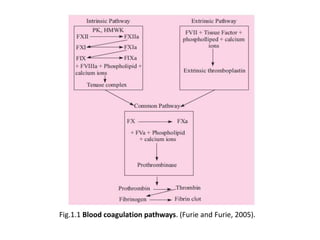
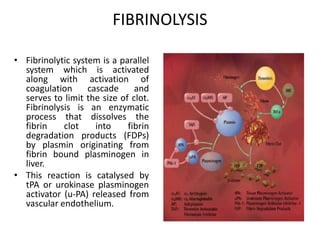
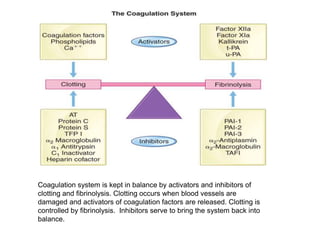
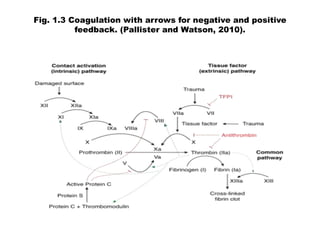
The document discusses the control of coagulation through various proteins and pathways that regulate clot formation and dissolution. Coagulation begins with tissue factor activating the coagulation cascade to form a clot. This is regulated by tissue factor pathway inhibitor and proteins that inhibit specific coagulation factors, such as protein C inhibiting factors V and VIII. Clot dissolution is mediated by plasmin and inhibited by alpha2-antiplasmin. Together these pathways maintain a balance between clot formation and removal. Deficiencies can lead to bleeding disorders or thrombosis.