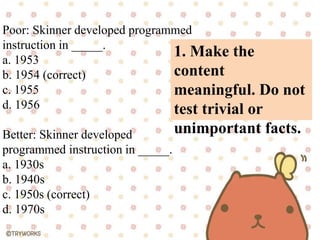
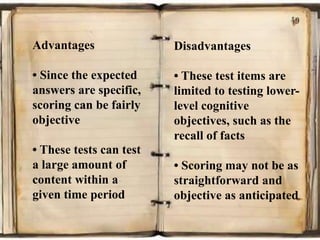
The document provides guidelines for constructing different types of assessment items including multiple choice, true/false, matching, short answer, and essay items. For multiple choice items, it recommends making all answer options plausible, reducing wordiness, and avoiding obvious correct answers. For true/false items, it advises ensuring statements are entirely true or false and conveying only one idea per statement. Matching items should have no more than 6-7 items and include extra distractors. Short answer items require a scoring key and avoid open-ended questions. Essay items need grading criteria and conditions explained to students.