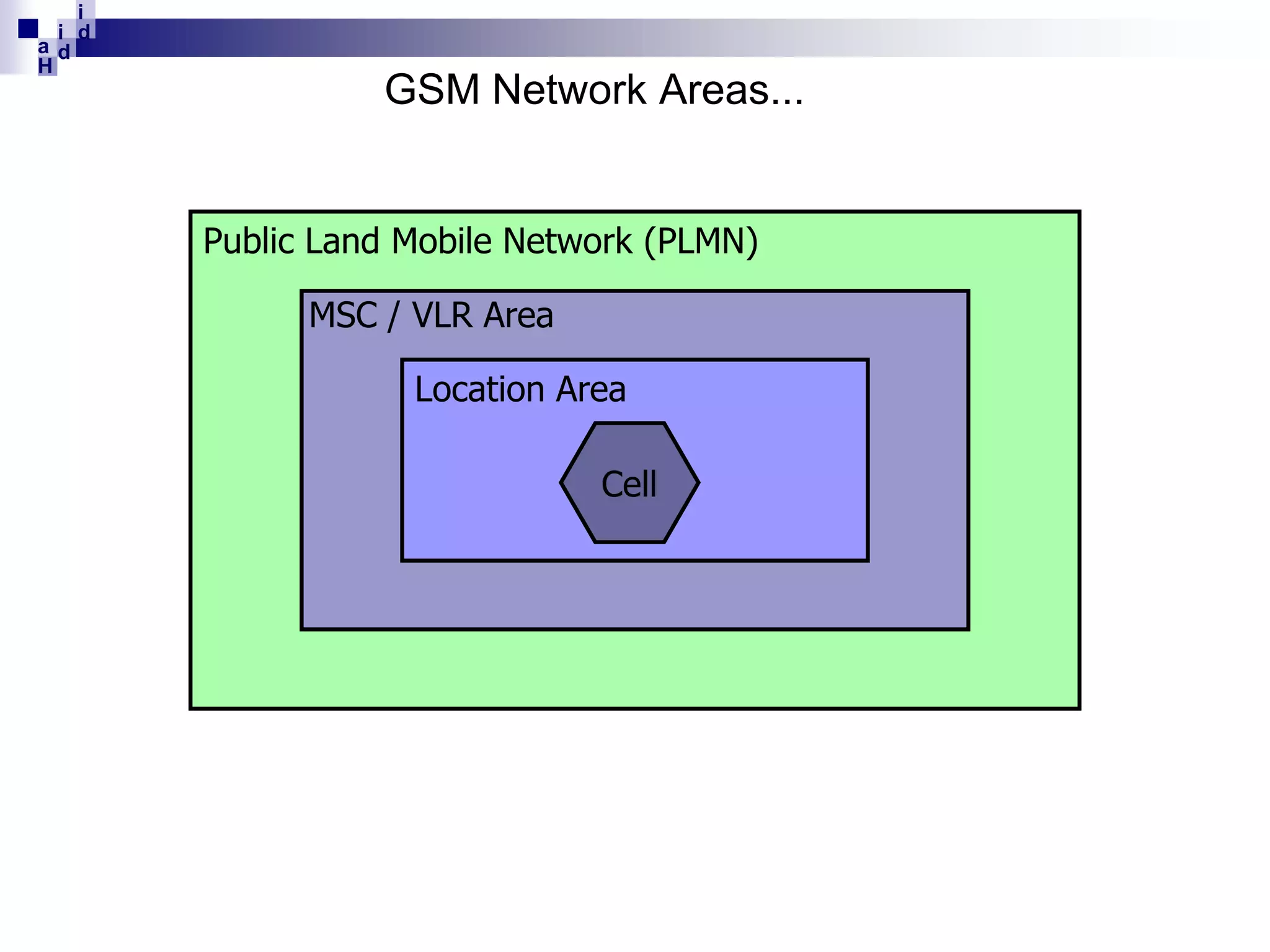
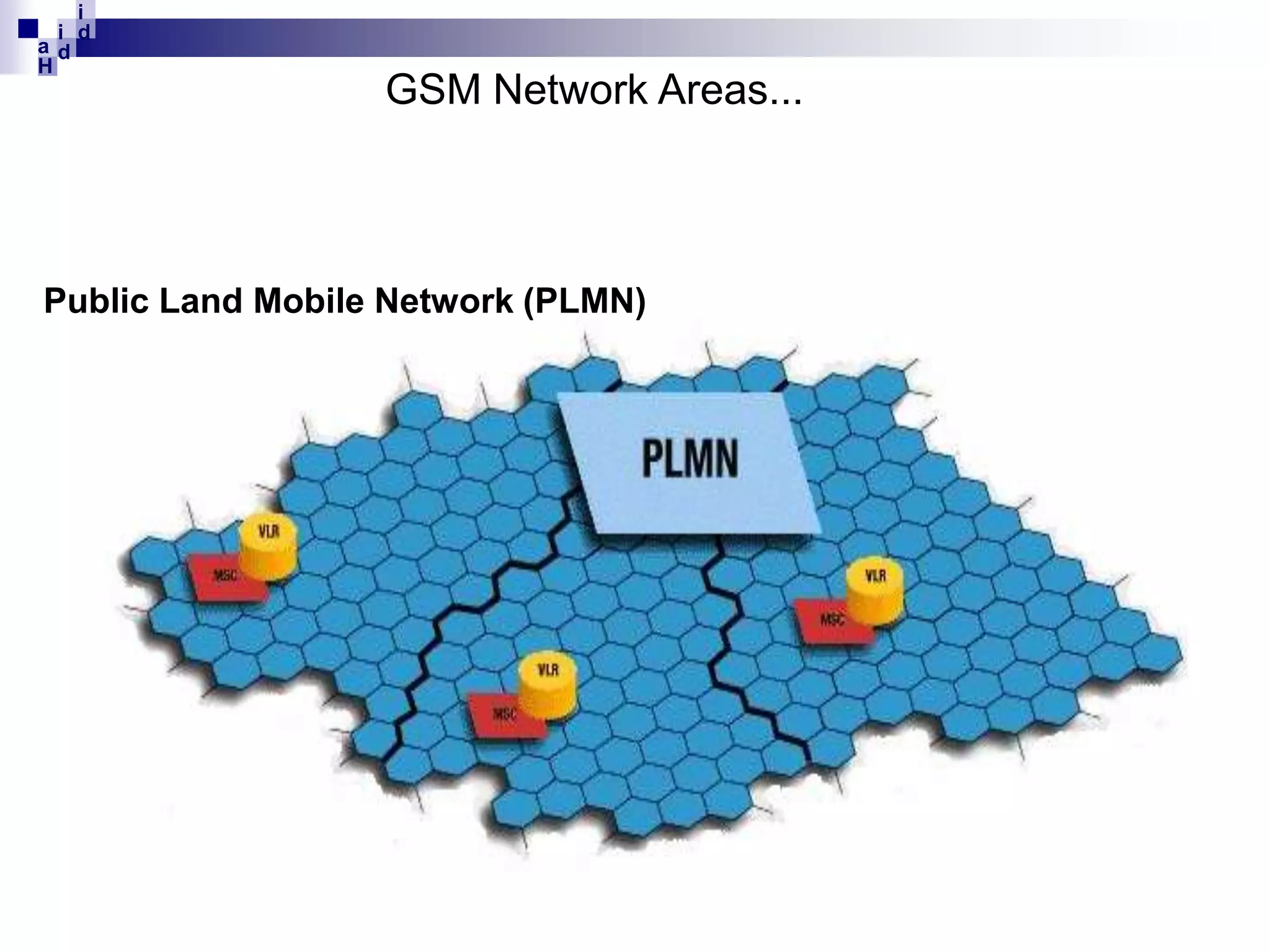
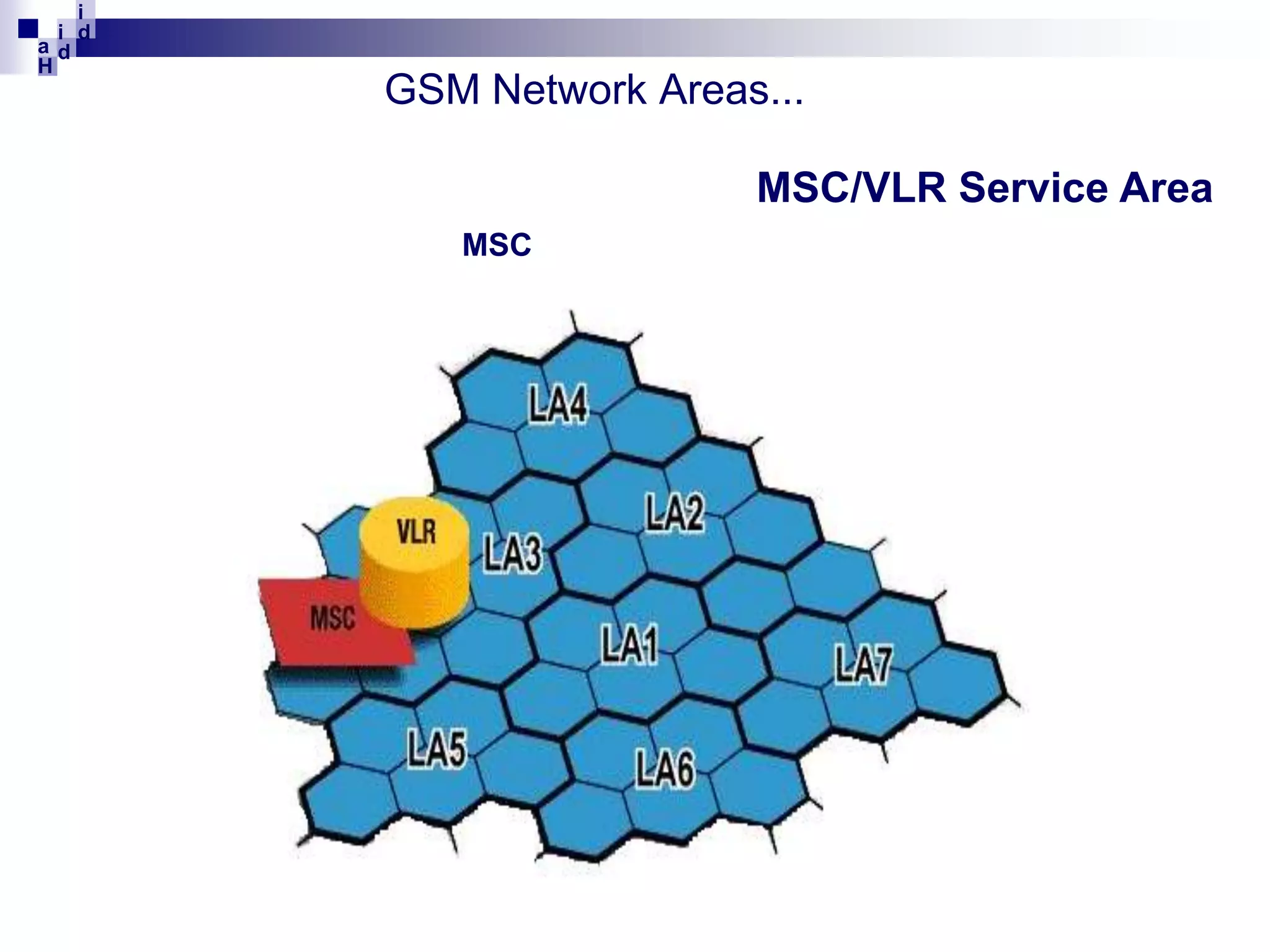
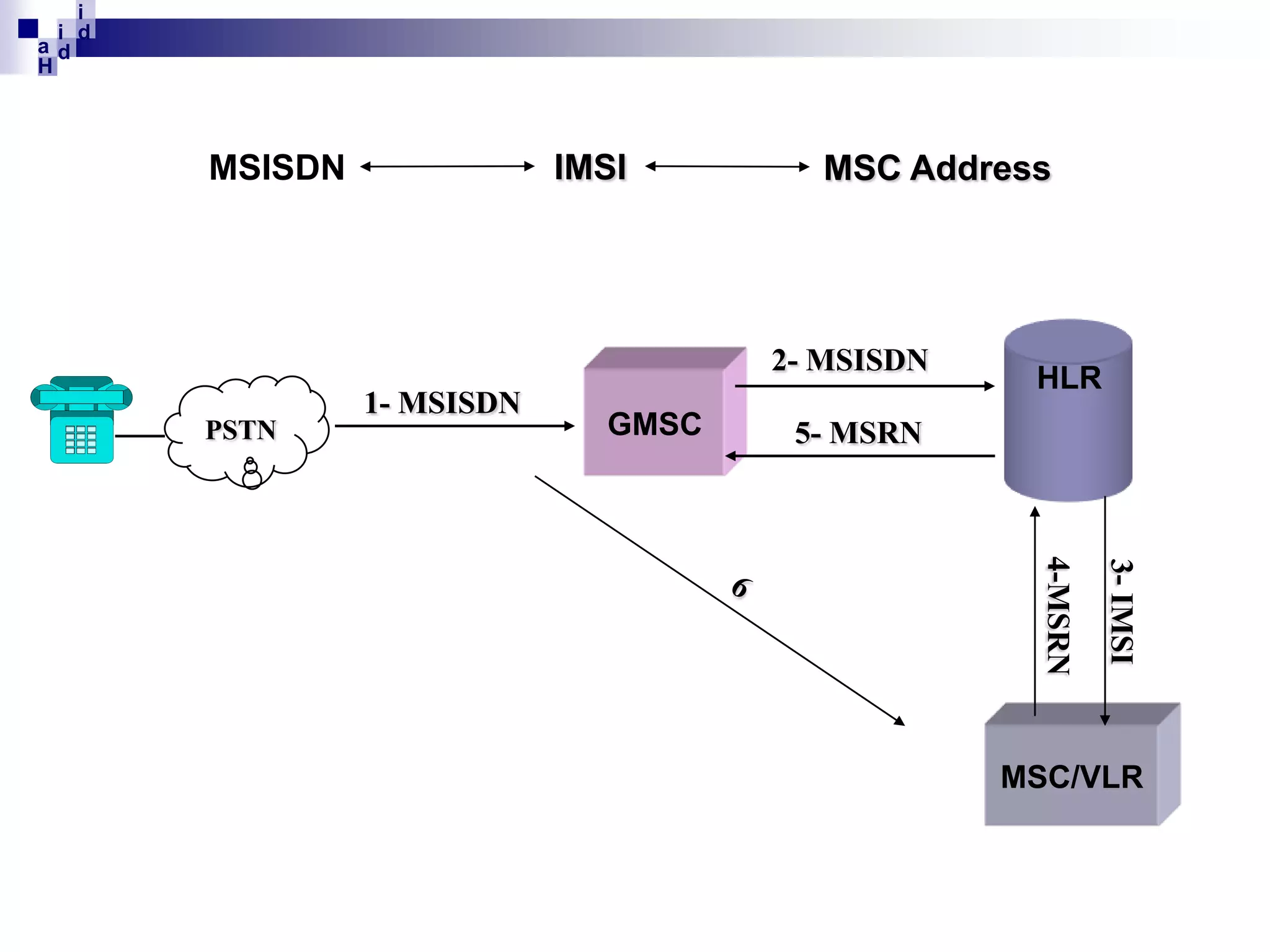
