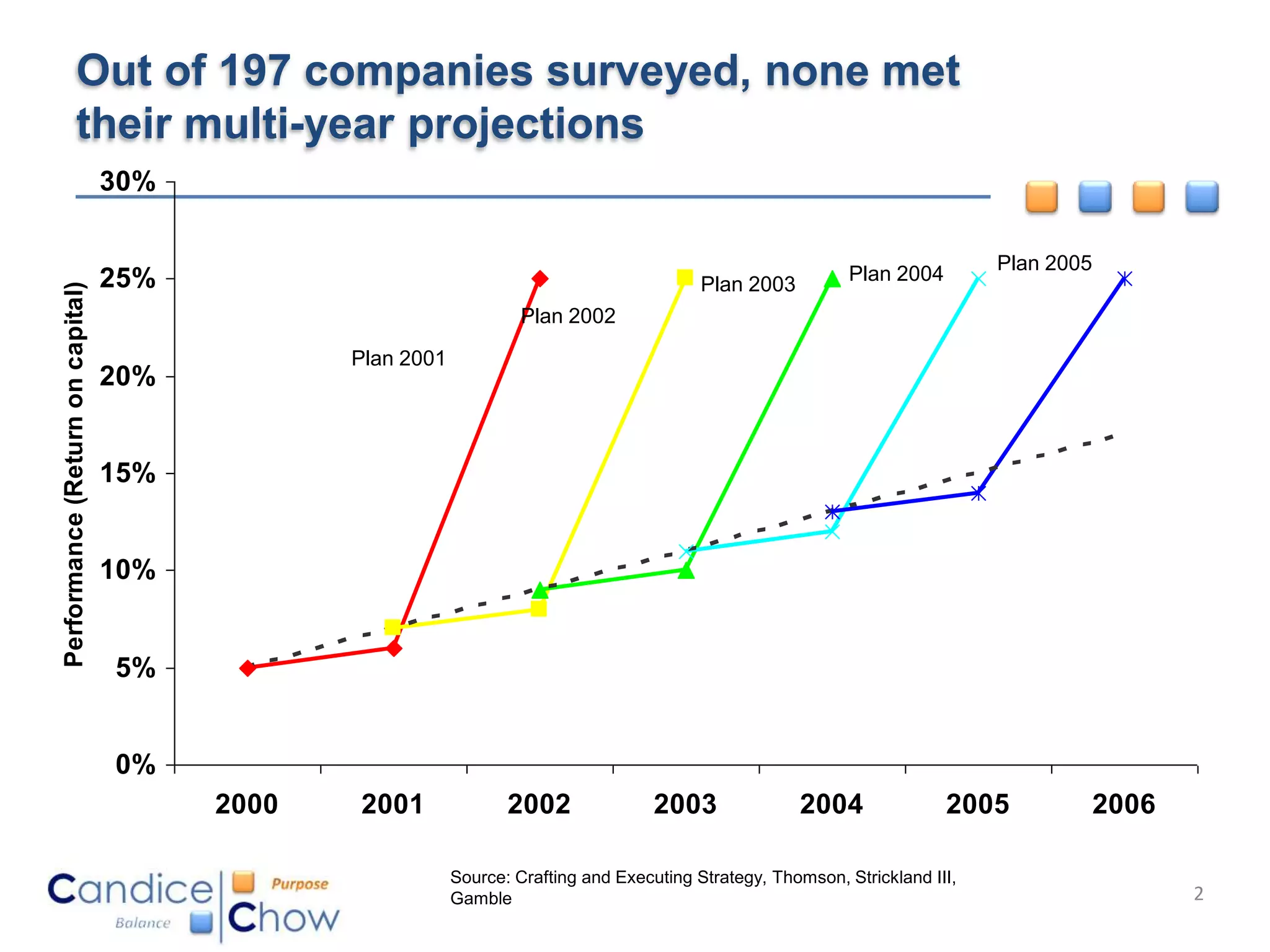
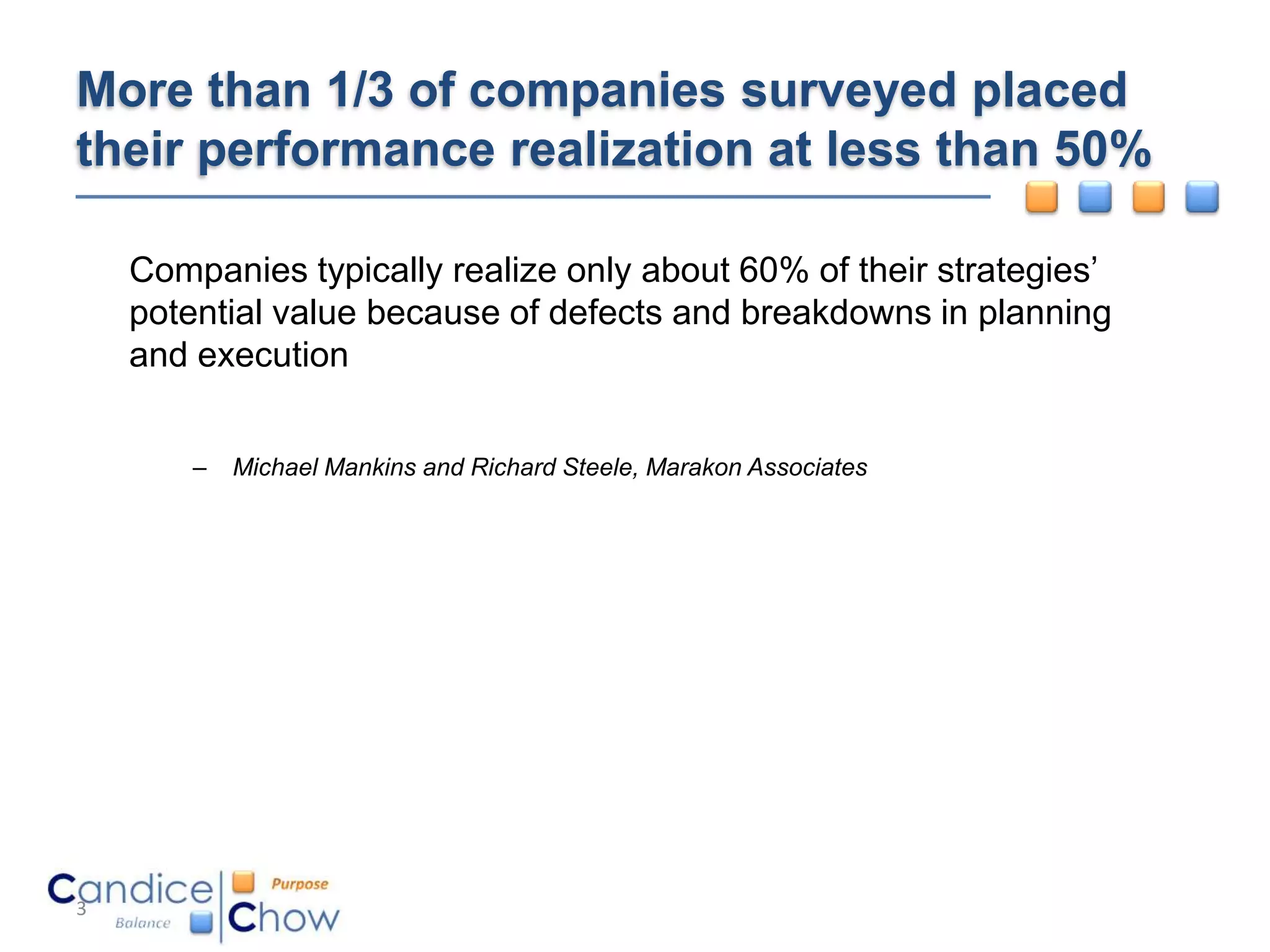
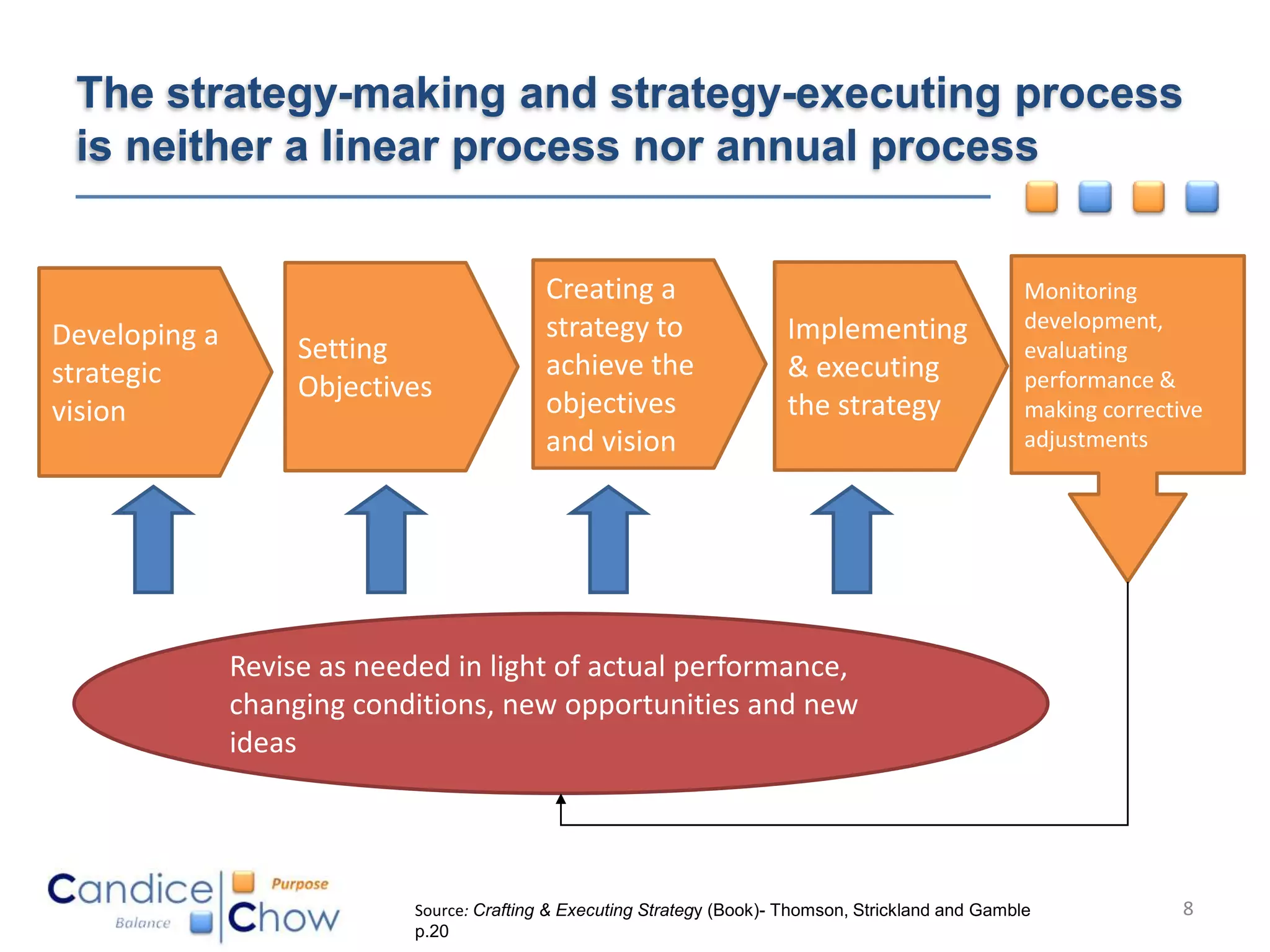
