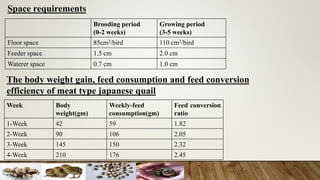
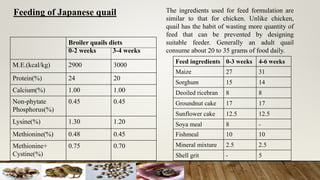
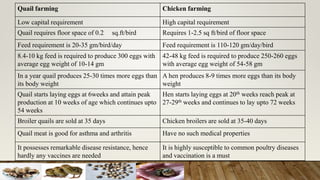
The document discusses the benefits of Japanese quail farming, highlighting their fast growth, prolific egg production, and low management costs. Japanese quails are hardy, have a relatively low risk of diseases, and require less space compared to chickens. Additionally, it provides guidance on the management of quail chicks, breeding, feeding, and hatchery practices to maximize production efficiency.