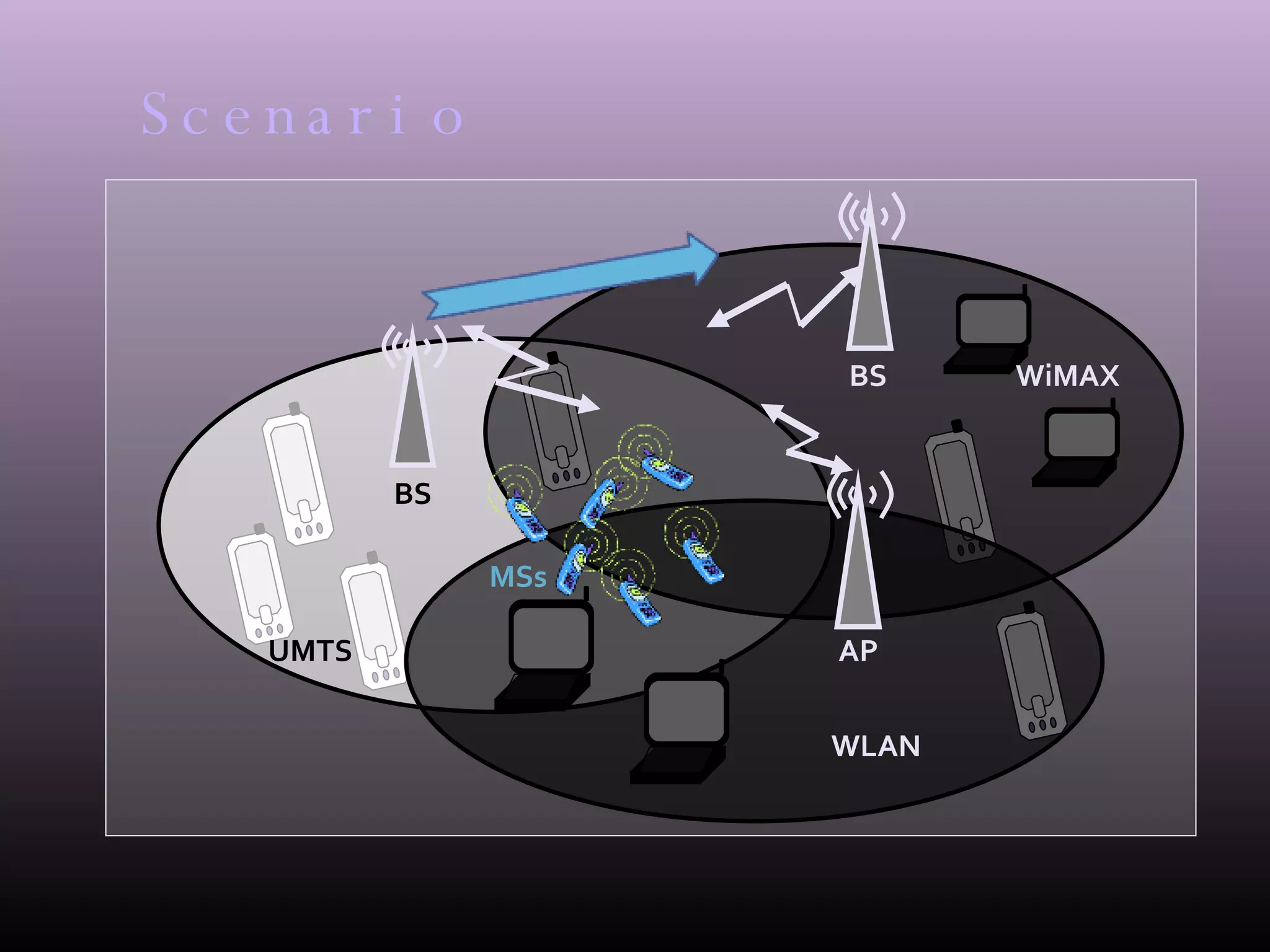
The document proposes an intelligent and adaptive algorithm to support the simultaneous handover of a group of mobile devices between networks with the best possible quality of service. It aims to study the performance of handovers for a group of mobile devices moving between a UMTS, WiMAX and WLAN network. The algorithm focuses on multiple users, adaptability, and vertical handovers between UMTS and 802.21 networks for both real-time and non-real-time applications. Simulations show that the randomized network selection algorithm reduces packet loss and increases throughput compared to always selecting the same network.