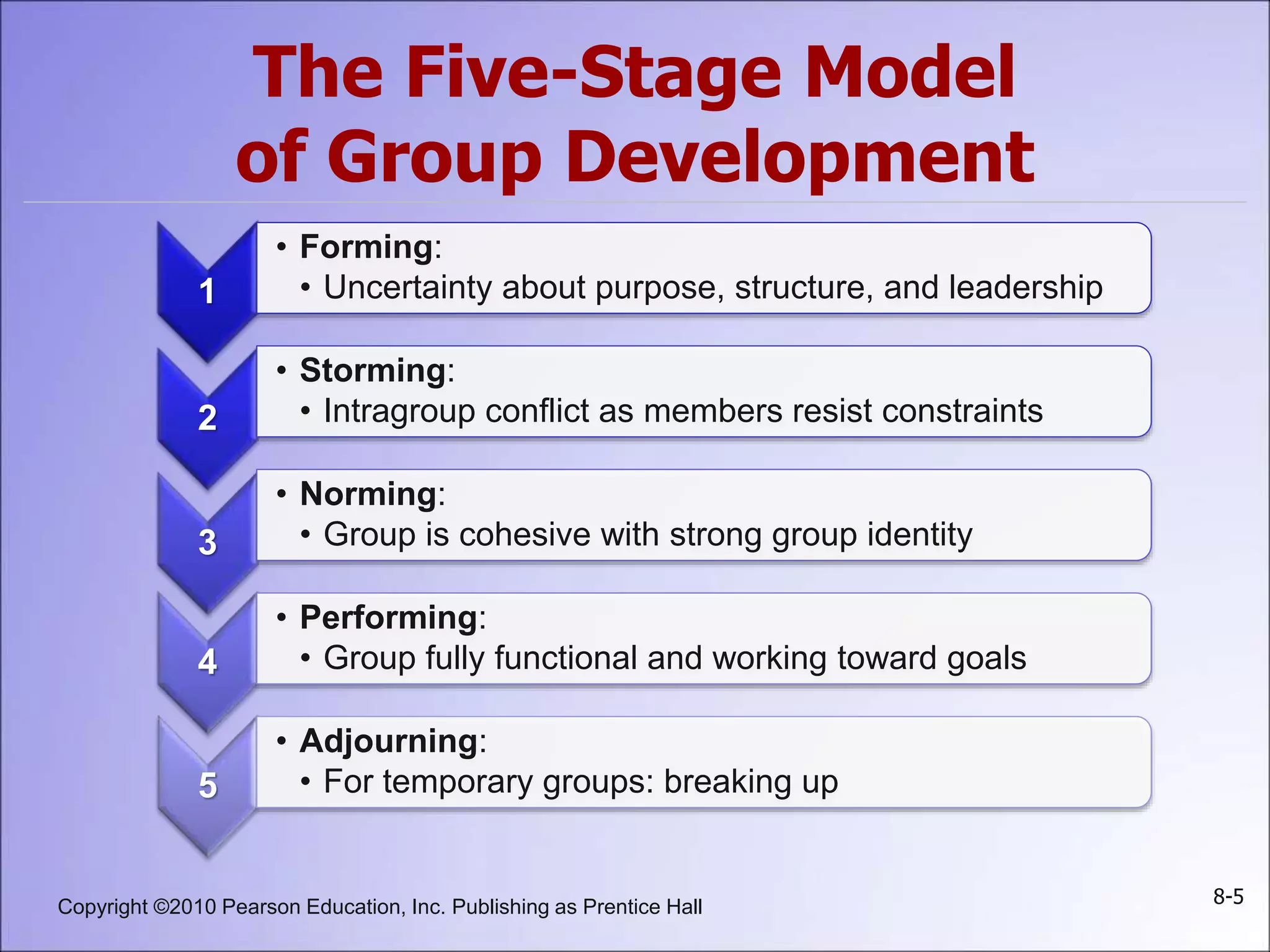
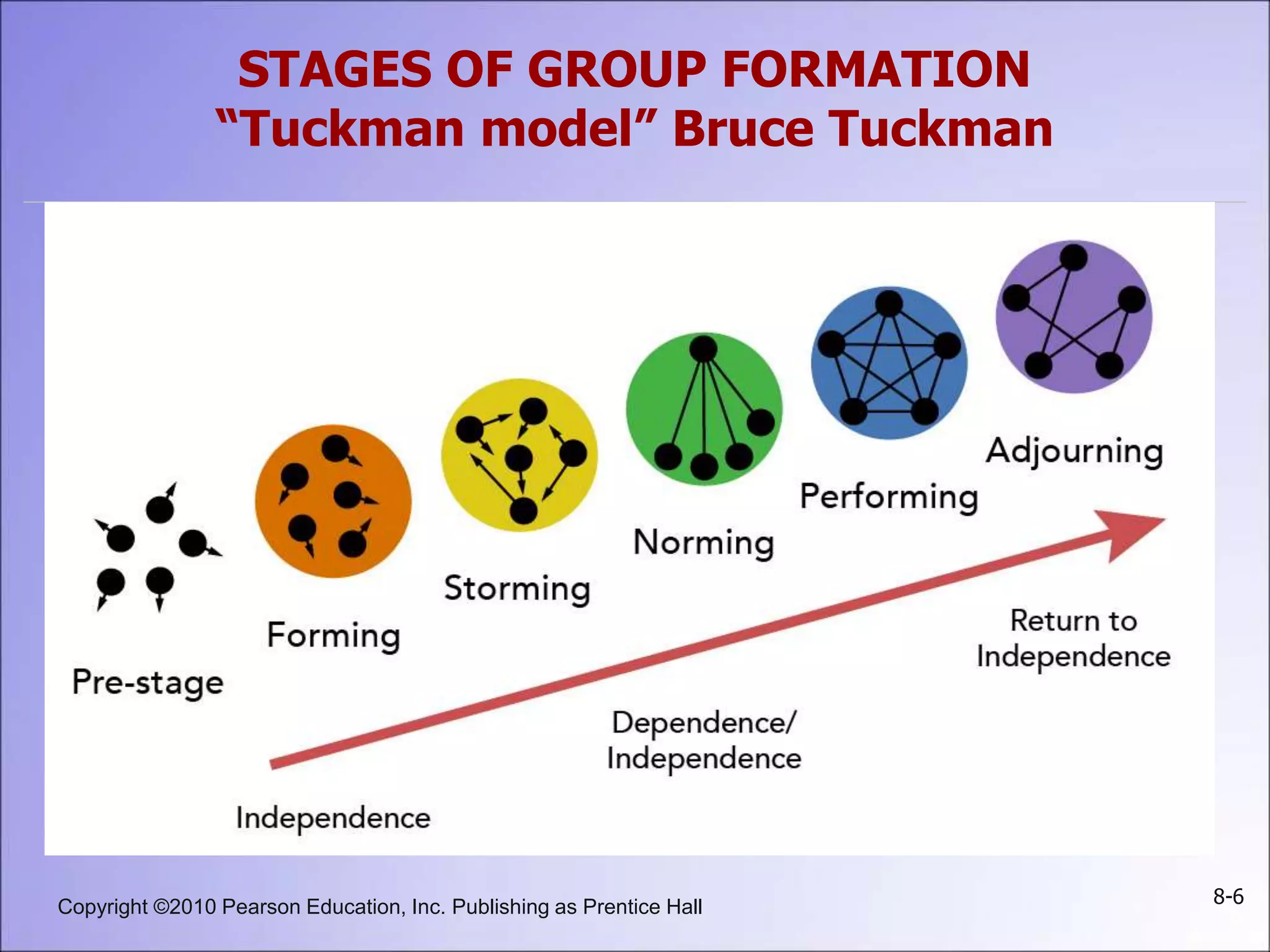
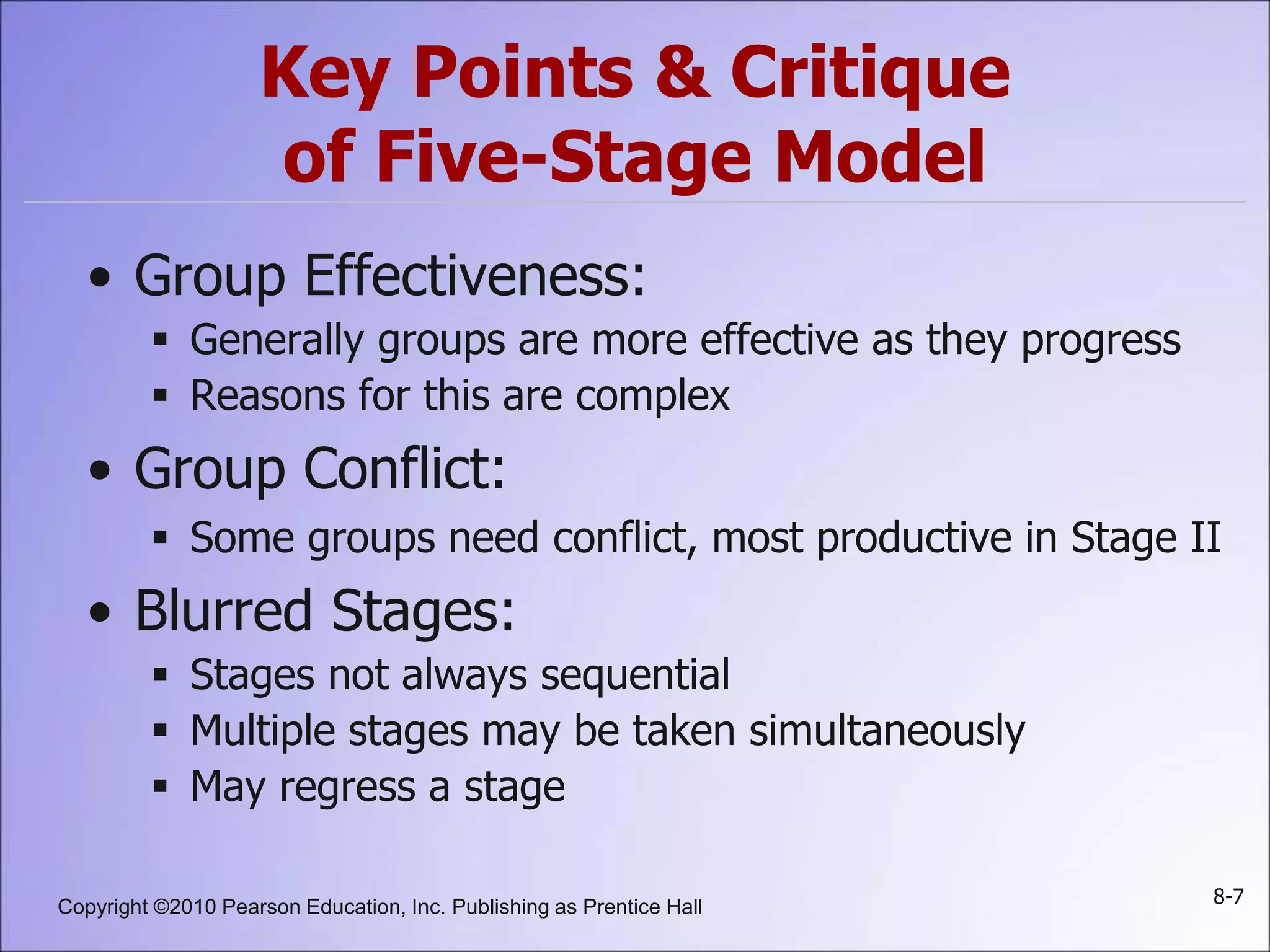
