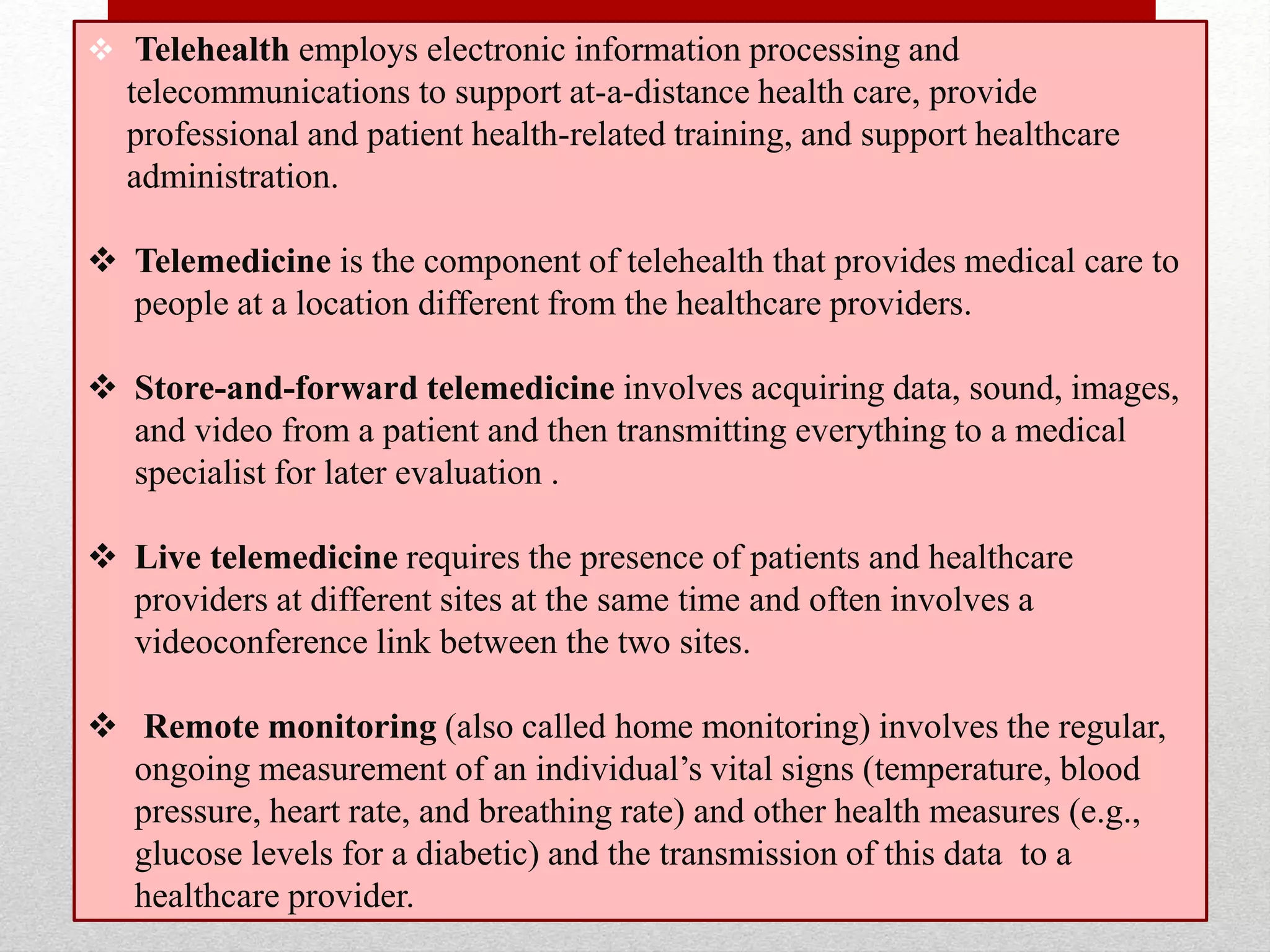
This document discusses the impact of information technology on productivity, quality of life, and healthcare costs. It covers topics such as telework, the digital divide, electronic health records, social networking, and virtual worlds. Telework allows employees to work remotely and provides advantages like reduced commuting times but also disadvantages like potential isolation. The digital divide refers to unequal access to technology. Electronic health records can reduce healthcare costs by improving record keeping. Social networking enables online communities but also raises issues like cyberbullying. Virtual worlds are online simulated environments that are also used for education and business.