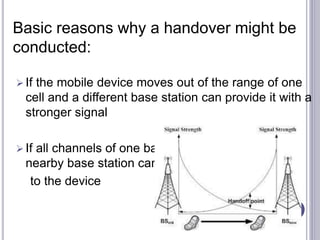
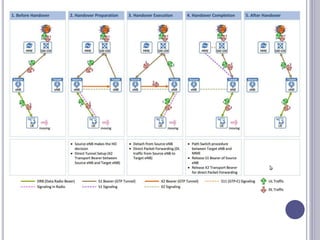
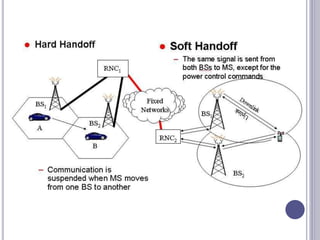
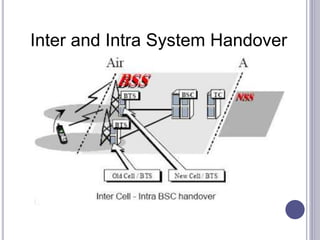
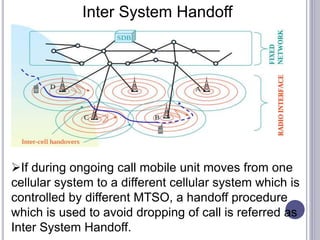
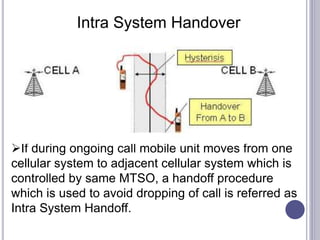
The document discusses different types of handovers in cellular networks. A handover occurs when a mobile device moves between different base stations. There are two main types - hard handovers where the existing radio link is dropped briefly as the call is transferred to a new base station, and soft handovers where the call can be transferred without being briefly disconnected by maintaining connections to multiple base stations simultaneously. Handovers are important for mobility in cellular networks to maintain call quality as users move between different coverage areas without dropping calls.












![References :
Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, [Online]:
http://en.wikipedia.org
MobileCompChap03L11GSMHandover
handoverinnetworks-13071790379332-phpapp01-
110604041918-phpapp01
trial_lecture on handover](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsnlhandover-150208071909-conversion-gate02/85/Handover-in-Telecom-20-320.jpg)