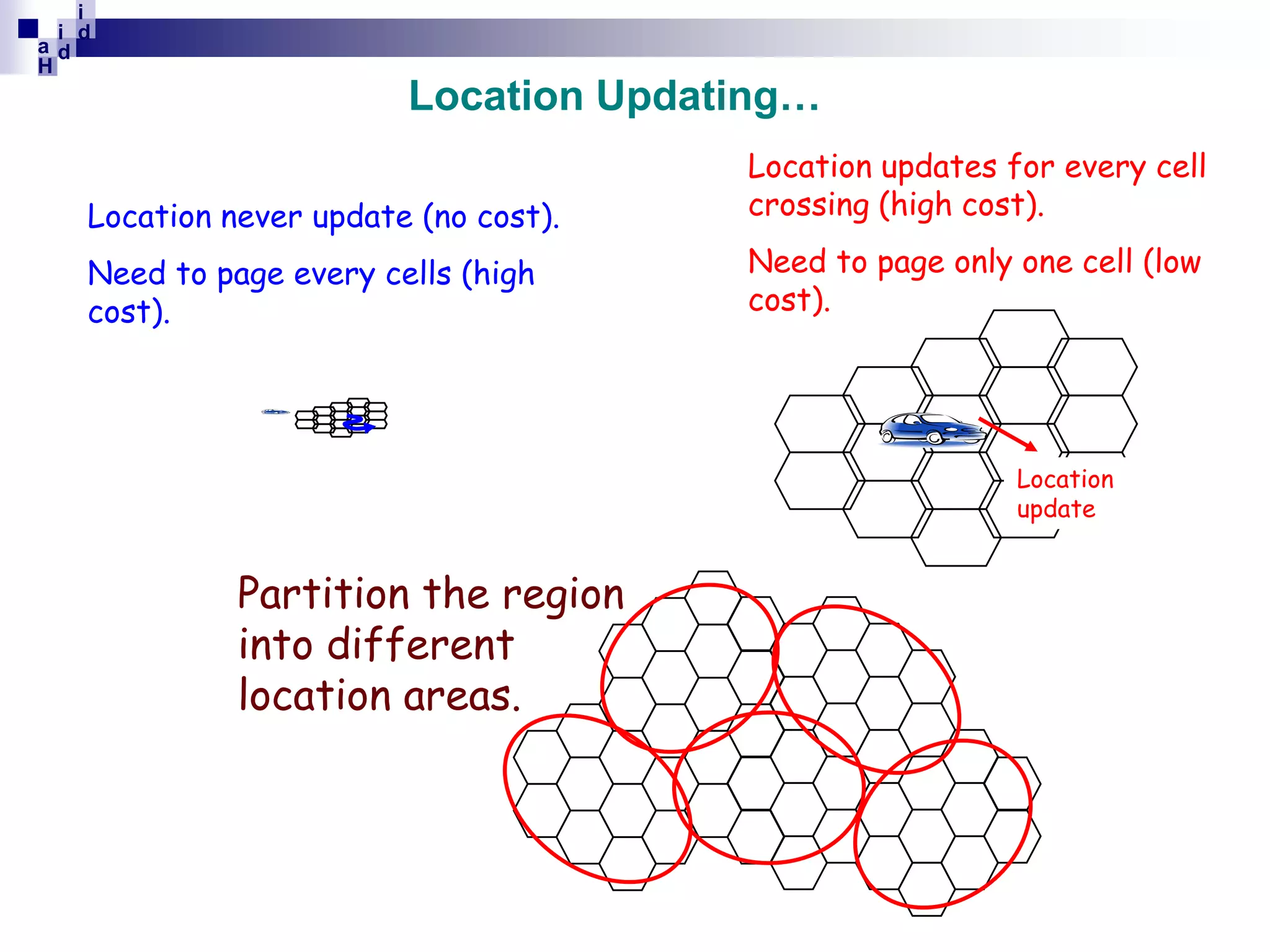
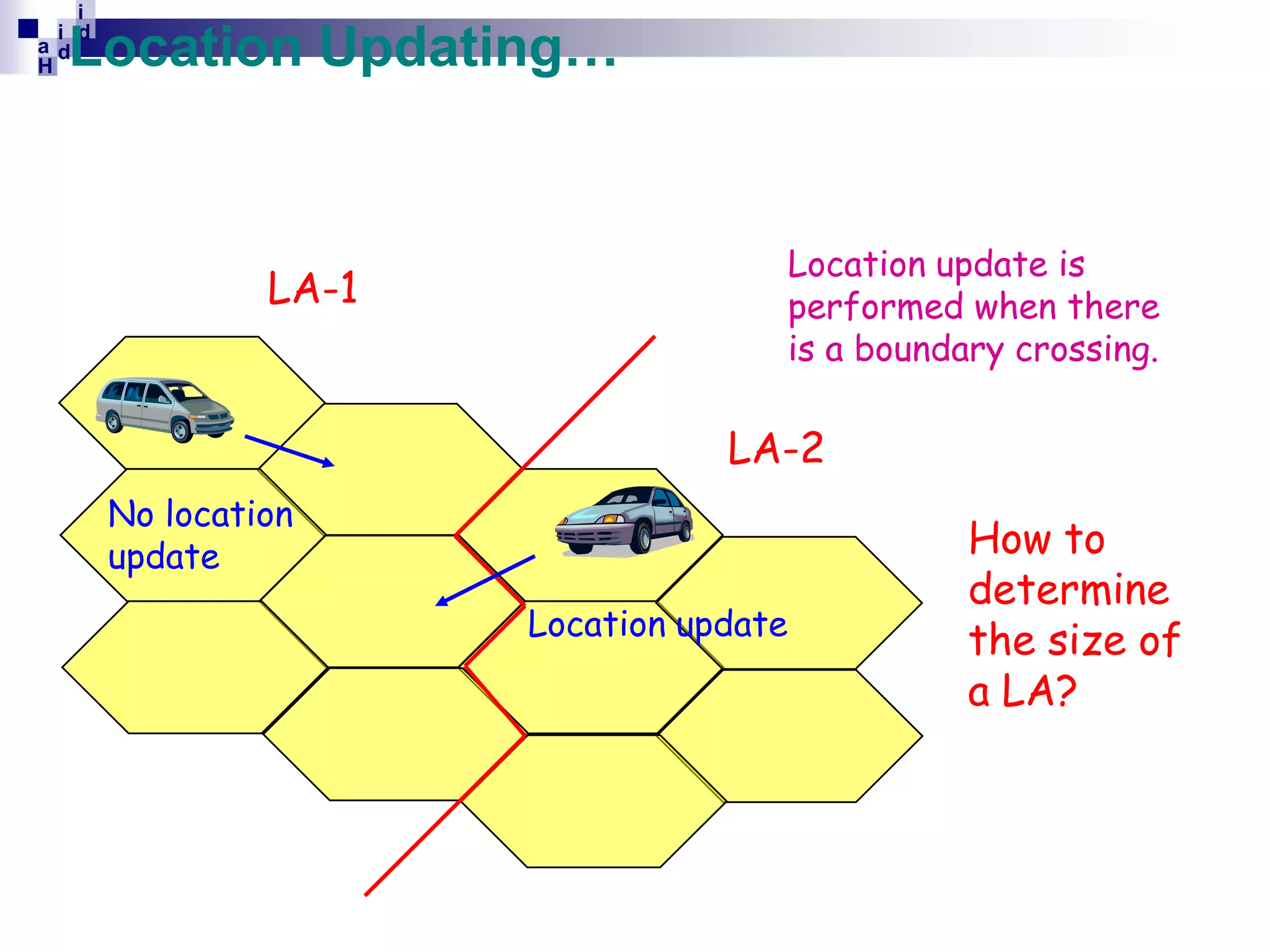
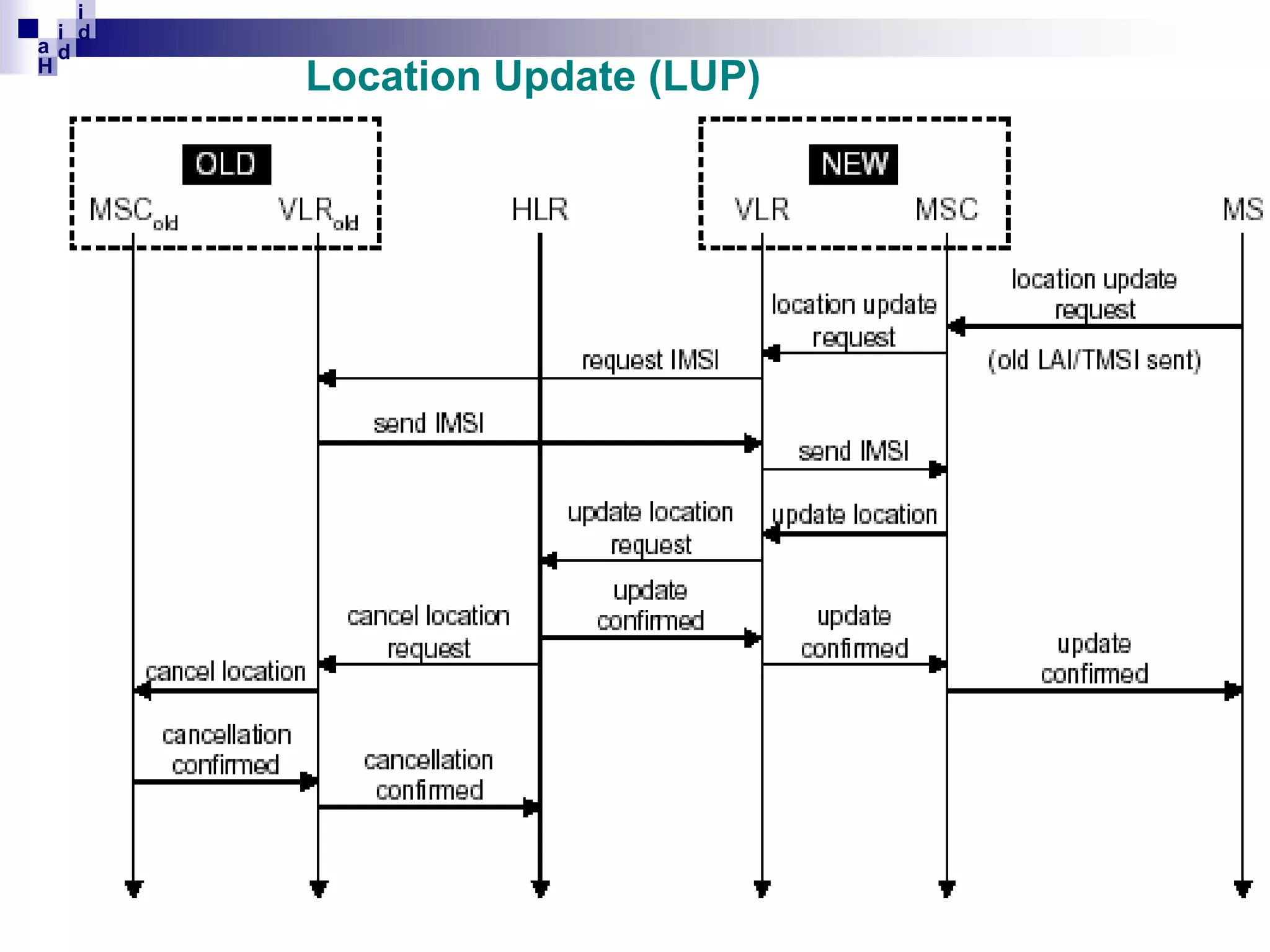
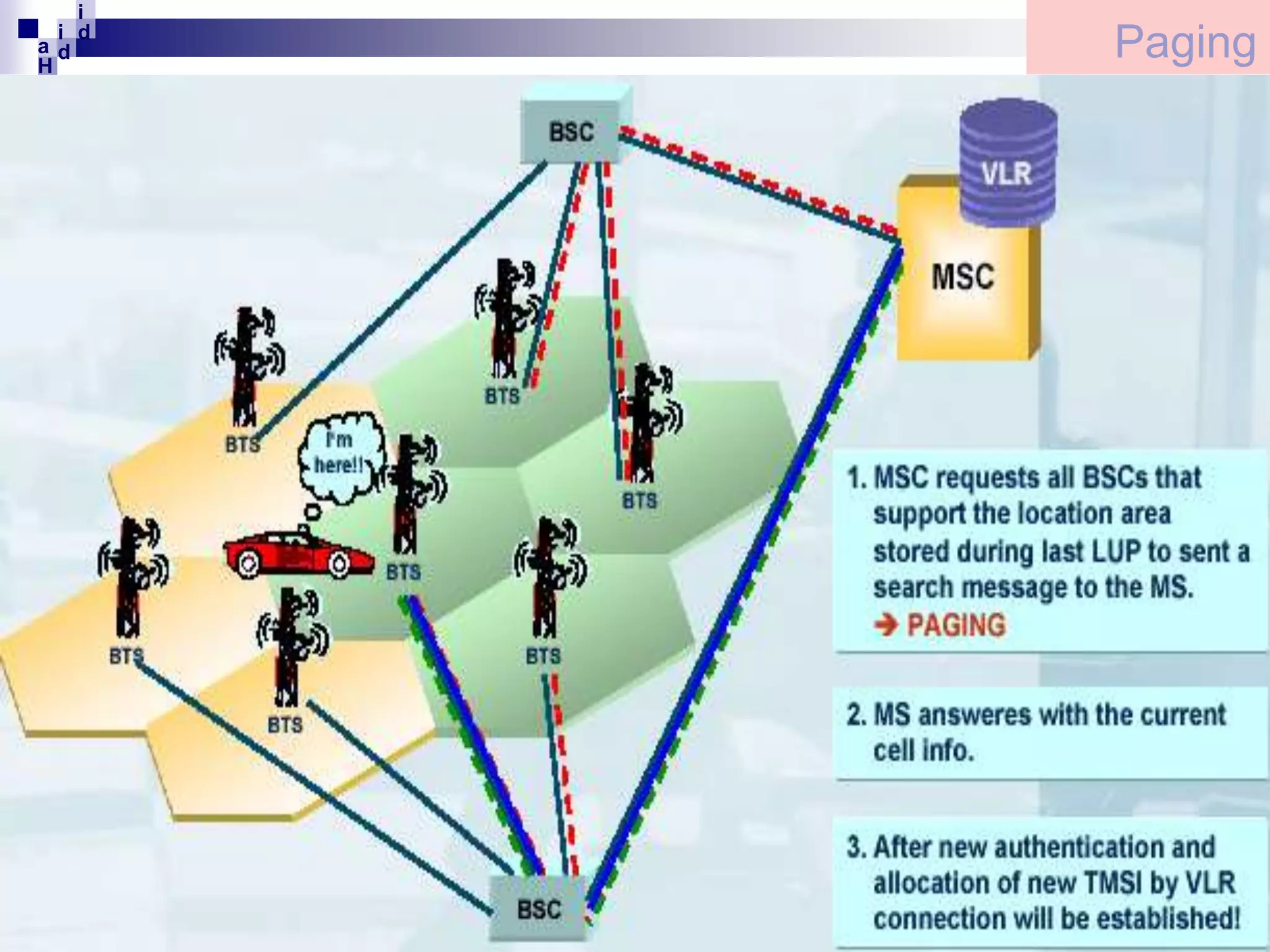
