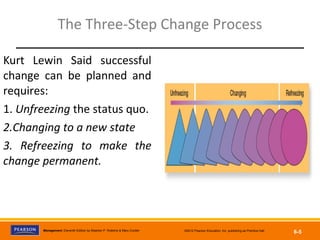
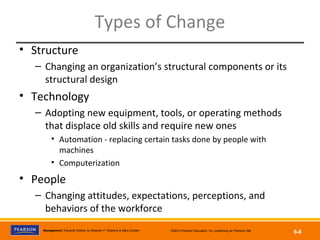
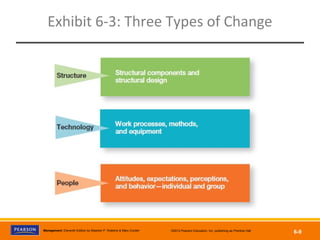
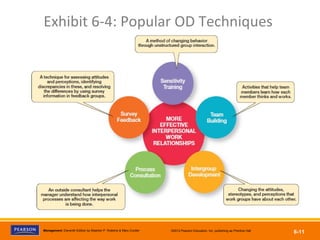
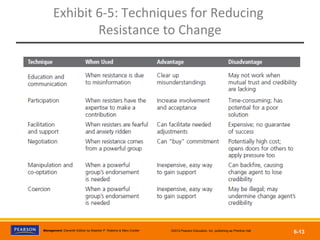
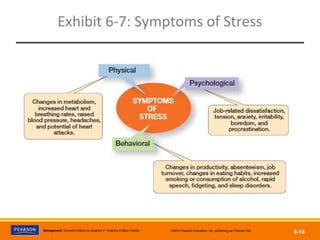
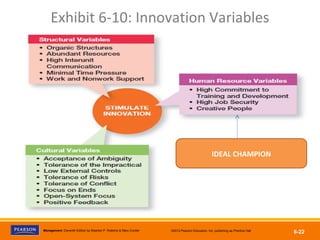
The document discusses managing organizational change and innovation. It describes Lewin's three-step change process of unfreezing, changing, and refreezing. It also identifies different types of change like structural, technological, and personnel changes. Managing resistance to change and stress during change processes is also addressed. Techniques for stimulating innovation include cultivating the right structural, cultural, and human resource environments within an organization. Idea champions are important for supporting new ideas and ensuring their implementation.