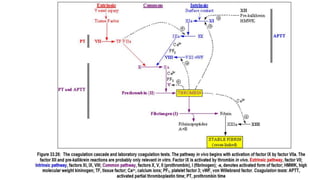
Haemostasis involves three components that work together to stop bleeding after an injury. The extravascular component involves pressure from accumulated blood in tissues around blood vessels. The vascular component involves constriction of blood vessels. The intravascular component involves platelets, coagulation factors, anticoagulants, and fibrinolytic factors that form a thrombus (blood clot) at the site of injury through a balance of pro-coagulant and anticoagulant processes. Disruptions to this balance can result in bleeding disorders or hypercoagulability.