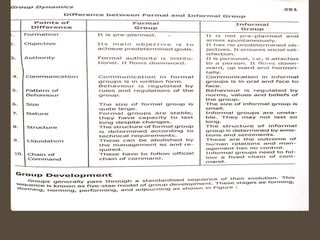
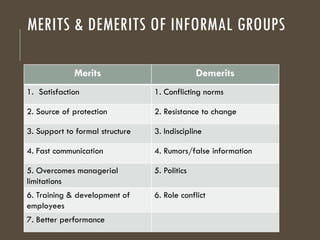
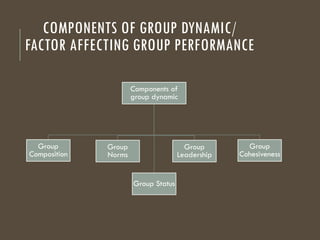
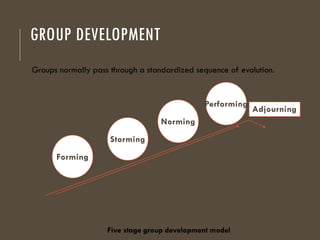
The document provides an overview of groups and teams, defining them as collections of individuals who interact regularly to achieve common goals. It distinguishes between various types of groups, such as primary and secondary, formal and informal, and discusses group dynamics, decision-making processes, and characteristics influencing group cohesiveness. Additionally, techniques for effective group decision-making are outlined, emphasizing the importance of collaboration and structured approaches.