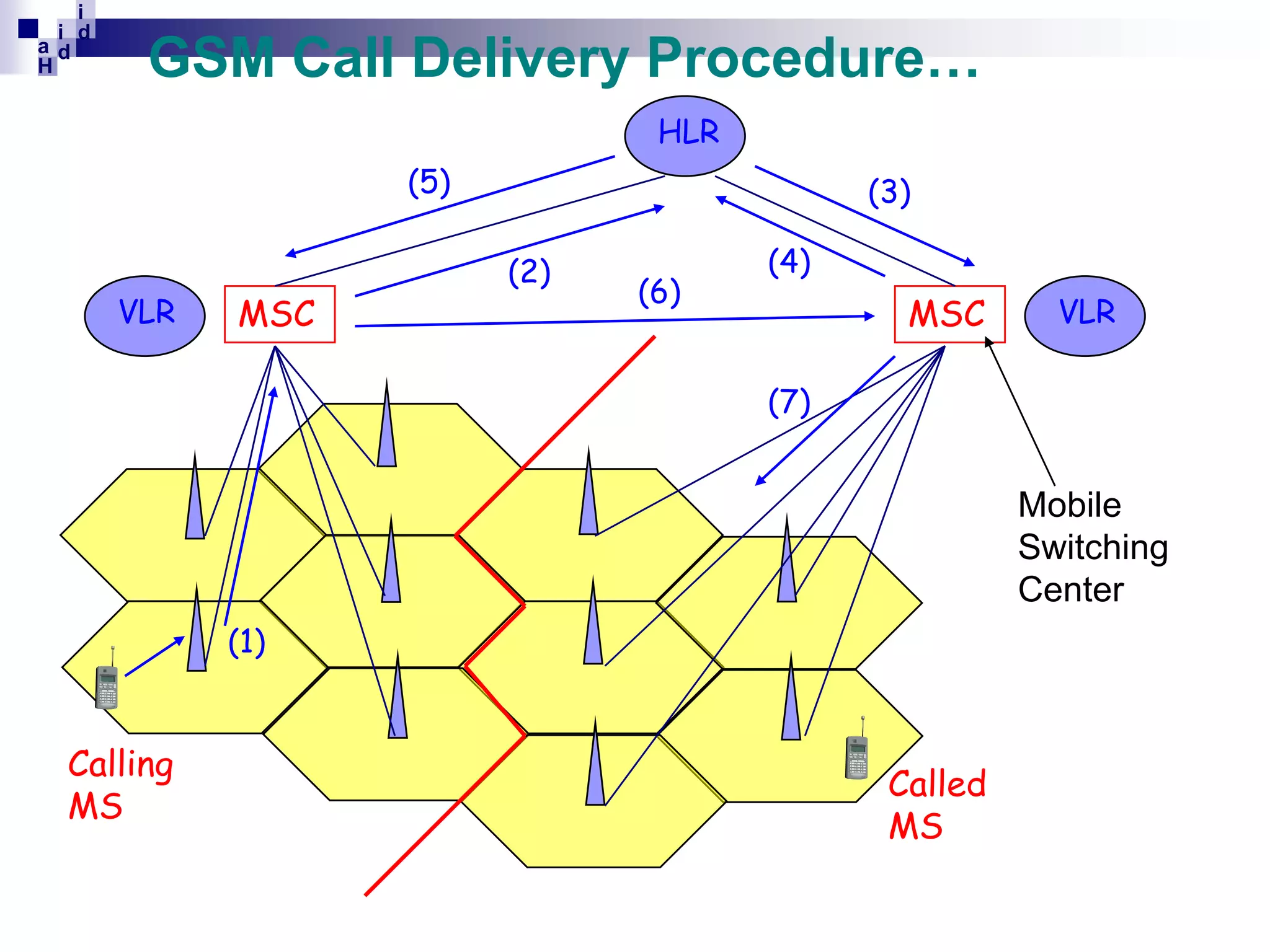
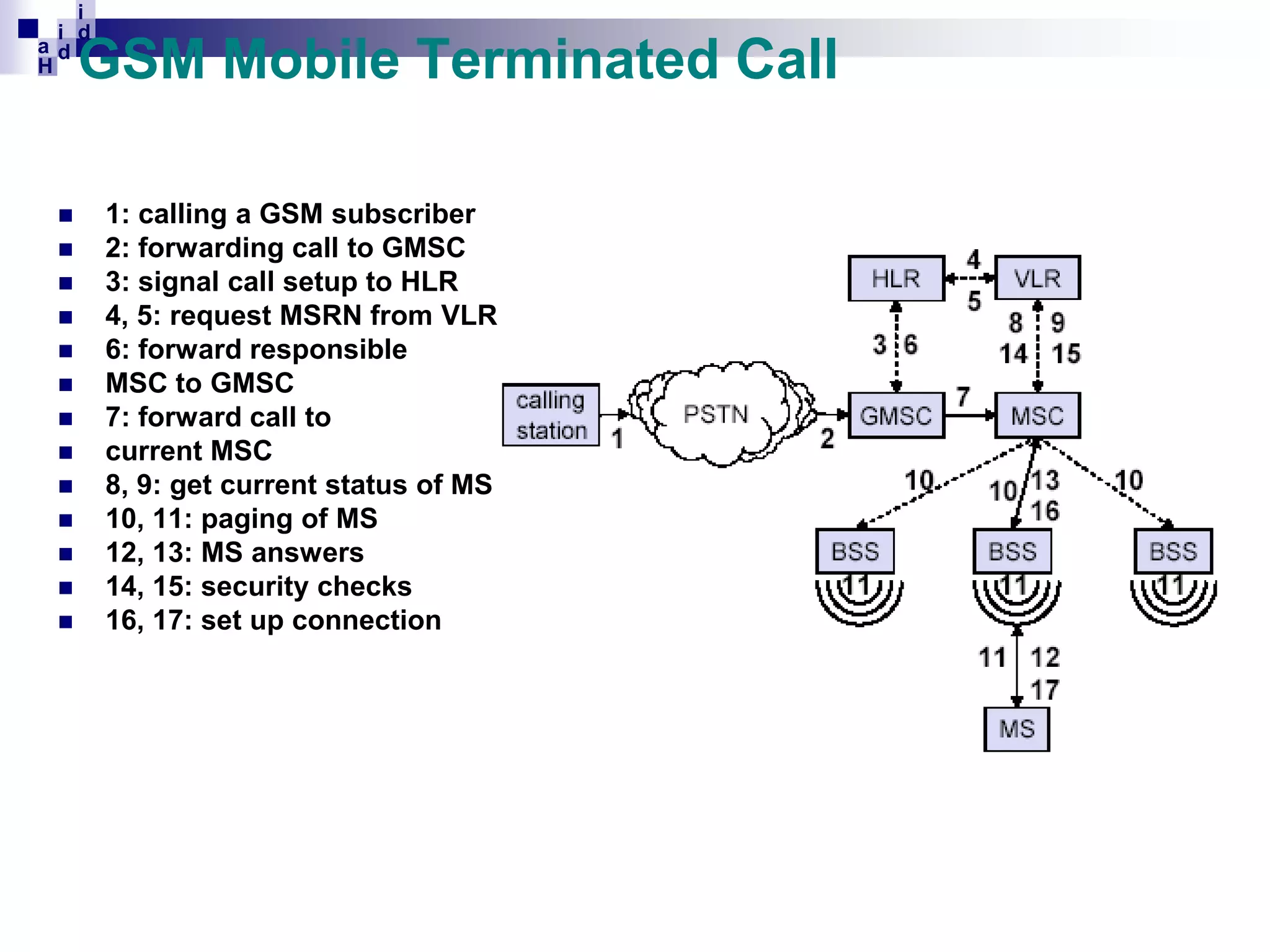
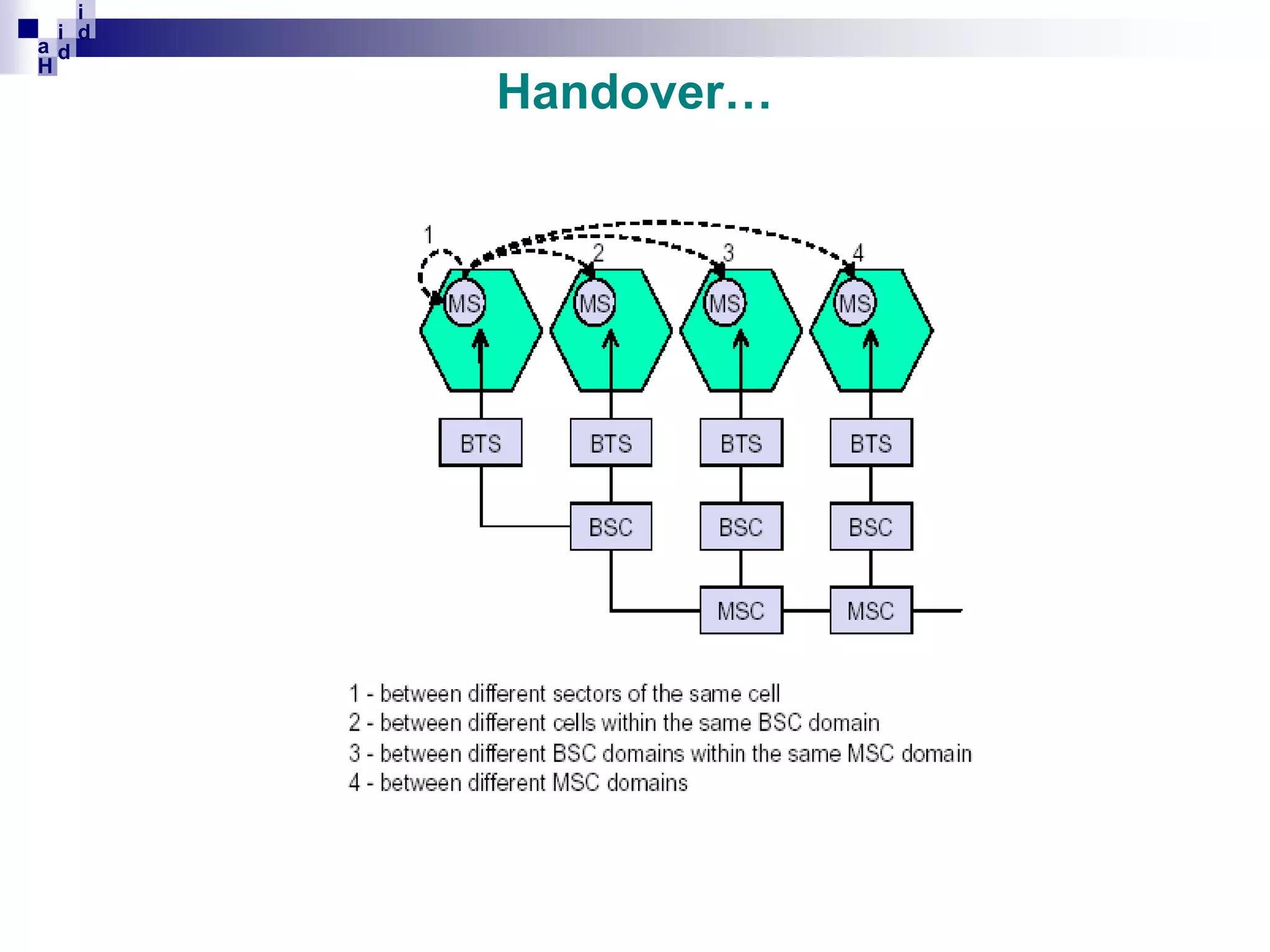
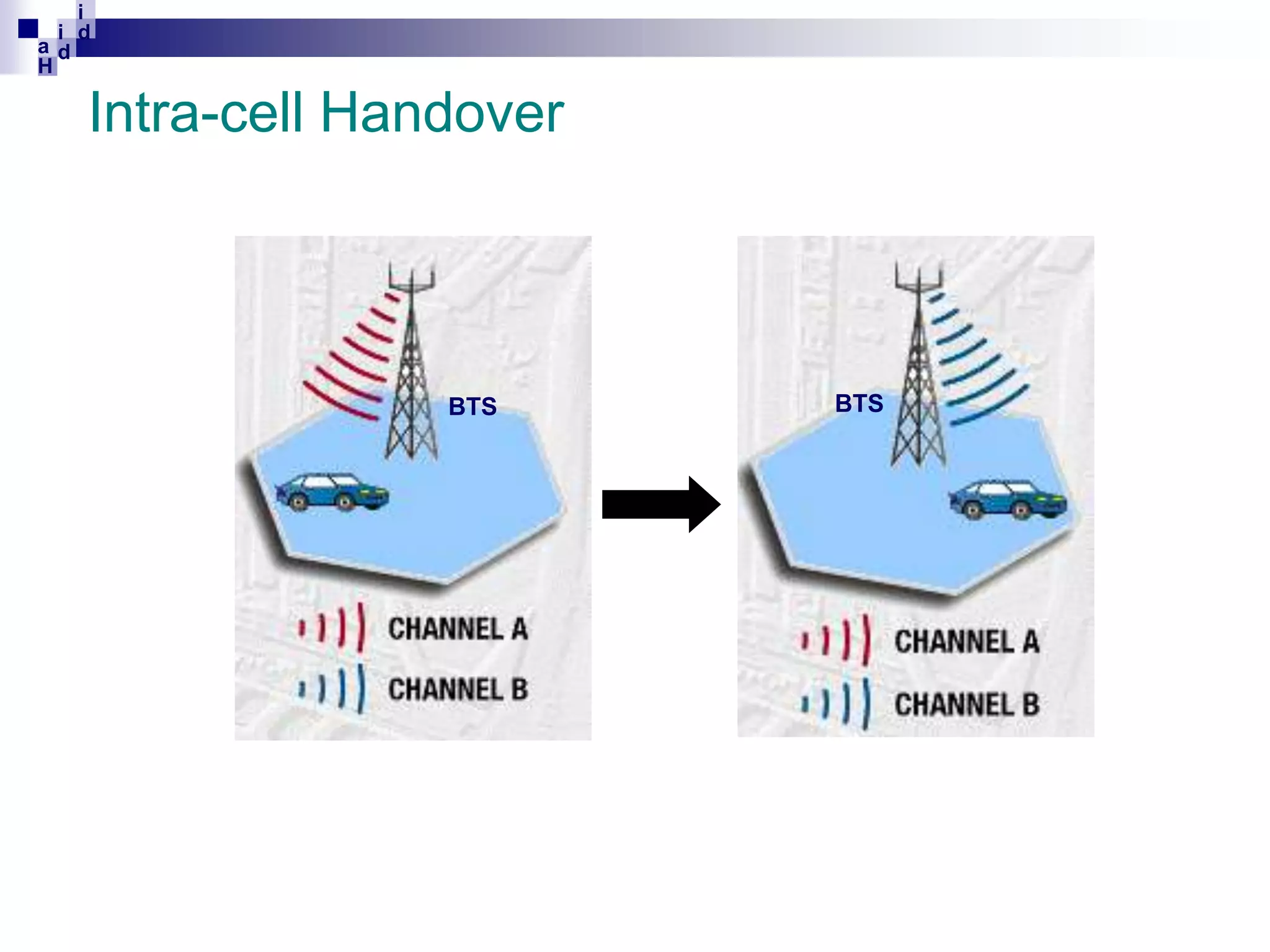
