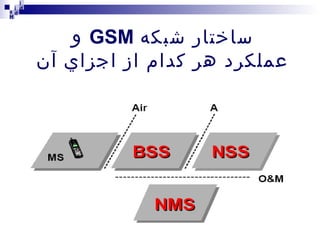
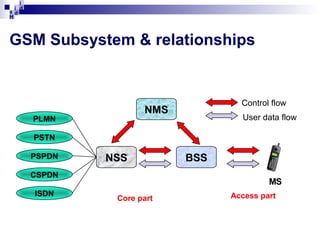
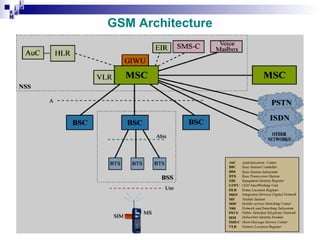
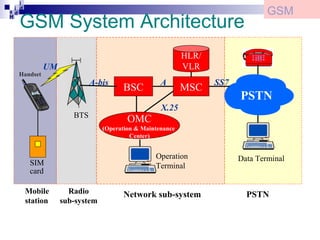
The document provides an overview of the architecture and components of a GSM network. It discusses the key subsystems including:
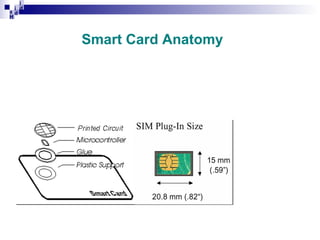
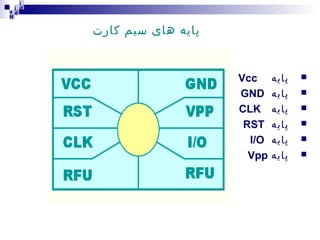
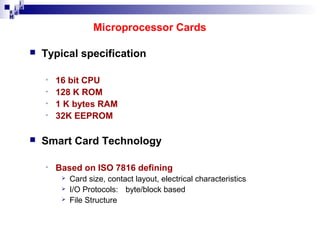
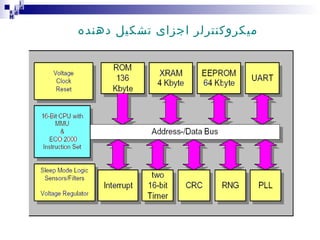
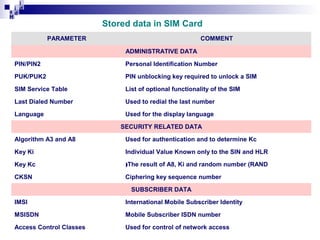
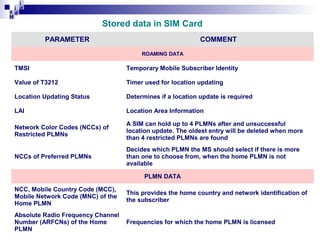
1) The Mobile Station (MS) which includes the Mobile Equipment (ME) and Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card. The SIM card stores subscriber identity and authentication information.
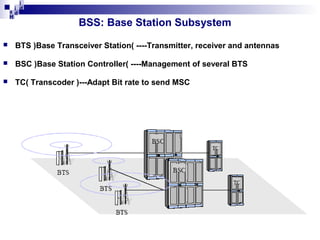
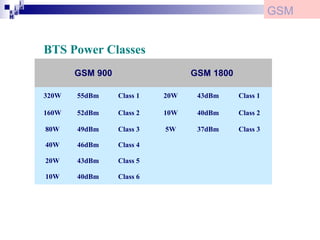
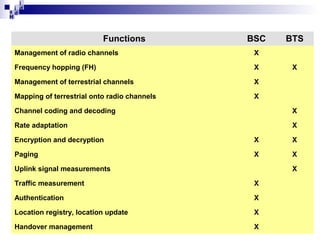
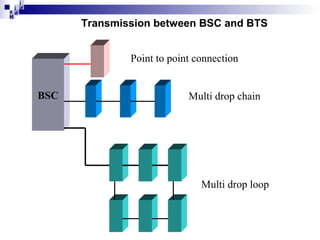
2) The Base Station Subsystem (BSS) which comprises the Base Transceiver Station (BTS) that provides radio coverage, and the Base Station Controller (BSC) that manages several BTSs.
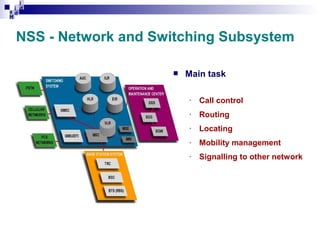
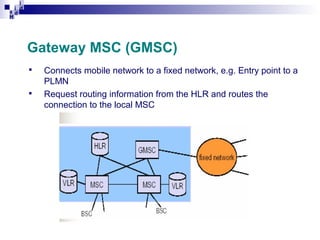
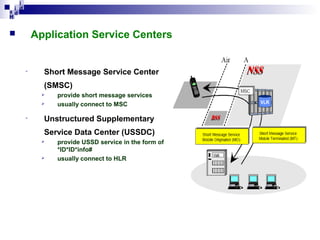
3) The Network Switching Subsystem (NSS) which includes critical components like the Mobile Switching Center (MSC), Home Location Register (HLR), Visitor Location Register (