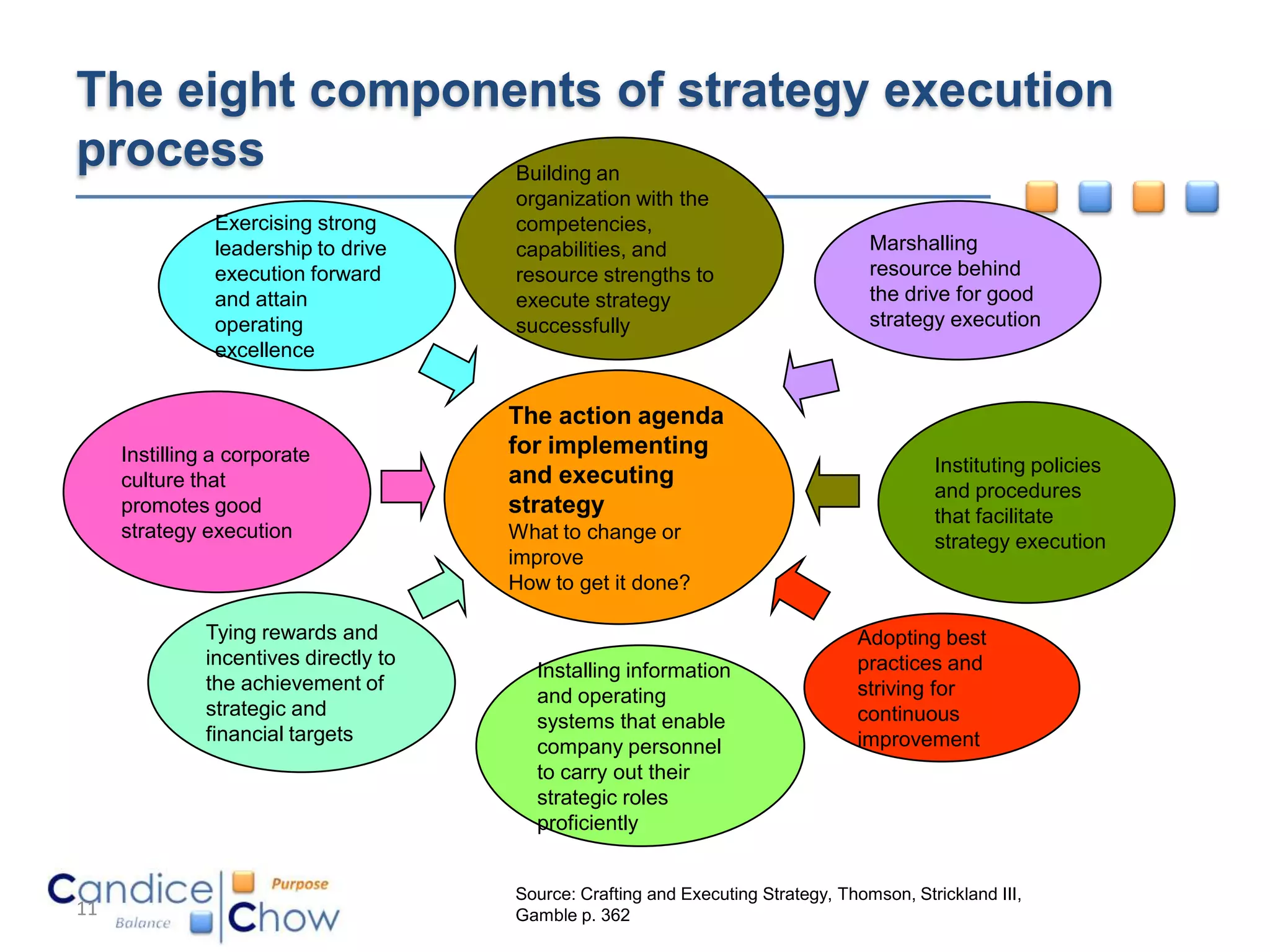
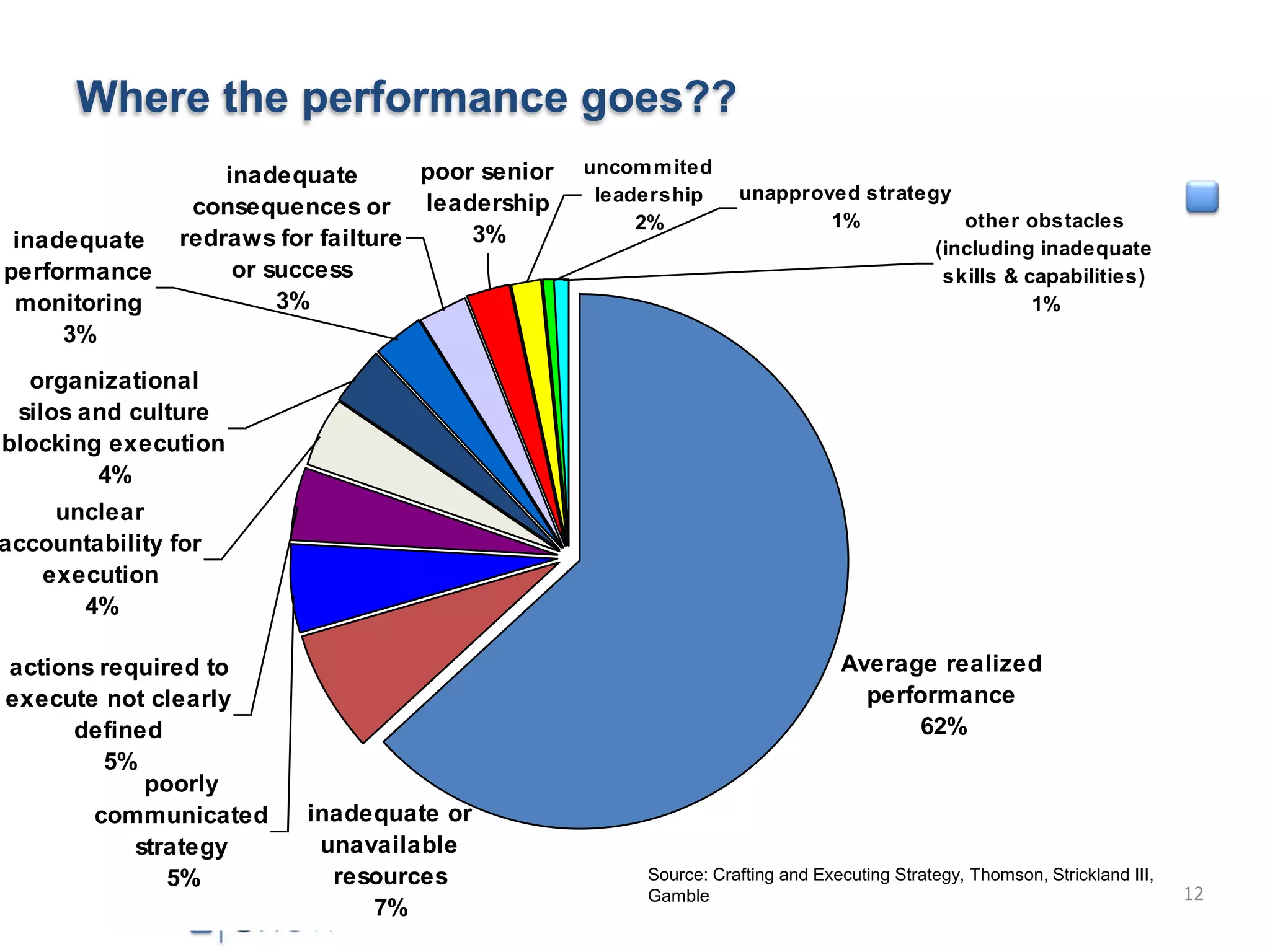
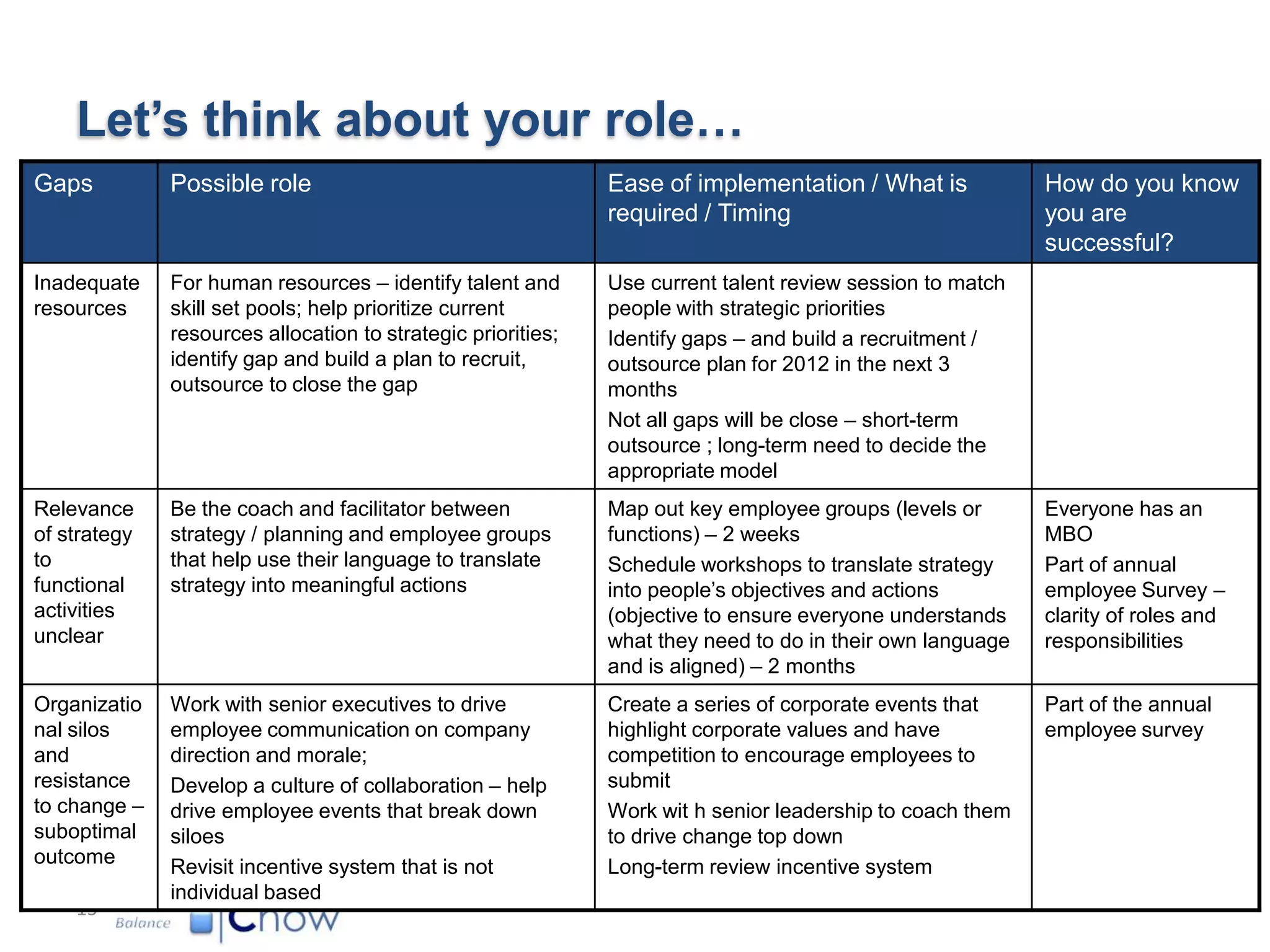
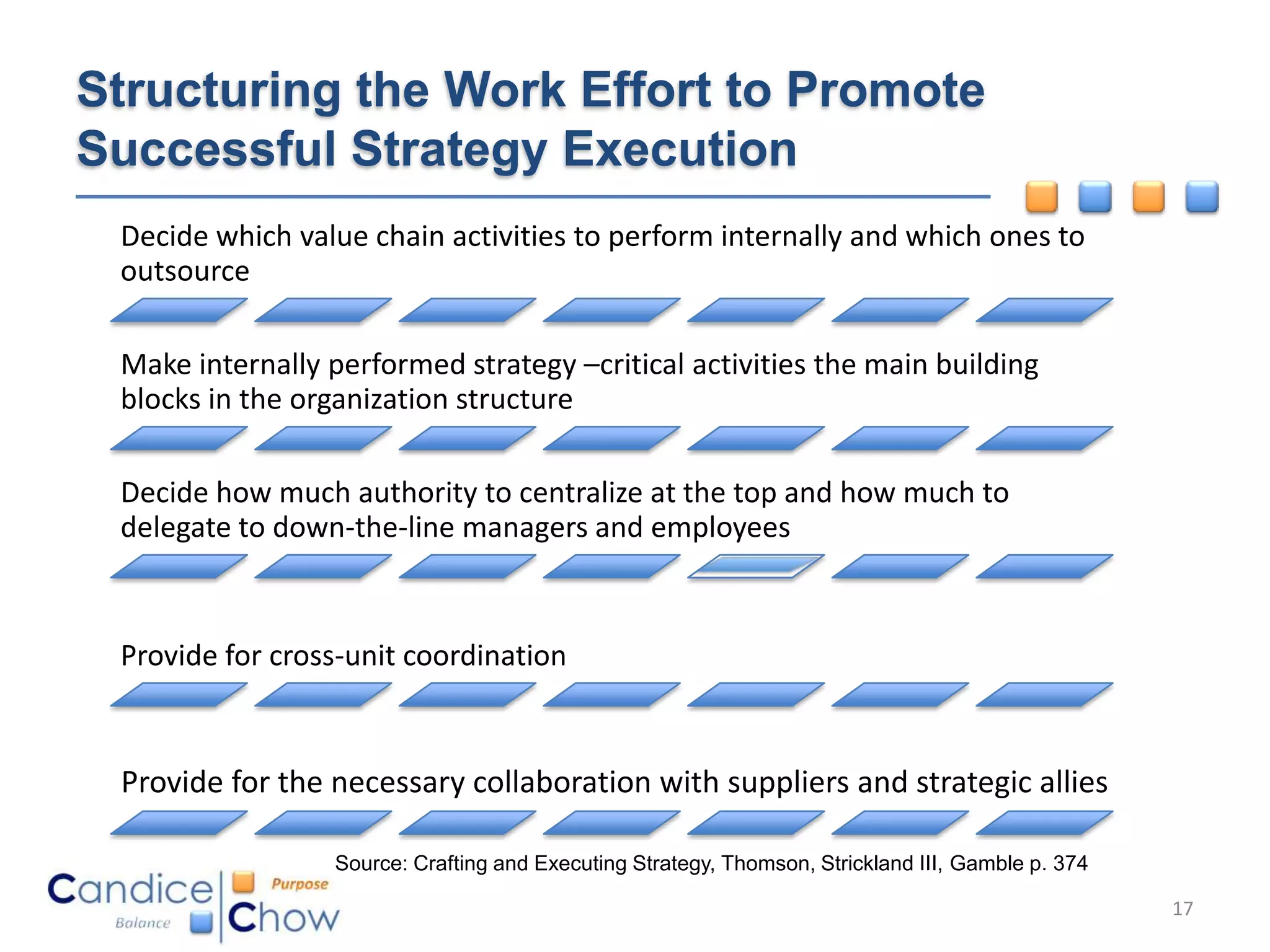
The document outlines key factors for executing strategy successfully:
1) It identifies 8 components of an effective strategy execution process including strong leadership, clear accountability, and resources to drive execution.
2) It discusses translating strategic plans into actionable plans by defining objectives, responsibilities, and timelines to implement changes.
3) HR can help by identifying talent needs, building core competencies, structuring work to promote collaboration, and linking rewards to strategic targets.
4) Building an organization capable of execution takes time and focuses on leadership, communication, clarity of roles and responsibilities, and performance management.