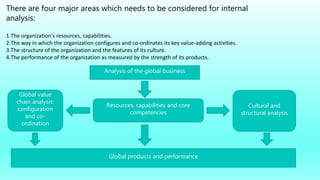
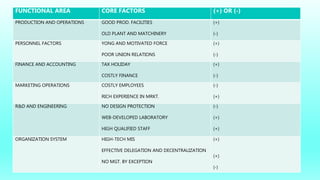
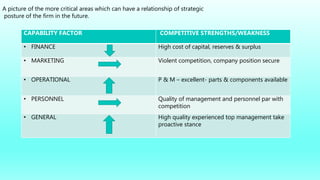
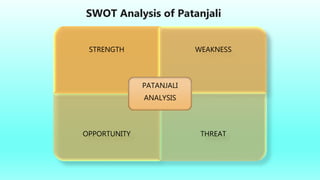
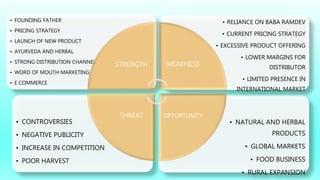
The document discusses strategic management tools like SWOT and PESTLE analyses to evaluate internal and external factors affecting organizations. It emphasizes the importance of accurate analysis for decision-making and strategic planning, highlighting the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for companies. The document concludes with a case study on Patanjali, showcasing its growth in the Indian FMCG market and the need to improve its communication strategy while leveraging its strengths.