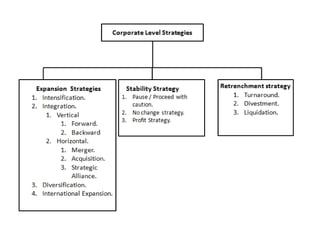
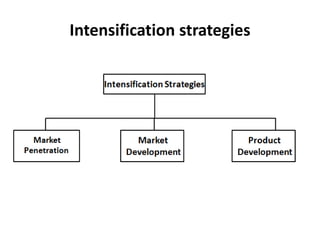
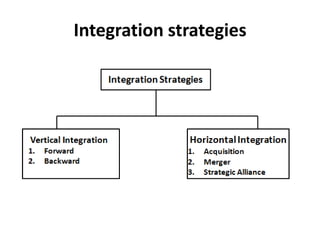
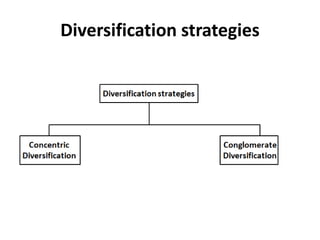
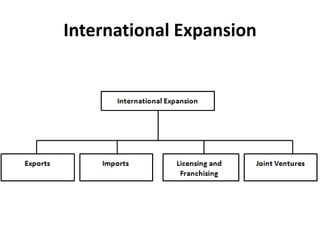
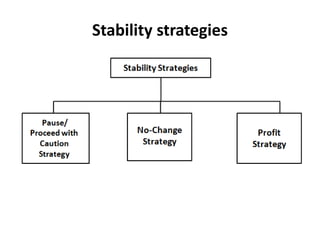
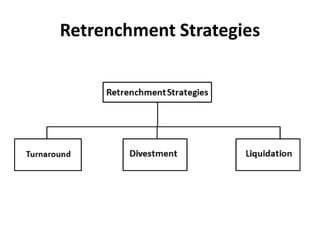
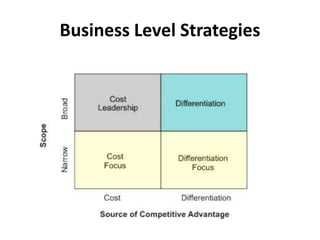
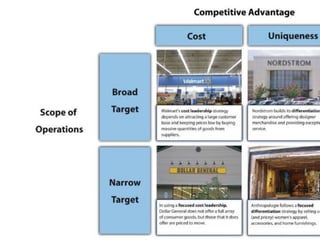
The document outlines various strategic management concepts, including business-level, corporate-level, and diversification strategies, with practical examples for each. It explains strategies like cost leadership, differentiation, market penetration, market development, and integration strategies along with their applications by companies such as Nike, Starbucks, and Disney. It also discusses stability and retrenchment strategies, including mergers, acquisitions, and turnaround strategies pertinent to business sustainability and growth.