The document summarizes key information about blood, including:
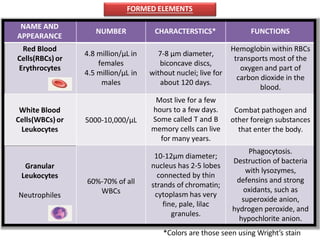
- Blood is composed of plasma and formed elements. Plasma is 91.5% water and contains proteins, electrolytes, nutrients, gases, and waste products. Formed elements include red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Red blood cells contain hemoglobin and transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. White blood cells help combat pathogens and foreign substances. Platelets help form blood clots during hemostasis.
- Blood functions include respiration, nutrient and hormone transport, waste removal, pH regulation, temperature control, water balance, and protection from pathogens through white blood cell activity and hemostasis.