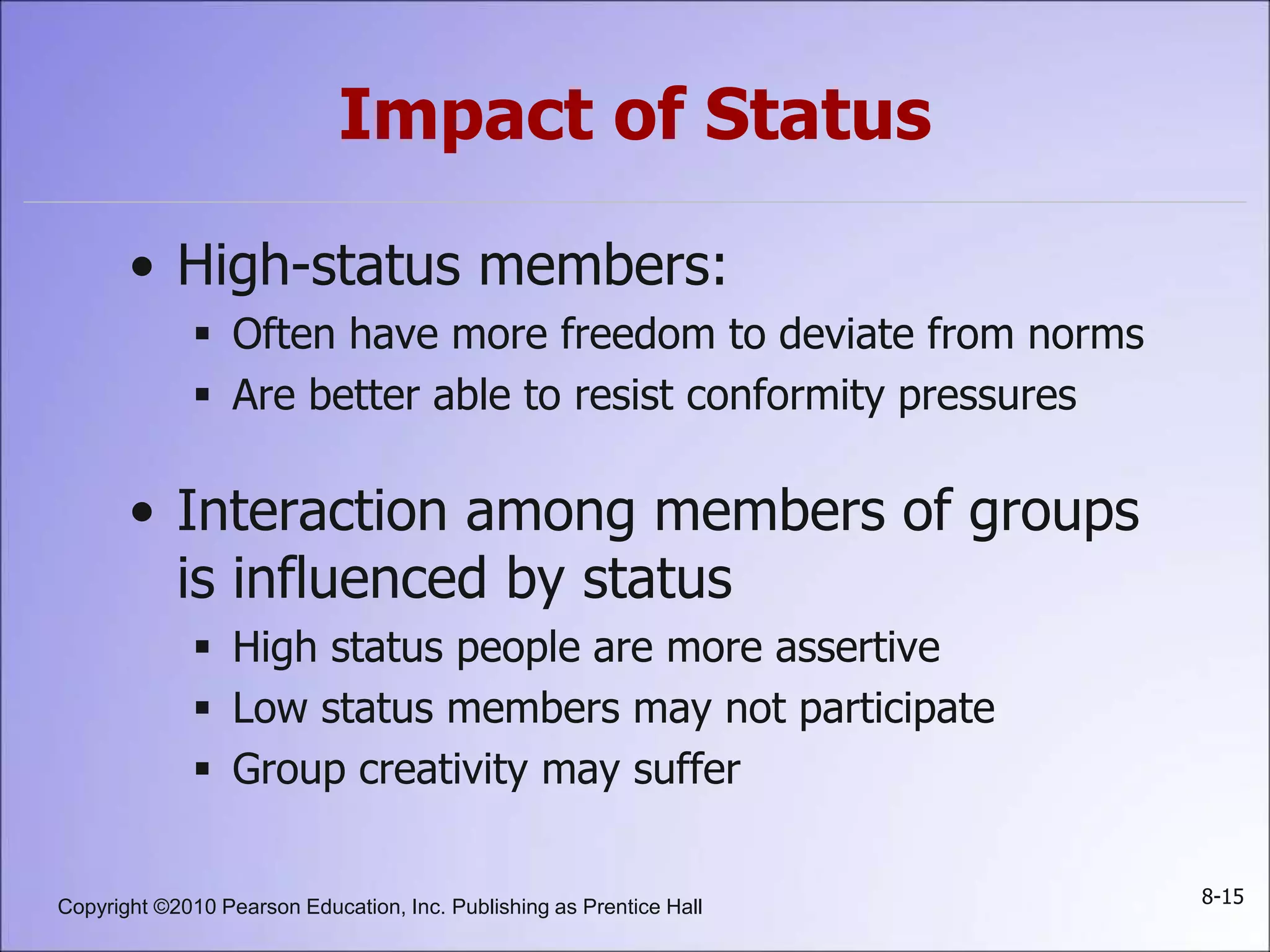
This document summarizes key concepts about groups and group behavior, including: defining groups and their types; the five stages of group development; the five properties of groups including roles, norms, status, size, and cohesiveness; how norms and status influence individual behavior; strengths and weaknesses of group decision-making; and implications for global business and management.