The document outlines three standards developed by the Office of Chinese Language Council International to support the growing need for Chinese language education worldwide:
1. Standards for Teachers of Chinese to Speakers of Other Languages (TCSOL) which defines the knowledge and skills required of Chinese teachers.
2. Chinese Language Proficiency Scales for Speakers of Other Languages (CLPS) which establishes proficiency benchmarks for learners.
3. International Curriculum for Chinese Language Education (ICCLE) which provides a framework for Chinese language curricula.
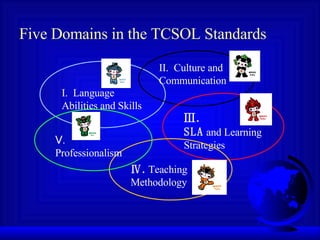
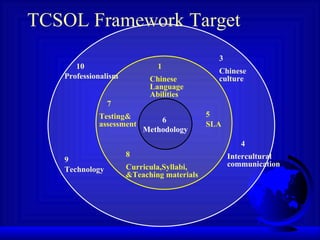
The TCSOL standards draw on research and teaching experience to define 10 domains of teacher competency. Variations will be developed to account for different teaching contexts.