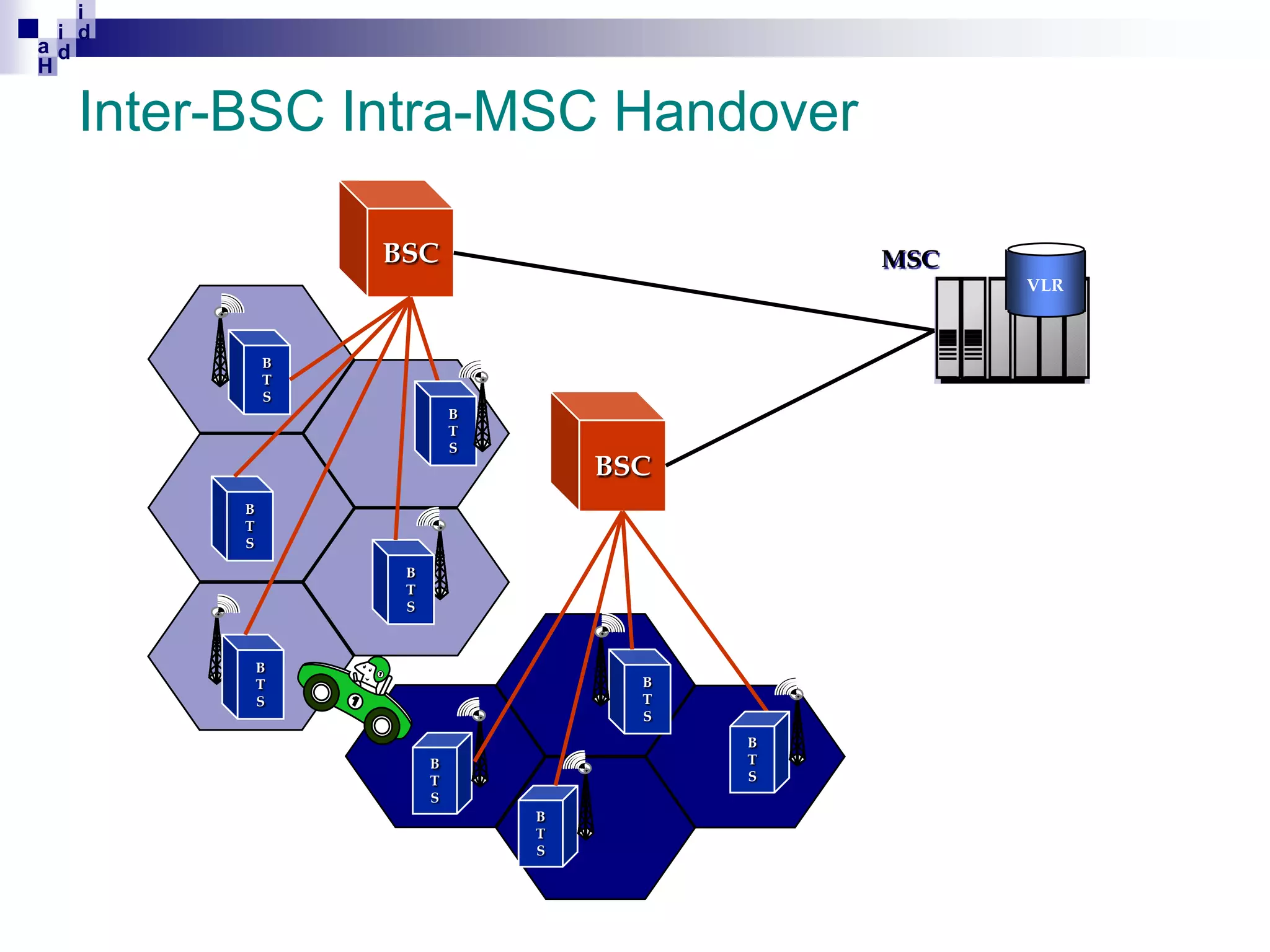
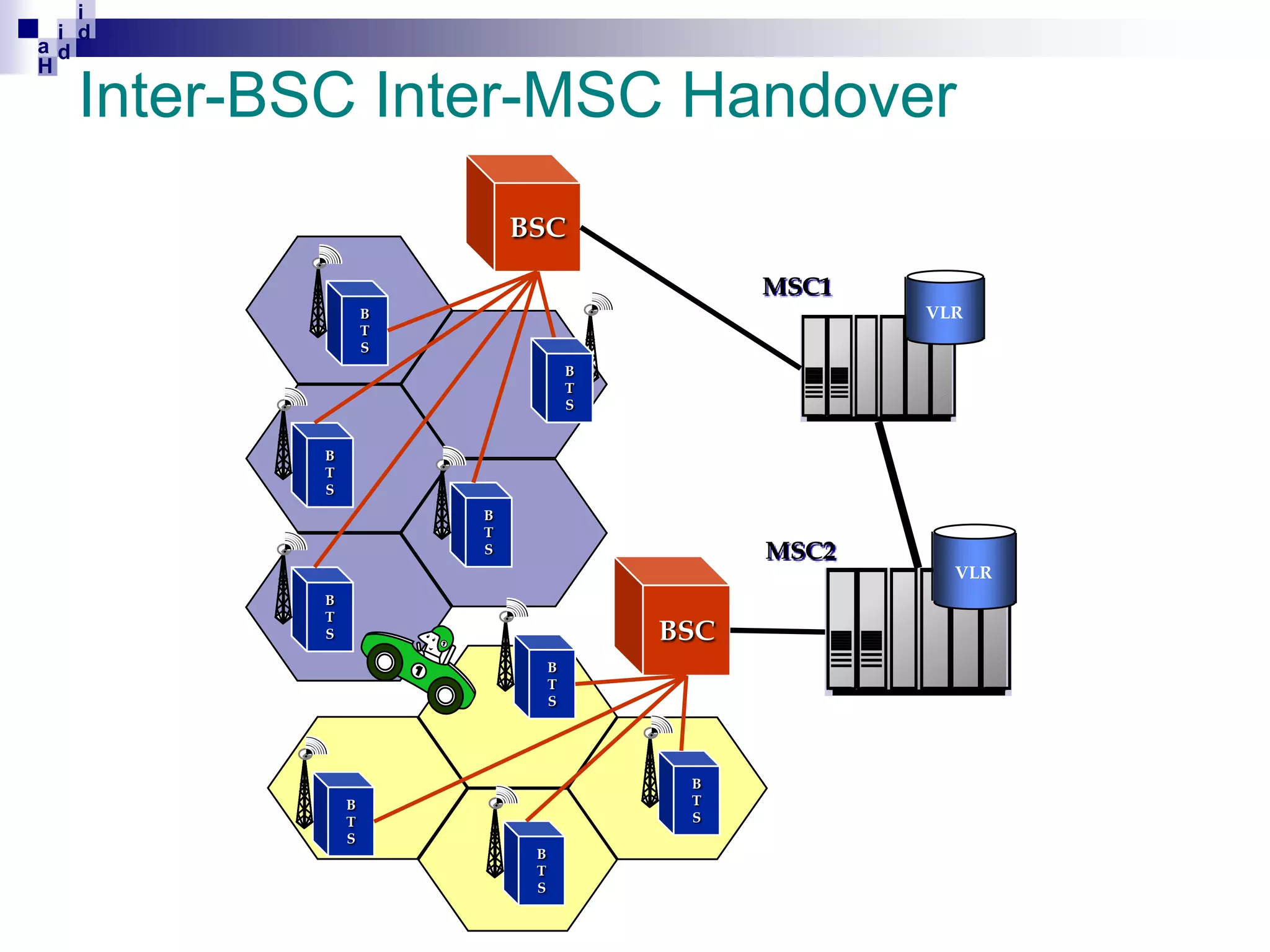
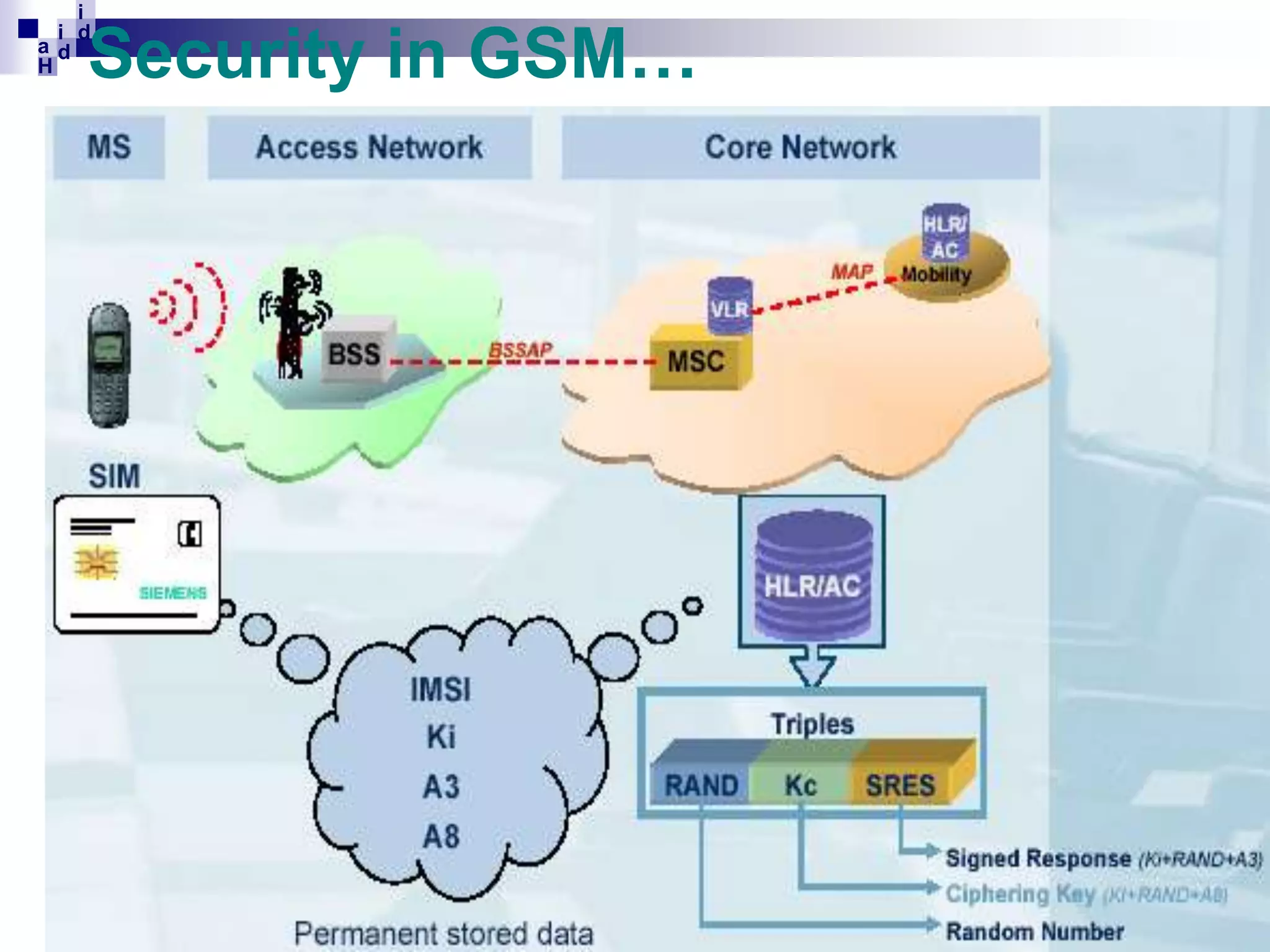
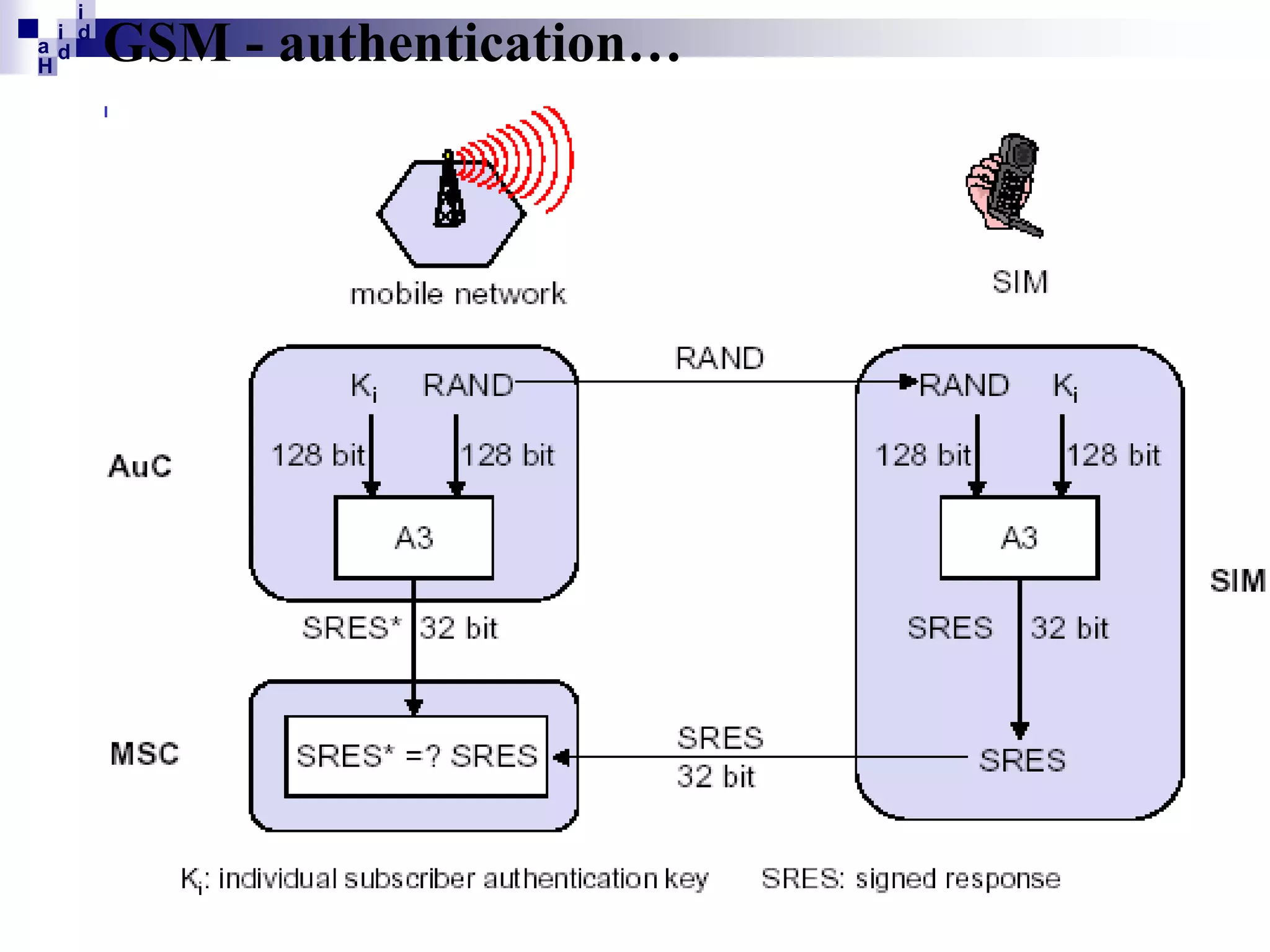
