabilities and external market conditions. It also details the necessary elements for successful strategy execution, highlighting the need for simplicity, alignment among teams, resource discussion, and continuous performance monitoring.