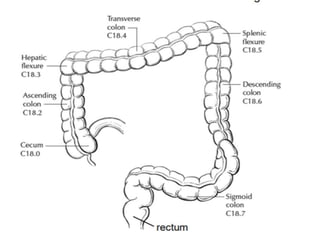
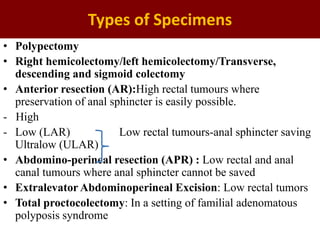
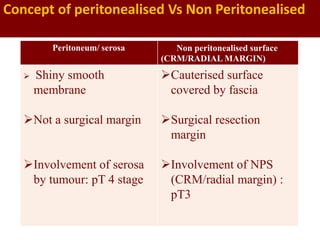
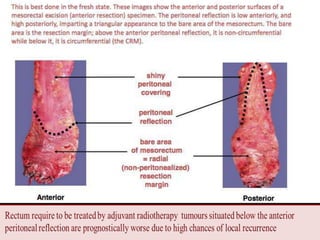
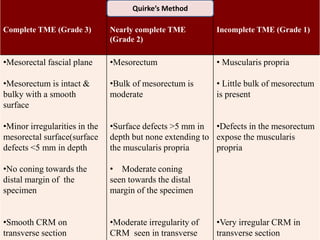
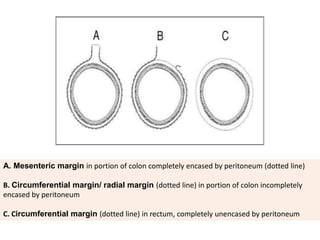
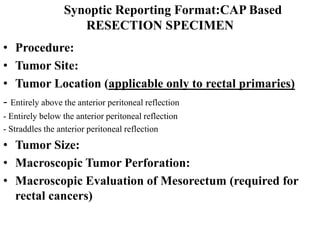
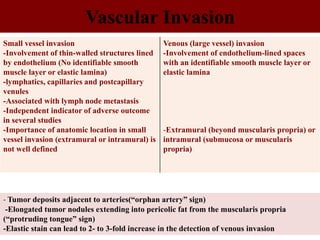
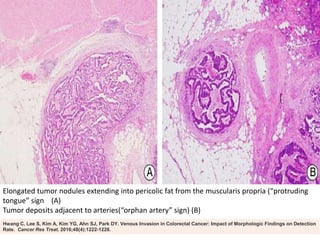
This document provides guidance on the pathological assessment of colorectal resection specimens. It describes the different types of colorectal surgery specimens and margins that need assessment. It discusses the total mesorectal excision technique for rectal cancers and how to evaluate the quality of the surgery. Key pathological features that require reporting are described, including tumor staging, lymphovascular invasion, perineural invasion, tumor budding and tumor deposits. The document provides details on lymph node assessment and reporting colorectal cancers using a synoptic format.