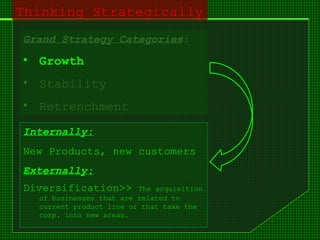
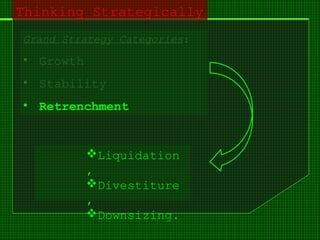
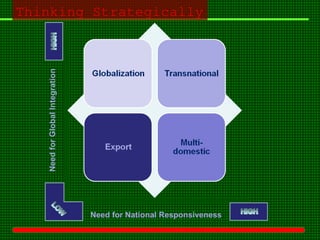
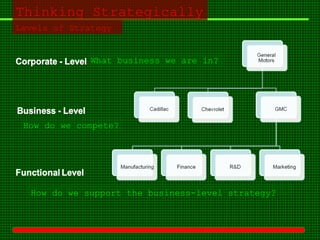
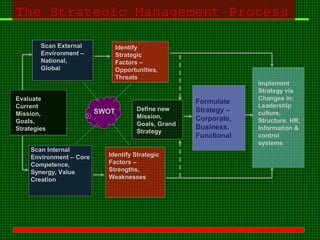
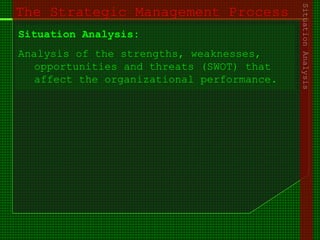
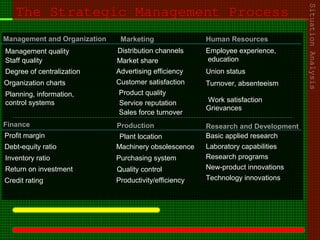
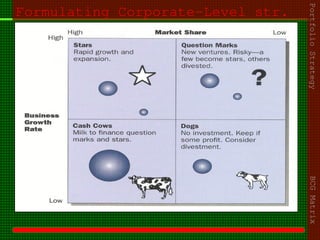
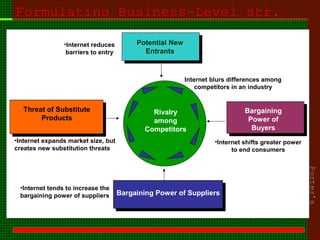
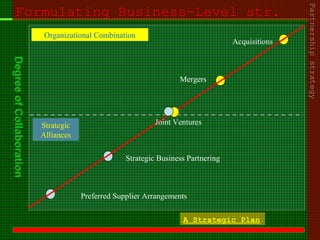
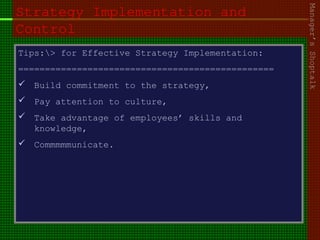
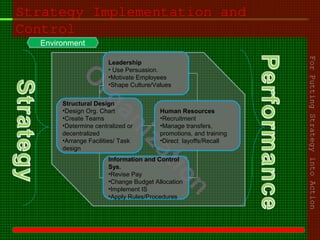
This document outlines the course content for an advanced healthcare management course. It covers key topics like strategic management processes, formulating corporate, business, and functional level strategies, and strategy implementation and control. Grand strategies like growth, stability, and retrenchment are discussed. Formulating business strategy addresses Porter's five forces model and competitive strategies of differentiation, cost leadership, and focus. Effective strategy implementation requires building commitment, culture change, communication, and adjusting leadership, resources, and structure.