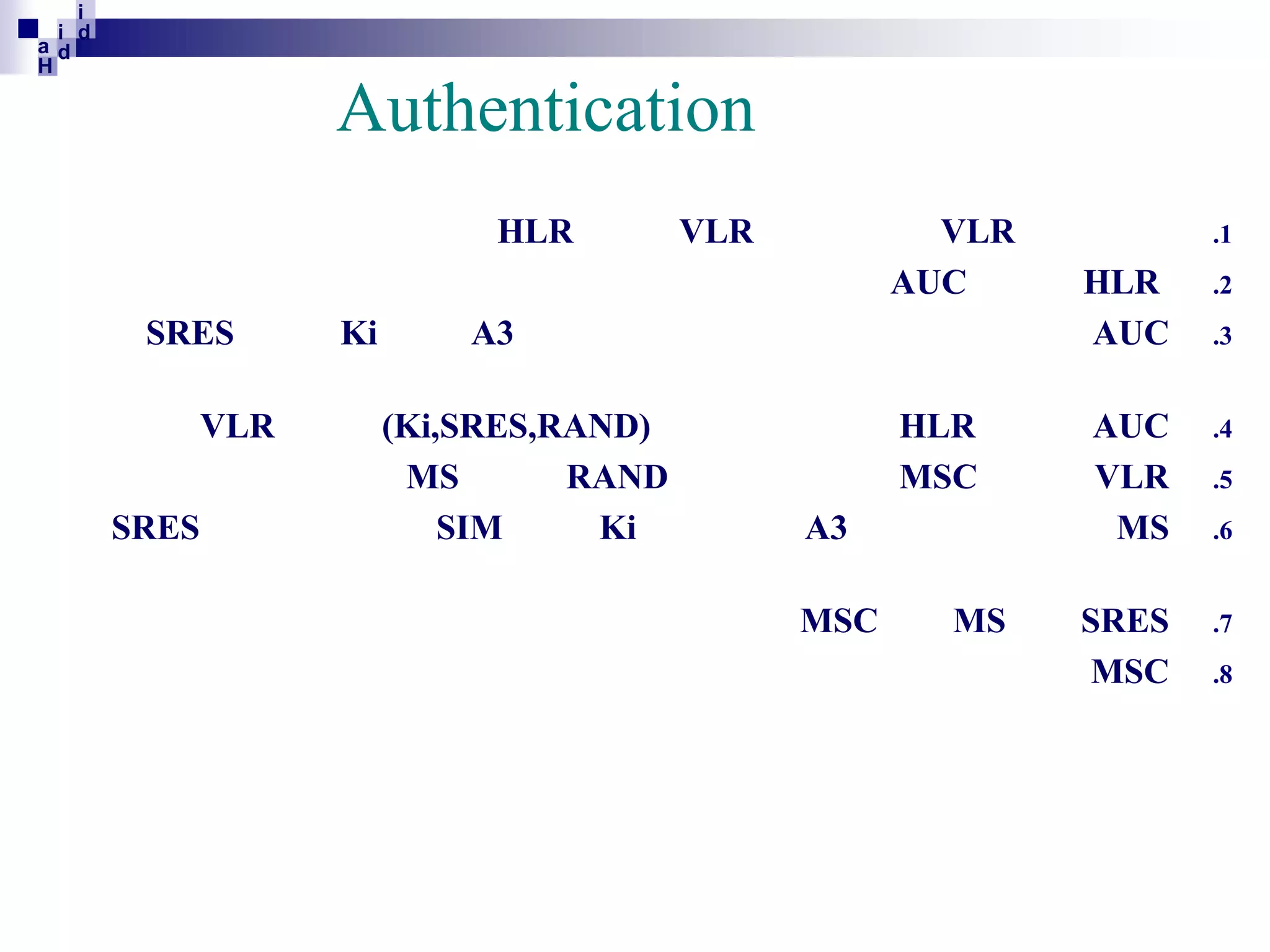
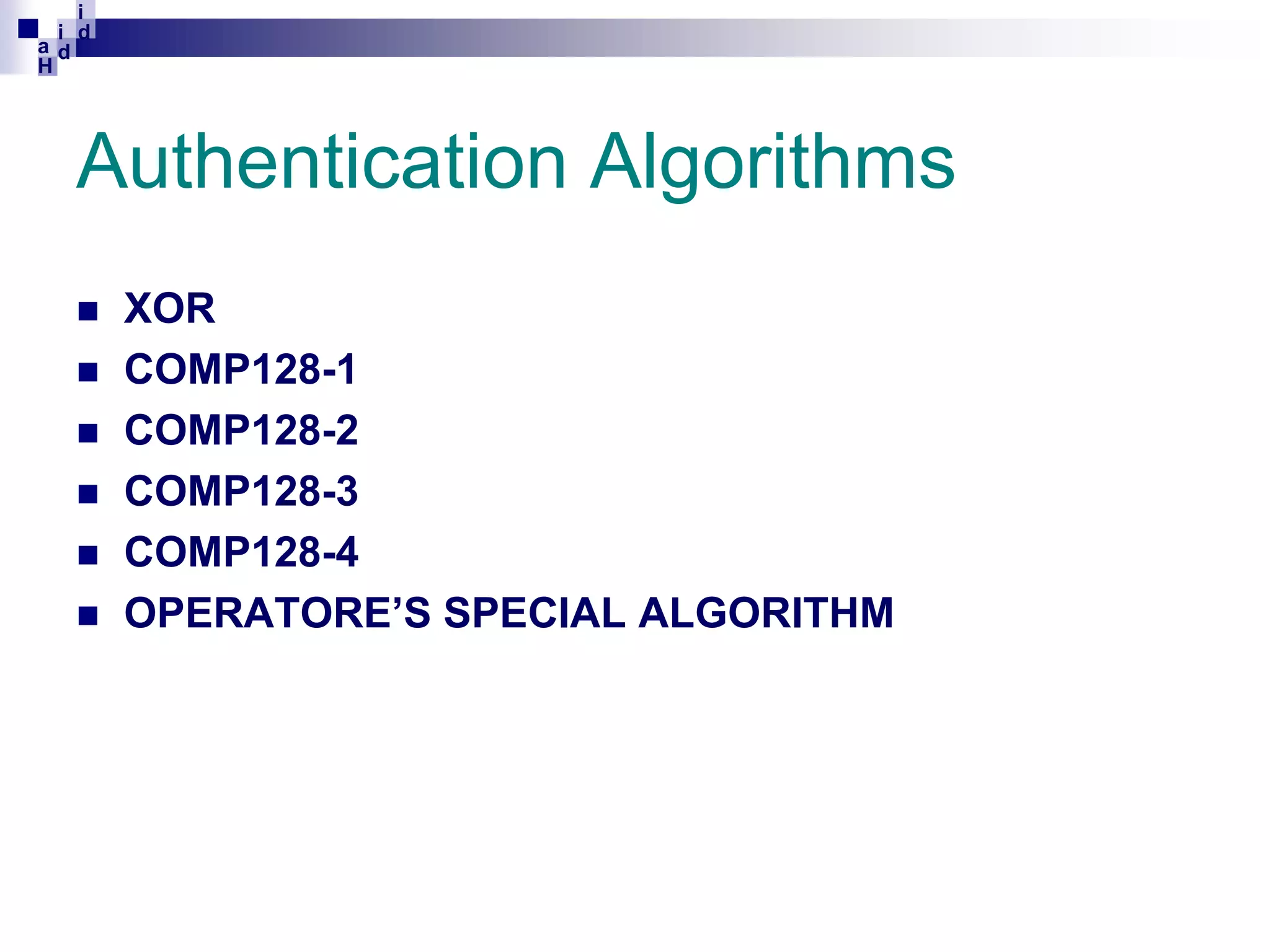
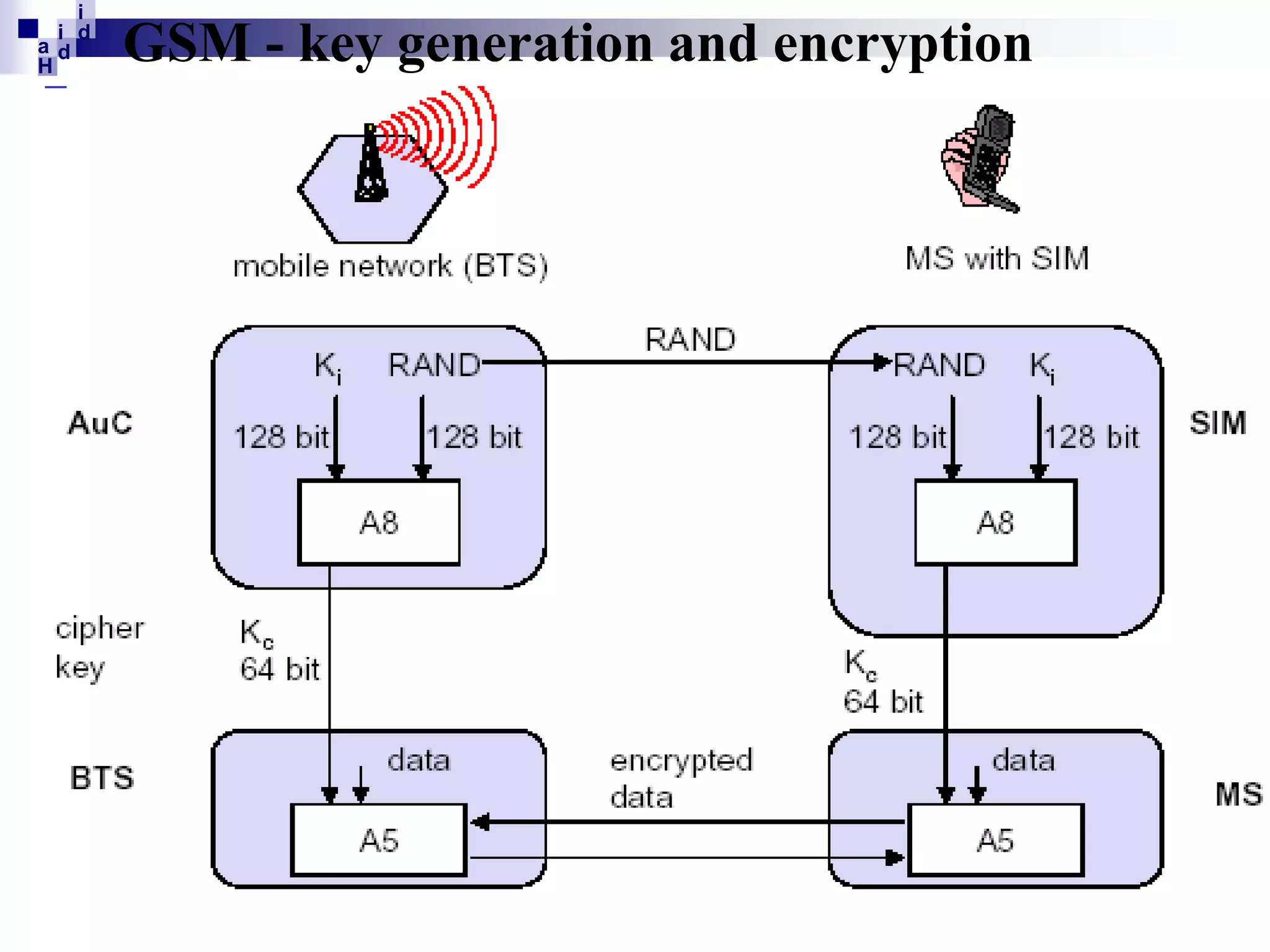
GSM networks divide coverage areas into a hierarchy of locations to efficiently manage subscriber location and enable call delivery. The largest division is the Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN). Within a PLMN are Mobile Switching Center/Visitor Location Register (MSC/VLR) service areas, which are further divided into Location Areas (LA) containing groups of cells. As subscribers move between areas, they perform location updates to inform the network of their position. This allows more efficient paging for call delivery. [END SUMMARY]